
What will be the product when Lithium aluminium hydride reacts with propanal?
A.$CH_3$-$CH_2$-$CH_2$-$OH$
B.${C_6}{H_5} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - OH$
C.$C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - OH$
D.None of these
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint:Lithium Aluminum hydride $\left( {LiAl{H_4}} \right)$ is a strong reducing agent and it reduces aldehyde to alcohol. If we reduce aldehyde or ketone then we will get primary alcohol or secondary alcohol as a product respectively.
Complete step by step answer:
In organic chemistry $\left( {LiAl{H_4}} \right)$ is a strong reducing agent which is used to reduce aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acids, amide and more organic compound types.
There are several advantages of using $\left( {LiAl{H_4}} \right)$ as reducing agent that it does not reduce carbon–carbon double or triple bonds (with the exception of propargylic alcohols) and also, all four carbon atoms have the ability to participate the reaction
When $\left( {LiAl{H_4}} \right)$is used to reduce aldehyde or ketone the product we will get is alcohol.
As in the case of aldehyde, the primary alcohol is given as a product.
While in the case of ketone we get secondary alcohol as a product.
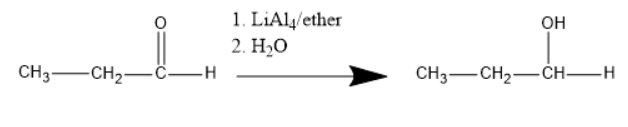
Therefore, Option A is correct.
The product we will get from the chemical reaction is $C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - OH$(Primary alcohol or propanol).
Note:
We can see in the above reaction that the first $Al - H$ bond attacks the positively charged carbonyl carbon. As a result, $Al - H$ bond is broken and carbonyl that is present will take the hydrogen atom.
Because of this one bond of carbonyl carbon and oxygen will be gone on to the oxygen atom.
As we know that oxygen is highly electronegative. Therefore \[{O^ - }\] attacks the positively charged hydrogen atom of water molecules present.
Finally we can see the water molecule hydrolysis and the final product will be given that is propanol.
Complete step by step answer:
In organic chemistry $\left( {LiAl{H_4}} \right)$ is a strong reducing agent which is used to reduce aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acids, amide and more organic compound types.
There are several advantages of using $\left( {LiAl{H_4}} \right)$ as reducing agent that it does not reduce carbon–carbon double or triple bonds (with the exception of propargylic alcohols) and also, all four carbon atoms have the ability to participate the reaction
When $\left( {LiAl{H_4}} \right)$is used to reduce aldehyde or ketone the product we will get is alcohol.
As in the case of aldehyde, the primary alcohol is given as a product.
While in the case of ketone we get secondary alcohol as a product.

Therefore, Option A is correct.
The product we will get from the chemical reaction is $C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - OH$(Primary alcohol or propanol).
Note:
We can see in the above reaction that the first $Al - H$ bond attacks the positively charged carbonyl carbon. As a result, $Al - H$ bond is broken and carbonyl that is present will take the hydrogen atom.
Because of this one bond of carbonyl carbon and oxygen will be gone on to the oxygen atom.
As we know that oxygen is highly electronegative. Therefore \[{O^ - }\] attacks the positively charged hydrogen atom of water molecules present.
Finally we can see the water molecule hydrolysis and the final product will be given that is propanol.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




