
The phenomenon of interference is shown by:
A. longitudinal mechanical waves only
B. electromagnetic waves only
C. transverse mechanical waves only
D. all of the above types of wave
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: Interference is the superposition of individual waves, such that the amplitude of the resultant wave is the vector sum of the amplitude of the individual waves. Their resultant wave can either be constructive or destructive, depending on the interaction of the individual waves.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Interference is the property of waves, where the resultant wave is the superposition of two waves. The resultant of the two waves can interfere constructively to give a bright spot or destructively to give a dark spot. The graph of the resultant waves is called interferograms. This property of waves is applicable to all waves, like lightwave, matter waves, or gravitational waves to name a few. This is based on the principle of superposition of waves, which states that when two or more waves are incident at a point, then their resultant amplitude is the vector sum of the individual amplitudes, provided the waves are of similar nature.
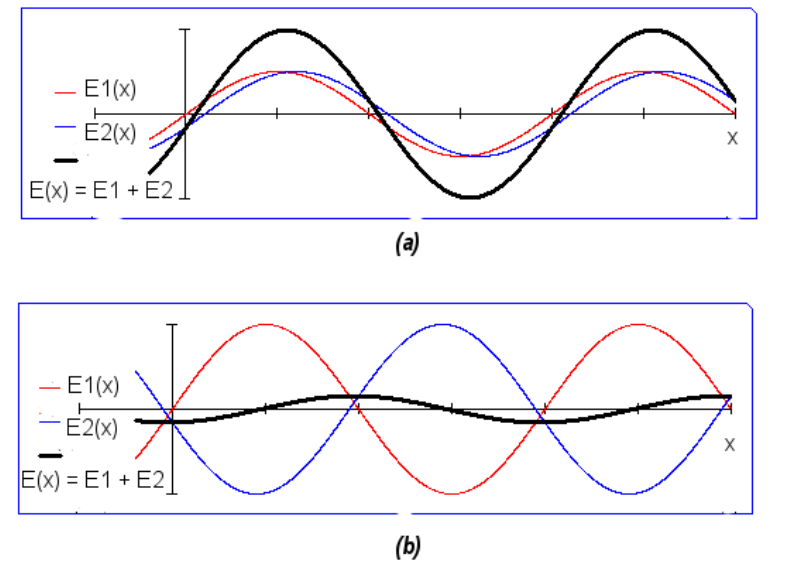
If two crests or troughs interfere then they are said to form constructive interference (a), here the amplitude of the resultant wave is greater than the individual waves. Similarly, if one trough and one crest interfere, they are said to form destructive interference (b), where the amplitude of the resultant wave is lesser than the individual waves.
As the interference is a wave property and is applicable to all types of waves, the answer is D. all of the above types of wave.
Note: Interference is observed only when the incident waves are coherent i.e. they are from the same source or the frequency of the sources must be nearly the same. Also, the amplitude of the resultant wave can either be greater, lesser, or equal to the amplitude of the incident waves.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Interference is the property of waves, where the resultant wave is the superposition of two waves. The resultant of the two waves can interfere constructively to give a bright spot or destructively to give a dark spot. The graph of the resultant waves is called interferograms. This property of waves is applicable to all waves, like lightwave, matter waves, or gravitational waves to name a few. This is based on the principle of superposition of waves, which states that when two or more waves are incident at a point, then their resultant amplitude is the vector sum of the individual amplitudes, provided the waves are of similar nature.

If two crests or troughs interfere then they are said to form constructive interference (a), here the amplitude of the resultant wave is greater than the individual waves. Similarly, if one trough and one crest interfere, they are said to form destructive interference (b), where the amplitude of the resultant wave is lesser than the individual waves.
As the interference is a wave property and is applicable to all types of waves, the answer is D. all of the above types of wave.
Note: Interference is observed only when the incident waves are coherent i.e. they are from the same source or the frequency of the sources must be nearly the same. Also, the amplitude of the resultant wave can either be greater, lesser, or equal to the amplitude of the incident waves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




