
The potential at a point P due to an electric dipole is $1.8 \times {10^5}V$. If P is at a distance of 50cm apart from the centre O of the dipole and if CP makes an angle ${60^ \circ }$ with the positive side of the axial line of the dipole, what is the moment of dipole?
A. $10C - m$
B. ${10^{ - 3}}C - m$
C. ${10^{ - 4}}C - m$
D. ${10^{ - 5}}C - m$
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: The electric dipole is a system of two charges that are separated by a finite distance. The dipole has a property called dipole moment which is equal to the product of the charges and the distance of separation among them. It is measured in debye (D) in atomic physics and chemistry and in regular, the SI unit is used which is coulomb-metre (C-m)
Complete step-by-step answer:
The dipole has a property called dipole moment which is equal to the product of the charges and the distance of separation among them.
Consider an electric dipole of charges +q and -q separated by a distance d and a point P at a distance of r from the center and at angle $\theta $.
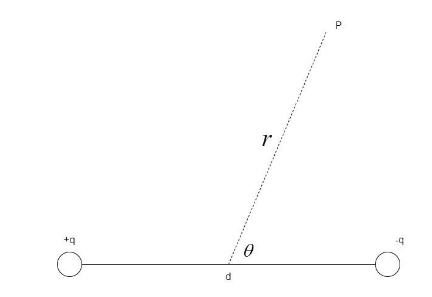
The electric potential at the point P in the figure, is given by the formula –
$V = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{p\cos \theta }}{{{r^2}}}$
where
${\varepsilon _0}$ = permittivity
$p$ = dipole moment
$\theta $ = angle made by the line joining the center of dipole and the point
r = distance of the point P from the center of dipole
Given data –
Potential at the point, $V = 1.8 \times {10^5}V$
Angle, $\theta = {60^ \circ }$
Distance of the point P, $r = 50cm = 0.5m$
$\dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} = 9 \times {10^9}N{m^2}/{C^2}$
The electric potential at the point P, $V = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{p\cos \theta }}{{{r^2}}}$
Substituting and rearranging the equation, we get –
\[
1.8 \times {10^5} = 9 \times {10^9} \times \dfrac{{p\cos {{60}^ \circ }}}{{{{0.5}^2}}} \\
p\cos {60^ \circ } = \dfrac{{1.8 \times {{10}^5} \times {{0.5}^2}}}{{9 \times {{10}^9}}} \\
Solving, \\
p\cos {60^ \circ } = 0.05 \times {10^{5 - 9}} \\
\to p\cos {60^ \circ } = 5 \times {10^{ - 6}} \\
\to p\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = 5 \times {10^{ - 6}}(\because \cos 60 = \dfrac{1}{2}) \\
\to p = 10 \times {10^{ - 6}} = {10^{ - 5}}C - m \\
\]
The dipole moment = ${10^{ - 5}}C - m$
Hence, the correct option is Option D.
Note: The maximum and minimum values of the potential are determined by $\cos \theta $
When $\theta = {0^ \circ } \to \cos \theta = 1$ . The electric potential will be maximum at the dipole axis.
When $\theta = {90^ \circ } \to \cos \theta = 0$ . The electric potential will be zero at the perpendicular axis of the dipole.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The dipole has a property called dipole moment which is equal to the product of the charges and the distance of separation among them.
Consider an electric dipole of charges +q and -q separated by a distance d and a point P at a distance of r from the center and at angle $\theta $.

The electric potential at the point P in the figure, is given by the formula –
$V = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{p\cos \theta }}{{{r^2}}}$
where
${\varepsilon _0}$ = permittivity
$p$ = dipole moment
$\theta $ = angle made by the line joining the center of dipole and the point
r = distance of the point P from the center of dipole
Given data –
Potential at the point, $V = 1.8 \times {10^5}V$
Angle, $\theta = {60^ \circ }$
Distance of the point P, $r = 50cm = 0.5m$
$\dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} = 9 \times {10^9}N{m^2}/{C^2}$
The electric potential at the point P, $V = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{p\cos \theta }}{{{r^2}}}$
Substituting and rearranging the equation, we get –
\[
1.8 \times {10^5} = 9 \times {10^9} \times \dfrac{{p\cos {{60}^ \circ }}}{{{{0.5}^2}}} \\
p\cos {60^ \circ } = \dfrac{{1.8 \times {{10}^5} \times {{0.5}^2}}}{{9 \times {{10}^9}}} \\
Solving, \\
p\cos {60^ \circ } = 0.05 \times {10^{5 - 9}} \\
\to p\cos {60^ \circ } = 5 \times {10^{ - 6}} \\
\to p\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = 5 \times {10^{ - 6}}(\because \cos 60 = \dfrac{1}{2}) \\
\to p = 10 \times {10^{ - 6}} = {10^{ - 5}}C - m \\
\]
The dipole moment = ${10^{ - 5}}C - m$
Hence, the correct option is Option D.
Note: The maximum and minimum values of the potential are determined by $\cos \theta $
When $\theta = {0^ \circ } \to \cos \theta = 1$ . The electric potential will be maximum at the dipole axis.
When $\theta = {90^ \circ } \to \cos \theta = 0$ . The electric potential will be zero at the perpendicular axis of the dipole.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




