
The process of separation of an organic compound from its aqueous solution by shaking with a suitable solvent is termed solvent extraction or differential extraction.
The organic compound present in aqueous layer moves to the organic solvent because:
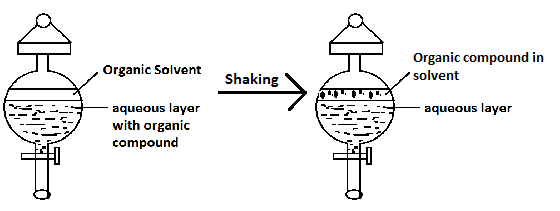
A.The organic substance is more soluble in the organic solvent.
B.Organic compound being lighter moves in the upper layer.
C.Organic solvent is soluble in water hence organic compound moves up.
D.From the supersaturated aqueous solution the solute starts diffusing.

Answer
542.7k+ views
Hint: The concept deals with tendency of miscibility. As we have heard, like dissolves like. So taking this concept into consideration, we will approach the solution with this point of view and will try to eliminate the options.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us discuss the first option mentioned in the question.
Option A. - The organic substance is more soluble in the organic solvent.
In this option, it satisfies the hint, which is like dissolves like. So, the solute and solvent with similar nature will be easily miscible because there will be attraction between the molecules of solute and solvent of similar kind. Also, such a solute will easily distribute itself in the organic solvent, as compared to aqueous phase. Thus, option A. will be kept into consideration and is the correct answer to the given question.
So, option A. is the correct answer to the given question.
Additional information:
Supersaturation is a must for the crystallization to take place. The most prominent example regarding Supersaturation is Sodium acetate. These solutions are highly unstable.
Along With this information, we should know the factors affecting the solubility. They are as follows:
1.Temperature
2.Polarity
3.Pressure
4.Molecular size
5.Stirring
Note: Supersaturation occurs when the concentration of solute exceeds the solubility concentration required at equilibrium. Since no such specifications are mentioned in the questions, option D. is discarded and is not taken in consideration.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us discuss the first option mentioned in the question.
Option A. - The organic substance is more soluble in the organic solvent.
In this option, it satisfies the hint, which is like dissolves like. So, the solute and solvent with similar nature will be easily miscible because there will be attraction between the molecules of solute and solvent of similar kind. Also, such a solute will easily distribute itself in the organic solvent, as compared to aqueous phase. Thus, option A. will be kept into consideration and is the correct answer to the given question.
So, option A. is the correct answer to the given question.
Additional information:
Supersaturation is a must for the crystallization to take place. The most prominent example regarding Supersaturation is Sodium acetate. These solutions are highly unstable.
Along With this information, we should know the factors affecting the solubility. They are as follows:
1.Temperature
2.Polarity
3.Pressure
4.Molecular size
5.Stirring
Note: Supersaturation occurs when the concentration of solute exceeds the solubility concentration required at equilibrium. Since no such specifications are mentioned in the questions, option D. is discarded and is not taken in consideration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




