
The product \[C\] may be:

Answer
514.2k+ views
Hint :Williamson’s ether reaction is an ether forming reaction from any product having a halide or a substituent attached to the ring. What happens is that organohalide and a deprotonated alcohol is reacted with the aromatic compound having a foreign substituent which gets replaced and the final product is an ether of the aromatic compound and the alkyl ring.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Here we are given a compound X and this X is made to go through the following reactions given above and the products are formed, now the questions ask the final product.
Now in the first reaction what happens is X reacts with $ C{H_3}ONa $ and $ C{H_3}OH $ . The compound X is basically a $ 1,2 - dichlorobenzene - 4 - sulphuric\,acid $ $ $ and it reacts with the above given two compounds. Now here we have an organohalide and a deprotonated alcohol, the solvent gives the deprotonated alcohol enough strength to attack the organohalide. Now the problem is at which position it will attack. The deprotonated alcohol will attack at the para position to the sulphuric acid and the final compound formed would have a $ - OC{H_3} $ at the para position to the sulphuric acid.
The compound formed now reacts with charged water. Now this reaction releases hydrogen ion and hydroxide ion, the hydroxide ion that is charged looks for an acidic site to react and it attacks at the sulphuric acid and the alkoxy group in the benzene ring and removes it completely and gets replaced by a hydrogen ion.
Now the product we have is that we have a hydroxy and choro group adjacent to each other in a benzene ring.
Now the product above is made to react with $ B{r_2}(excess) $ in a water solution, this is a bromination reaction in which the excess of bromine starts to attack at every fairly positive sight it comes across. Now the ring that we have is a benzene ring and we have two substituents attached adjacent to each other which are hydroxy and chloride groups. The hydroxy and chloride group due to the induction effect would create attackable fairly positive sites for charged bromine, at their ortho and para position. And also, the bromination would take place until the product B is all consumed.
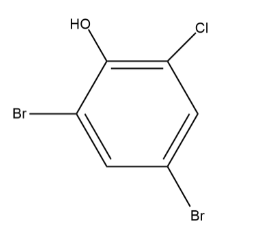
The final product C that will form would be called $ 4,6 - bromo - 2 - chloro\,phenol $ and the structure would look something like
Note :
The bromination reaction can take place for any halogen like chlorine or fluorine. Fluorine is a very highly reactive halogen which doesn’t need any solution while chlorine needs a fairly less activating environment than bromine.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Here we are given a compound X and this X is made to go through the following reactions given above and the products are formed, now the questions ask the final product.
Now in the first reaction what happens is X reacts with $ C{H_3}ONa $ and $ C{H_3}OH $ . The compound X is basically a $ 1,2 - dichlorobenzene - 4 - sulphuric\,acid $ $ $ and it reacts with the above given two compounds. Now here we have an organohalide and a deprotonated alcohol, the solvent gives the deprotonated alcohol enough strength to attack the organohalide. Now the problem is at which position it will attack. The deprotonated alcohol will attack at the para position to the sulphuric acid and the final compound formed would have a $ - OC{H_3} $ at the para position to the sulphuric acid.
The compound formed now reacts with charged water. Now this reaction releases hydrogen ion and hydroxide ion, the hydroxide ion that is charged looks for an acidic site to react and it attacks at the sulphuric acid and the alkoxy group in the benzene ring and removes it completely and gets replaced by a hydrogen ion.
Now the product we have is that we have a hydroxy and choro group adjacent to each other in a benzene ring.
Now the product above is made to react with $ B{r_2}(excess) $ in a water solution, this is a bromination reaction in which the excess of bromine starts to attack at every fairly positive sight it comes across. Now the ring that we have is a benzene ring and we have two substituents attached adjacent to each other which are hydroxy and chloride groups. The hydroxy and chloride group due to the induction effect would create attackable fairly positive sites for charged bromine, at their ortho and para position. And also, the bromination would take place until the product B is all consumed.
The final product C that will form would be called $ 4,6 - bromo - 2 - chloro\,phenol $ and the structure would look something like

Note :
The bromination reaction can take place for any halogen like chlorine or fluorine. Fluorine is a very highly reactive halogen which doesn’t need any solution while chlorine needs a fairly less activating environment than bromine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




