
The period of ${{\sin} ^ {2}} x$ is \[\]
A.$\dfrac{\pi} {2}$\[\]
B. $\pi $\[\]
C. $\dfrac{3\pi }{2}$\[\]
D. $2\pi $\[\]
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: We recall the definition of period and try find the minimum value positive value of $P$ such that ${{\sin }^{2}}\left( x+P \right)={{\sin }^{2}}x$. We use the formula ${{\sin }^{2}}\theta =\dfrac{1-\cos 2\theta }{2}$ , find all the solution of $\cos \theta =\cos \alpha $ that is $\theta =2n\pi +\alpha $and check for which value of $n$ we get minimum $P$, which will be the period.\[\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
We know from cosine double angle formula that for any acute angle $\theta $,
\[\begin{align}
& \cos 2\theta =1-2{{\sin }^{2}}\theta \\
& \Rightarrow {{\sin }^{2}}\theta =\dfrac{1-\cos 2\theta }{2}....\left( 1 \right) \\
\end{align}\]
We know that the solutions of the equation $\cos \theta =\cos \alpha $ are given by
\[\theta =2n\pi +\alpha ,n\in Z\]
We know that the period of a real valued function $f\left( x \right)$ is a nonzero positive constant $P$ for all $x$ in the domain of $f$ if
\[f\left( x+P \right)=f\left( x \right)\]
$P$ is also called the fundamental period or basic period. All the functional values of $f\left( x \right)$ will repeat after the interval of length $P$. The plot of periodic function exhibits translational symmetry which means the graph of function $f\left( x \right)$ is invariant in $x-$ axis with respect to translation by a length $P$. We can also writ for some positive integer $n$
\[f\left( x+nP \right)=f\left( x \right)\]
Here the given function is $f\left( x \right)={{\sin }^{2}}x$ where $f:{{R}^{+}}\bigcup \left\{ 0 \right\}\to {{R}^{+}}\bigcup \left\{ 0 \right\}$. Let us assume the period of ${{\sin }^{2}}x$ is $P$. So we have
\[{{\sin }^{2}}\left( x+P \right)={{\sin }^{2}}x\]
We use relation (1) for $\theta =x+P,x$ and have
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1-\cos \left( 2\left( x+P \right) \right)}{2}=\dfrac{1-\cos 2x}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( 2x+2P \right)=\cos 2x \\
\end{align}\]
The solutions of the above equation with some integer $n$ are
\[\begin{align}
& 2x+2P=2x+2n\pi \\
& \Rightarrow x+P=x+n\pi \\
& \Rightarrow P=n\pi \\
\end{align}\]
The fundamental period is the minimum non-zero positive value of $P$ which we find with $n=1$ and hence the period of ${{\sin }^{2}}x$ is $P=1\times \pi =\pi $. So the correct option is C. If we plot $y={{\sin }^{2}}x$ then we can see the repeat of functional values after a period$\pi =3.14$.\[\]
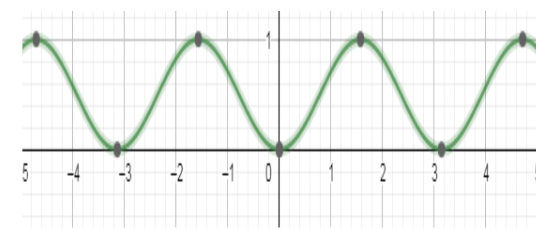
Note: We can alternatively solve by first finding the period of $\cos 2x$ using the fact that the period of $f\left( ax \right)$ is $\dfrac{P}{\left| a \right|}$. We then use the fact that the period of functions $f\left( x \right)$ and $g\left( x \right)$ are equal if and only if $f\left( x \right)=a+bg\left( x \right)$for ${{\sin }^{2}}x=\dfrac{1-\cos 2x}{2}$. If a function foes not have a period it is called aperiodic and if $f\left( x+T \right)=-f\left( x \right)$ then it is called anti-periodic.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We know from cosine double angle formula that for any acute angle $\theta $,
\[\begin{align}
& \cos 2\theta =1-2{{\sin }^{2}}\theta \\
& \Rightarrow {{\sin }^{2}}\theta =\dfrac{1-\cos 2\theta }{2}....\left( 1 \right) \\
\end{align}\]
We know that the solutions of the equation $\cos \theta =\cos \alpha $ are given by
\[\theta =2n\pi +\alpha ,n\in Z\]
We know that the period of a real valued function $f\left( x \right)$ is a nonzero positive constant $P$ for all $x$ in the domain of $f$ if
\[f\left( x+P \right)=f\left( x \right)\]
$P$ is also called the fundamental period or basic period. All the functional values of $f\left( x \right)$ will repeat after the interval of length $P$. The plot of periodic function exhibits translational symmetry which means the graph of function $f\left( x \right)$ is invariant in $x-$ axis with respect to translation by a length $P$. We can also writ for some positive integer $n$
\[f\left( x+nP \right)=f\left( x \right)\]
Here the given function is $f\left( x \right)={{\sin }^{2}}x$ where $f:{{R}^{+}}\bigcup \left\{ 0 \right\}\to {{R}^{+}}\bigcup \left\{ 0 \right\}$. Let us assume the period of ${{\sin }^{2}}x$ is $P$. So we have
\[{{\sin }^{2}}\left( x+P \right)={{\sin }^{2}}x\]
We use relation (1) for $\theta =x+P,x$ and have
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1-\cos \left( 2\left( x+P \right) \right)}{2}=\dfrac{1-\cos 2x}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( 2x+2P \right)=\cos 2x \\
\end{align}\]
The solutions of the above equation with some integer $n$ are
\[\begin{align}
& 2x+2P=2x+2n\pi \\
& \Rightarrow x+P=x+n\pi \\
& \Rightarrow P=n\pi \\
\end{align}\]
The fundamental period is the minimum non-zero positive value of $P$ which we find with $n=1$ and hence the period of ${{\sin }^{2}}x$ is $P=1\times \pi =\pi $. So the correct option is C. If we plot $y={{\sin }^{2}}x$ then we can see the repeat of functional values after a period$\pi =3.14$.\[\]

Note: We can alternatively solve by first finding the period of $\cos 2x$ using the fact that the period of $f\left( ax \right)$ is $\dfrac{P}{\left| a \right|}$. We then use the fact that the period of functions $f\left( x \right)$ and $g\left( x \right)$ are equal if and only if $f\left( x \right)=a+bg\left( x \right)$for ${{\sin }^{2}}x=\dfrac{1-\cos 2x}{2}$. If a function foes not have a period it is called aperiodic and if $f\left( x+T \right)=-f\left( x \right)$ then it is called anti-periodic.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




