
The peak voltage of 220 volt AC mains (in volt) is:
(A)$155.6$
(B)$220$
(C)$311$
(D) $440$
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint:Given AC source voltage is in root mean square value. We have to find here peak value corresponding to given root mean square (rms) value by using formula${V_{peak}} = \sqrt 2 {V_{rms}}$ .
Formula used:
${V_{peak}} = \sqrt 2 {V_{rms}}$ where, ${V_{peak}}$ is peak voltage of source and ${V_{rms}}$ is rms value of AC voltage.
Complete step by step answer:
Alternate current (AC) is the flow of charge which continuously changes magnitude in a fixed pattern and reverses its direction in a fixed interval of time period. It changes its direction many times in a second is called its frequency. In India AC supply has frequency of $50Hz$ and in many countries of the world it may vary to $60Hz$.
Root Mean Square value of AC voltage is the effective voltage experienced by a resistance, it can be calculated by giving AC voltage to resistance and comparing it with equivalent resistance offered to DC voltage. In graphical representation it is shown as:
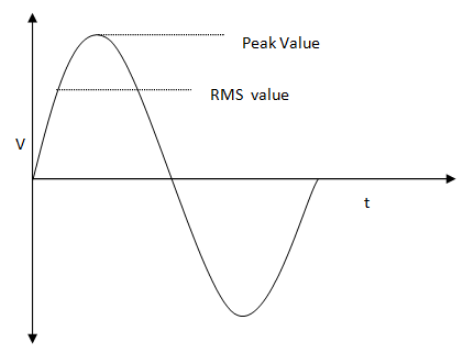
To calculate peak voltage from RMS value we have formula as following:
${V_{peak}} = \sqrt 2 {V_{rms}}$ where, ${V_{peak}}$ is peak voltage of source and ${V_{rms}}$ is rms value of AC voltage.
We have been given ${V_{rms}} = 220V$. By putting this value in above formula we get,
$
{V_{peak}} = \sqrt 2 \times 220V \\
\therefore{V_{peak}} = 311.12V \\
$
Hence, option (C) $311$ is the correct answer.
Note: Student should not be confused between rms value and average value of alternate current. Average value of alternate current is average taken of AC over the one complete cycle, but it will be always zero in symmetrical AC waveform. To avoid this problem one half cycle is taken in such a case as work is done by both positive and negative cycles which should be taken into consideration.
Formula used:
${V_{peak}} = \sqrt 2 {V_{rms}}$ where, ${V_{peak}}$ is peak voltage of source and ${V_{rms}}$ is rms value of AC voltage.
Complete step by step answer:
Alternate current (AC) is the flow of charge which continuously changes magnitude in a fixed pattern and reverses its direction in a fixed interval of time period. It changes its direction many times in a second is called its frequency. In India AC supply has frequency of $50Hz$ and in many countries of the world it may vary to $60Hz$.
Root Mean Square value of AC voltage is the effective voltage experienced by a resistance, it can be calculated by giving AC voltage to resistance and comparing it with equivalent resistance offered to DC voltage. In graphical representation it is shown as:

To calculate peak voltage from RMS value we have formula as following:
${V_{peak}} = \sqrt 2 {V_{rms}}$ where, ${V_{peak}}$ is peak voltage of source and ${V_{rms}}$ is rms value of AC voltage.
We have been given ${V_{rms}} = 220V$. By putting this value in above formula we get,
$
{V_{peak}} = \sqrt 2 \times 220V \\
\therefore{V_{peak}} = 311.12V \\
$
Hence, option (C) $311$ is the correct answer.
Note: Student should not be confused between rms value and average value of alternate current. Average value of alternate current is average taken of AC over the one complete cycle, but it will be always zero in symmetrical AC waveform. To avoid this problem one half cycle is taken in such a case as work is done by both positive and negative cycles which should be taken into consideration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




