
The power factor of an L-R circuit is,
$\begin{align}
& A.1 \\
& B\text{.zero} \\
& C.\text{between zero and one} \\
& D.\infty \\
\end{align}$
Answer
526k+ views
Hint: In usual AC circuits, the power factor depends on the passive devices which are connected to the load. The resistance of an L-R circuit is given as the resistance of turns of the coil of the inductor. For an inductive-resistive circuit which is a most commonly seen circuit, the power factor is defined as “lagging”.
Complete step by step answer:
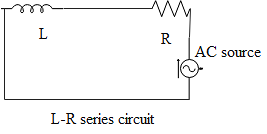
A resistor–inductor circuit also known as L-R network, is an electric circuit included of resistors and inductors connected to a voltage or a current source. A first-order RL circuit includes only one resistor and one inductor. This is the simplest L-R circuit. The actual reason for a low power factor in a circuit is due to the inductive load. The major inductive loads which are the reason for the low power factor are the three-phase induction motors. Even the transformers, lamps and welding equipment are operating at low lagging power factors.
In an L-R series circuit, the current is lagging behind the voltage by an angle $\phi $ , because of the effect of the inductor. The power factor is given as the cosine of lagging angle $\phi $
That means,
$\cos \phi =\dfrac{R}{Z}$$\cos \phi =0.6$
$Z$ is the impedance and $R$ is the resistance.
Generally the power factor of an L-R circuit is given as
$\cos \phi =0.6$
Therefore we can conclude that the power factor of the L-r circuit is in between one and zero. Hence the correct answer is option C.
Note:
Power factor is an important concept of an AC circuit which can also be shown in terms of impedance of circuit and the power of circuit. Power factor is expressed as the ratio of real power abbreviated as P to apparent power abbreviated as S. this is expressed generally as decimal quantity or in percentage. The ideal power factor is found to be unity, or one. A power factor less than one means that there is a requirement of extra power in order to complete the function. All the flow of current results in losses both in the supply as well as in the distribution system. A load with an ideal power factor is the most efficient one.
Complete step by step answer:
A resistor–inductor circuit also known as L-R network, is an electric circuit included of resistors and inductors connected to a voltage or a current source. A first-order RL circuit includes only one resistor and one inductor. This is the simplest L-R circuit. The actual reason for a low power factor in a circuit is due to the inductive load. The major inductive loads which are the reason for the low power factor are the three-phase induction motors. Even the transformers, lamps and welding equipment are operating at low lagging power factors.
In an L-R series circuit, the current is lagging behind the voltage by an angle $\phi $ , because of the effect of the inductor. The power factor is given as the cosine of lagging angle $\phi $
That means,
$\cos \phi =\dfrac{R}{Z}$$\cos \phi =0.6$
$Z$ is the impedance and $R$ is the resistance.
Generally the power factor of an L-R circuit is given as
$\cos \phi =0.6$
Therefore we can conclude that the power factor of the L-r circuit is in between one and zero. Hence the correct answer is option C.

Note:
Power factor is an important concept of an AC circuit which can also be shown in terms of impedance of circuit and the power of circuit. Power factor is expressed as the ratio of real power abbreviated as P to apparent power abbreviated as S. this is expressed generally as decimal quantity or in percentage. The ideal power factor is found to be unity, or one. A power factor less than one means that there is a requirement of extra power in order to complete the function. All the flow of current results in losses both in the supply as well as in the distribution system. A load with an ideal power factor is the most efficient one.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




