
The period of oscillation of compass needle will be $8s$ at a place where dip angle is ${{30}^{\circ }}$ and magnetic field will be${{B}_{1}}$. At another place where dip angle is ${{60}^{\circ }}$and magnetic field is${{B}_{2}}$, the period of oscillation has been given as $4s$, then what will be the ratio of the magnetic field,$\dfrac{{{B}_{2}}}{{{B}_{1}}}$?
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: in order to find the ratio of $\dfrac{{{B}_{2}}}{{{B}_{1}}}$ we require to get the value of the horizontal component ${{B}_{H}}$ and by the use of the concept and formula of time period magnetic field the required value can be found. The time period can be found by taking the product of twice the pi and the square root of the ratio of the moment of inertia and the product of the magnetic moment and magnetic field at the horizontal component.
Complete step by step solution:
Here in the equation, the period of oscillation of a compass needle has been given as $8s$ at a specific place where the angle of dip is ${{30}^{\circ }}$and the value of magnetic field has been given as ${{B}_{1}}$. At so many other place where the angle of dip is ${{60}^{\circ }}$the value of magnetic field will be ${{B}_{2}}$ and the period of oscillation of the compass needle will be $4s$. We should know the formula for time period at first.
$T=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{I}{M{{B}_{H}}}}$……………. (1)
Where, $T$ will be representing the time period, $I$will be representing the moment of inertia, $M$ will be representing the magnetic moment, ${{B}_{H}}$ will be representing the horizontal component of the magnetic field. Here, by the diagram of the magnetic field of earth, we can write that,
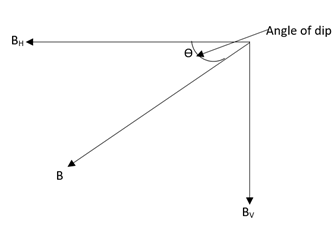
$\theta $ be the angle of the dip, ${{B}_{V}}$ will be representing the vertical component of the magnetic field, $B$ is representing the net magnetic field of the earth. From the above figure we can write that,
${{B}_{H}}=B\cos \theta $………….. (2)
Therefore from the equation (1) and (2), we can write that,
\[\begin{align}
& {{T}_{1}}=\text{ }2\pi ~\sqrt{\dfrac{I}{M{{B}_{1}}\cos 60{}^\circ }}..........(3) \\
& {{T}_{2}}=\text{ }2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{I}{M{{B}_{2}}\cos 60{}^\circ }}...........(4) \\
\end{align}\]
As for the compass needle, the moment of inertia and magnetic moment are constant so \[I\] and \[M\]will not vary. Now by putting all the mentioned values of the time and the angles and dividing (3) and (4) we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{8}{4}=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{B}_{2}}\cos 60{}^\circ }}{\sqrt{{{B}_{1}}\cos 30{}^\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow 2=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{B}_{2}}\cos 60{}^\circ }}{\sqrt{{{B}_{1}}\cos 30{}^\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Now taking square on both sides we can write that,
\[\Rightarrow 4=\dfrac{{{B}_{2}}\cos 60{}^\circ }{{{B}_{1}}\cos 30{}^\circ }\]
By applying the values of \[\cos 60{}^\circ \]and \[\cos 30{}^\circ \] as $\dfrac{1}{2}$ and $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$ respectively, we get that,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 4=\dfrac{{{B}_{2}}}{{{B}_{1}}}\times \dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow 4\times \sqrt{3}=\dfrac{{{B}_{2}}}{{{B}_{1}}} \\
& \therefore \dfrac{{{B}_{2}}}{{{B}_{1}}}=4\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Now the ratio of $\dfrac{{{B}_{2}}}{{{B}_{1}}}$ has been obtained as \[4\sqrt{3}\].
Note:
A magnetic field is a vector that defines the magnetic impact on the moving electric charges, electric currents and magnetic materials. The angle of dip is the angle between the earth’s net magnetic field and its horizontal component.
Complete step by step solution:
Here in the equation, the period of oscillation of a compass needle has been given as $8s$ at a specific place where the angle of dip is ${{30}^{\circ }}$and the value of magnetic field has been given as ${{B}_{1}}$. At so many other place where the angle of dip is ${{60}^{\circ }}$the value of magnetic field will be ${{B}_{2}}$ and the period of oscillation of the compass needle will be $4s$. We should know the formula for time period at first.
$T=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{I}{M{{B}_{H}}}}$……………. (1)
Where, $T$ will be representing the time period, $I$will be representing the moment of inertia, $M$ will be representing the magnetic moment, ${{B}_{H}}$ will be representing the horizontal component of the magnetic field. Here, by the diagram of the magnetic field of earth, we can write that,

$\theta $ be the angle of the dip, ${{B}_{V}}$ will be representing the vertical component of the magnetic field, $B$ is representing the net magnetic field of the earth. From the above figure we can write that,
${{B}_{H}}=B\cos \theta $………….. (2)
Therefore from the equation (1) and (2), we can write that,
\[\begin{align}
& {{T}_{1}}=\text{ }2\pi ~\sqrt{\dfrac{I}{M{{B}_{1}}\cos 60{}^\circ }}..........(3) \\
& {{T}_{2}}=\text{ }2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{I}{M{{B}_{2}}\cos 60{}^\circ }}...........(4) \\
\end{align}\]
As for the compass needle, the moment of inertia and magnetic moment are constant so \[I\] and \[M\]will not vary. Now by putting all the mentioned values of the time and the angles and dividing (3) and (4) we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{8}{4}=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{B}_{2}}\cos 60{}^\circ }}{\sqrt{{{B}_{1}}\cos 30{}^\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow 2=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{B}_{2}}\cos 60{}^\circ }}{\sqrt{{{B}_{1}}\cos 30{}^\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Now taking square on both sides we can write that,
\[\Rightarrow 4=\dfrac{{{B}_{2}}\cos 60{}^\circ }{{{B}_{1}}\cos 30{}^\circ }\]
By applying the values of \[\cos 60{}^\circ \]and \[\cos 30{}^\circ \] as $\dfrac{1}{2}$ and $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$ respectively, we get that,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 4=\dfrac{{{B}_{2}}}{{{B}_{1}}}\times \dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow 4\times \sqrt{3}=\dfrac{{{B}_{2}}}{{{B}_{1}}} \\
& \therefore \dfrac{{{B}_{2}}}{{{B}_{1}}}=4\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Now the ratio of $\dfrac{{{B}_{2}}}{{{B}_{1}}}$ has been obtained as \[4\sqrt{3}\].
Note:
A magnetic field is a vector that defines the magnetic impact on the moving electric charges, electric currents and magnetic materials. The angle of dip is the angle between the earth’s net magnetic field and its horizontal component.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




