
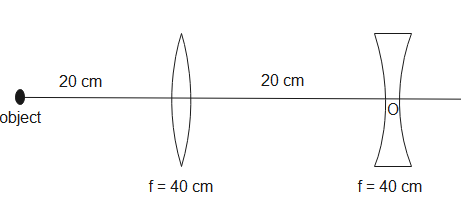
The position of final image from O for the arrangement as shown
(A). $-24cm$
(B). $-120cm$
(C). $-40cm$
(D). $-20cm$

Answer
543.9k+ views
Hint: Two lenses are kept at a distance from each other. By refraction from the first lens, the image formed by the first lens will act as the object for the second lens. The final image is formed by the second lens. Respective distances can be calculated using lens formula which gives relation between object distance, image distance and focal length.
Formulas used:
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Complete answer:
The image in lenses is formed by the phenomenon of refraction. When a light travels from one medium to another medium, it changes its path, this phenomenon is known as refraction.
Given, focal length of convex lens is $40cm$ and the focal length of concave lens is $-40cm$.
The lens formula is given as-
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$ - (1)
Here, $v$ is the image distance
$u$ is the object distance
$f$ is the focal length
For refraction at first surface,
$u=-20cm$, $f=40cm$. Substituting given values in eq (1), we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{-20}=\dfrac{1}{40} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{20}=\dfrac{1}{40} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{40}-\dfrac{1}{20} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{-1}{40} \\
& \therefore v=-40cm \\
\end{align}$
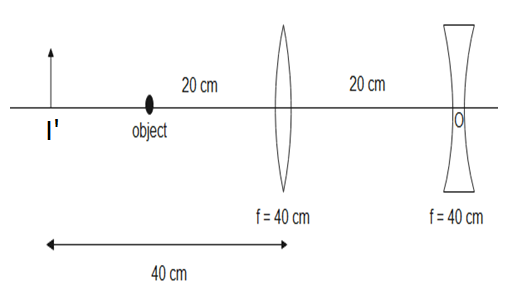
The image formed by the first lens is 40 cm behind the lens which means it is $40+20=60cm$ behind the second lens.
Therefore, for refraction by second lens, $u=-60cm$, $f=-40cm$
Substituting given values in eq (1), we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{-60}=\dfrac{1}{-40} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{60}=-\dfrac{1}{40} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=-\dfrac{1}{60}-\dfrac{1}{40} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{-5}{120} \\
& \therefore v=-24cm \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the final image is $24cm$ away from the point O behind the lens.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note:
By convention, all distances measured from right to left are taken as positive and distances from left to right are taken as negative. The focal length of a convex lens is taken as positive and the focal length of a concave lens is taken as negative. The object distance is always negative. The convex lens is a converging lens while the concave lens is a diverging lens.
Formulas used:
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Complete answer:
The image in lenses is formed by the phenomenon of refraction. When a light travels from one medium to another medium, it changes its path, this phenomenon is known as refraction.
Given, focal length of convex lens is $40cm$ and the focal length of concave lens is $-40cm$.
The lens formula is given as-
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$ - (1)
Here, $v$ is the image distance
$u$ is the object distance
$f$ is the focal length
For refraction at first surface,
$u=-20cm$, $f=40cm$. Substituting given values in eq (1), we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{-20}=\dfrac{1}{40} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{20}=\dfrac{1}{40} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{40}-\dfrac{1}{20} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{-1}{40} \\
& \therefore v=-40cm \\
\end{align}$

The image formed by the first lens is 40 cm behind the lens which means it is $40+20=60cm$ behind the second lens.
Therefore, for refraction by second lens, $u=-60cm$, $f=-40cm$
Substituting given values in eq (1), we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{-60}=\dfrac{1}{-40} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{60}=-\dfrac{1}{40} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=-\dfrac{1}{60}-\dfrac{1}{40} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{-5}{120} \\
& \therefore v=-24cm \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the final image is $24cm$ away from the point O behind the lens.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note:
By convention, all distances measured from right to left are taken as positive and distances from left to right are taken as negative. The focal length of a convex lens is taken as positive and the focal length of a concave lens is taken as negative. The object distance is always negative. The convex lens is a converging lens while the concave lens is a diverging lens.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




