
The organic compounds that give the following qualitative analysis is:
Test Inference (a) Dil. $\text{ HCl }$ Insoluble (b) $\text{ NaOH }$solution soluble (c) $\text{ B}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ / water }$ Decolourisation
(A)
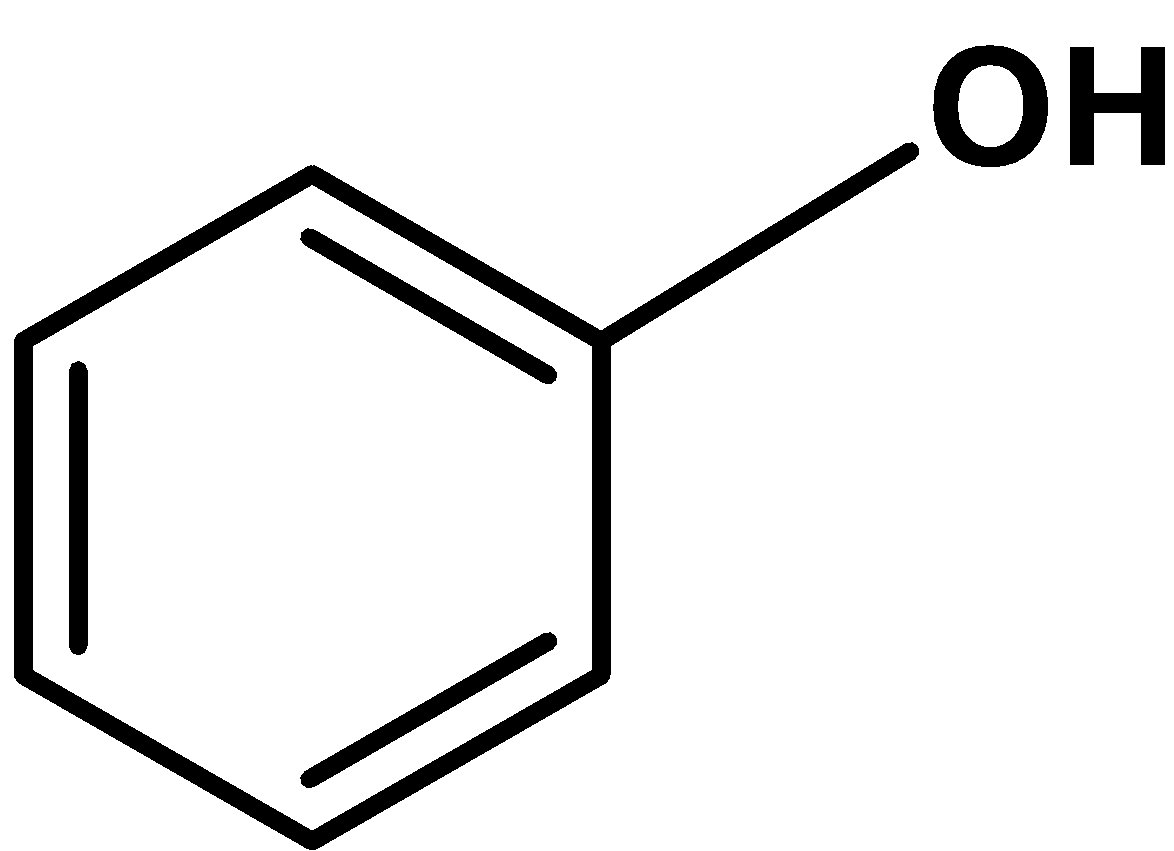
(B)
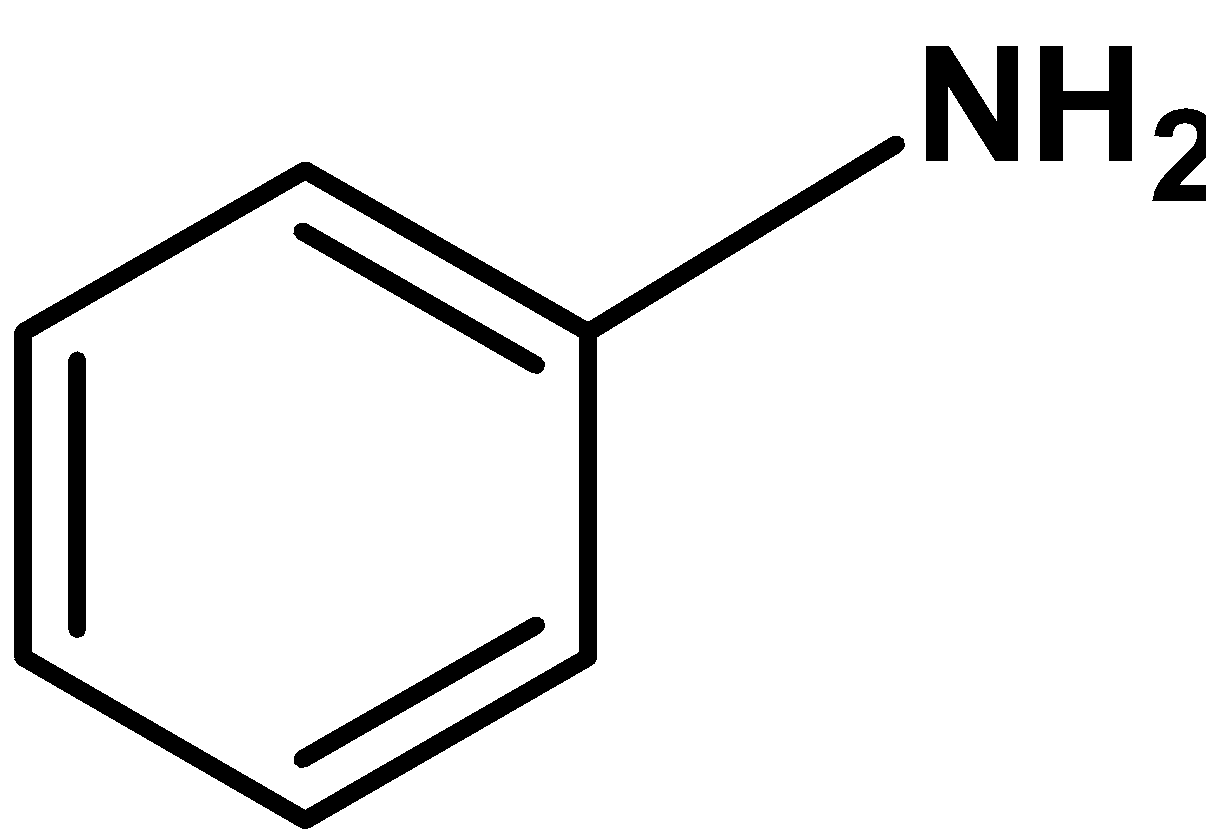
(C)
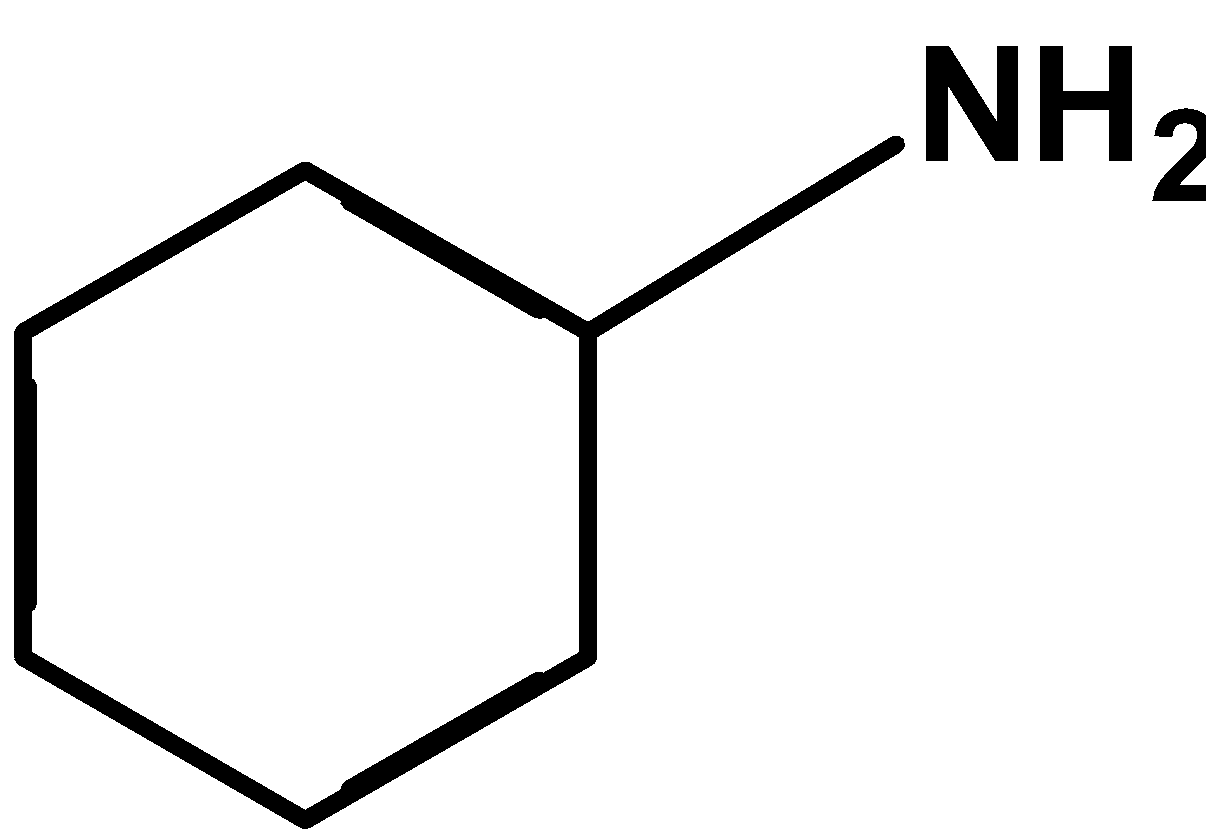
(D)
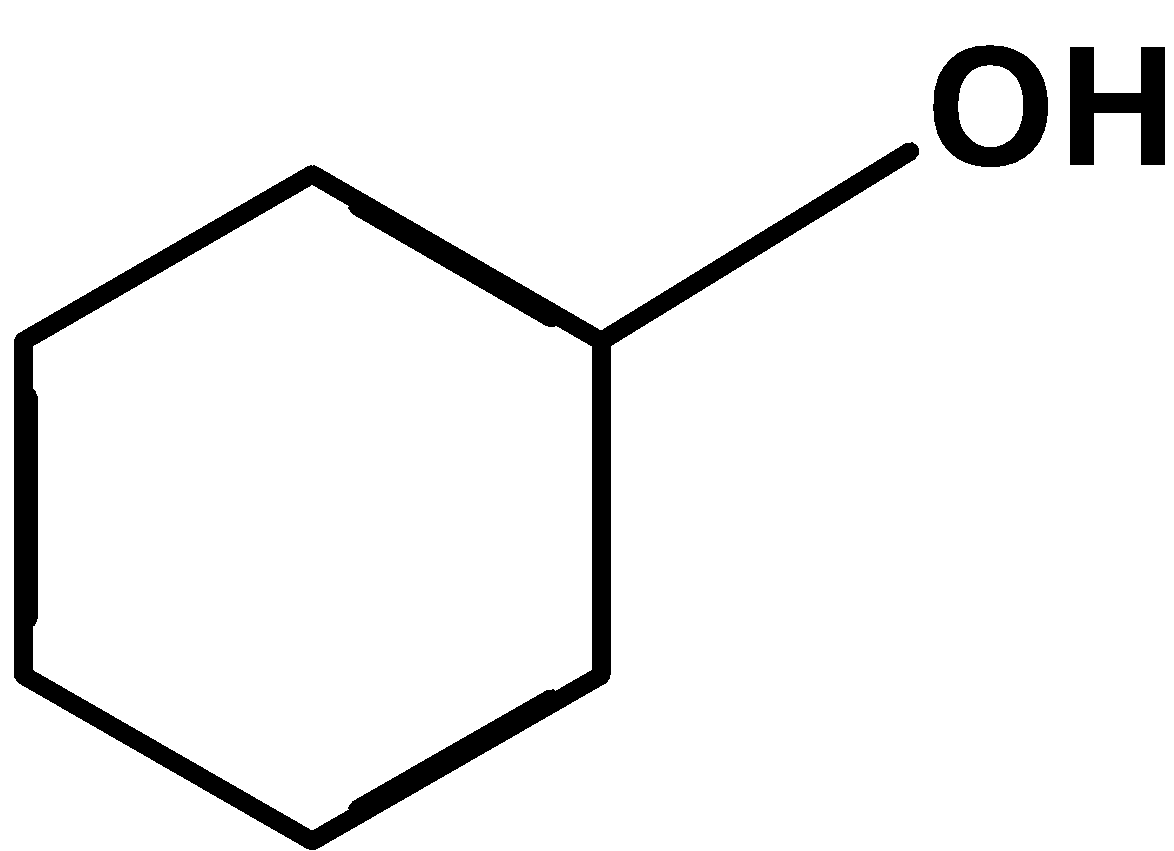 .
.
| Test | Inference |
| (a) Dil. $\text{ HCl }$ | Insoluble |
| (b) $\text{ NaOH }$solution | soluble |
| (c) $\text{ B}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ / water }$ | Decolourisation |
| (A) | 
|
| (B) | 
|
| (C) | 
|
| (D) | 
|
Answer
579k+ views
Hint: The chemical nature of the organic compounds are identified by treating it with the reagent. The compound which can neutralize the acidic reagent like $\text{ HCl }$ forms soluble salt in the solution. However, those do not react or insoluble may be acidic. Such compounds can undergo the reaction with the alkali and form a soluble salt. These organic compounds are weakly acidic and undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions with the bromine water.
Complete step by step answer:
-We are given that the given compound is insoluble in the dilute hydrochloric acid but soluble in sodium hydroxide. When the compound is added to the $\text{ 1: 1 }$ (or dilute acid) solution.
-The phenol is weakly acidic. Their acidic character is due to the formation of resonance stabilized phenoxide ion which is formed by losing the proton from the $\text{ }-\text{OH }$ group.
-In an acidic medium, the hydrogen ion suppresses the solubility of the phenoxide ion as the equilibrium shifts to the left-hand side. Phenol is insoluble in an acidic medium.
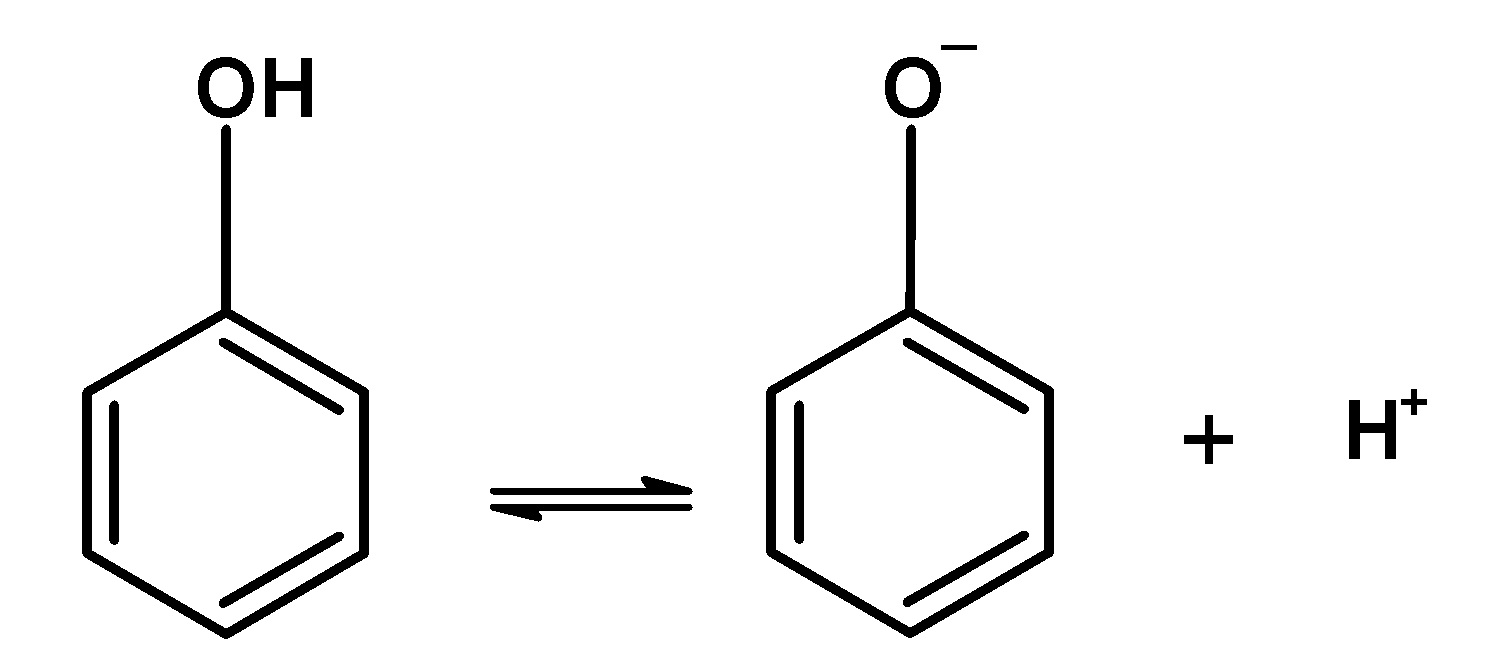
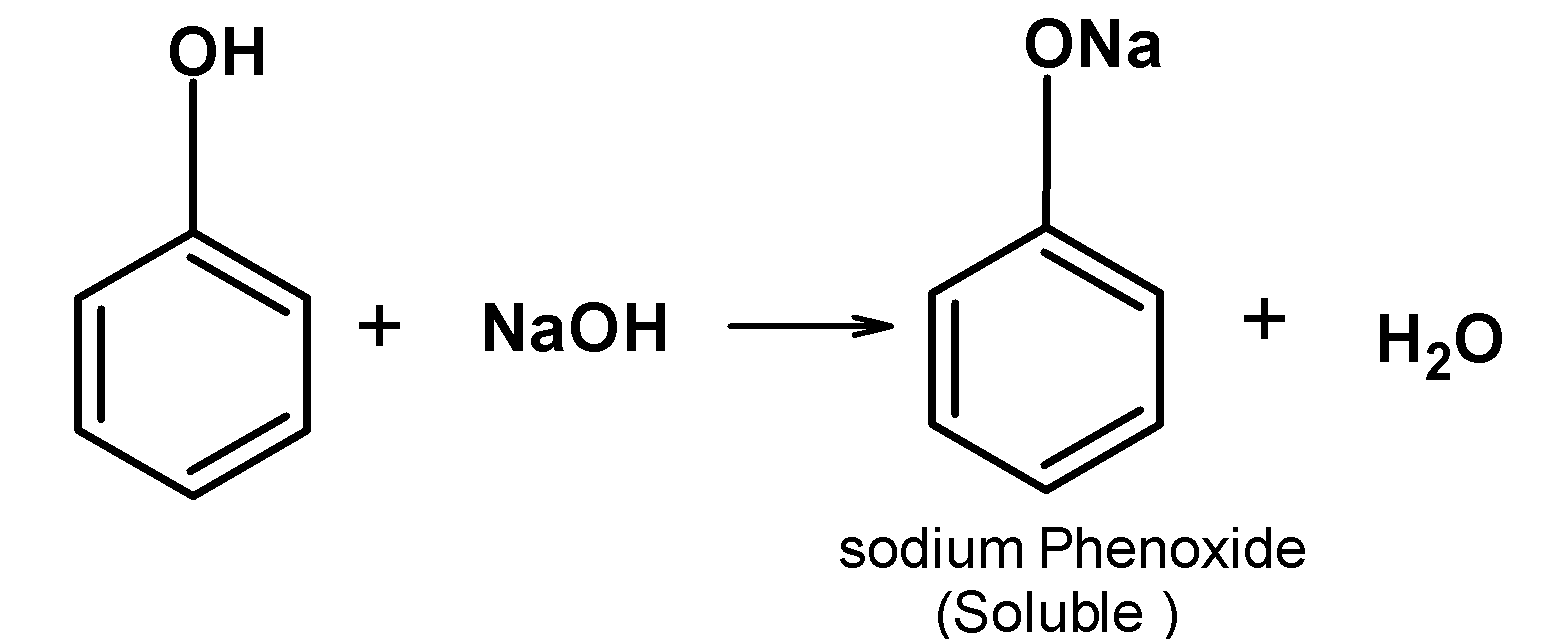
-When alkalis are added to the phenol, the equilibrium between the phenol and phenoxide ions shift towards the right-hand side as the hydrogen ions $\text{ }{{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}\text{ }$ are removed by the $\text{ O}{{\text{H}}^{-}}\text{ }$. -Therefore more phenol in the solution is converted into the phenoxide ion and thus solubility of the phenol is increased. The sodium phenoxide is soluble in water. Since water is a polar solvent the phenoxide easily gets soluble.
-Phenols undergo the electrophilic substitution reaction. The $\text{ }-\text{OH }$ group is a ring activating group, these reactions occur at a faster rate than the reaction of benzene itself. The $\text{ }-\text{OH }$ group is an ortho-para directing and therefore, the incoming group comes at ortho and para position. The phenol undergoes the electrophilic substitution reaction when reacted with the bromine molecule. The bromine acts as an electrophile and attacks on the phenolic ring.
-Phenols react with the bromine in water and give a white precipitate. This precipitate is due to the formation of 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol.
-The reaction of the phenol with the bromine water is as shown below,
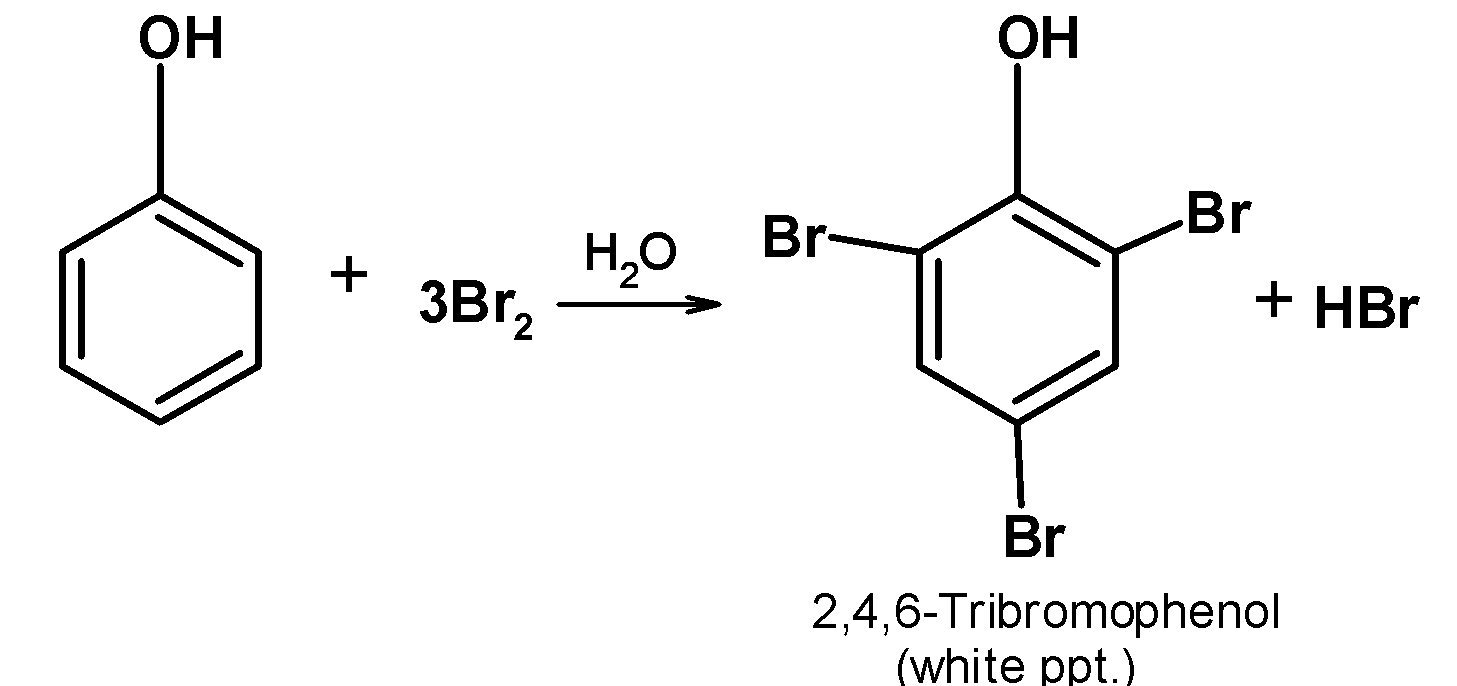
-Thus, the compound which is insoluble in dilute$\text{ HCl }$ but soluble in $\text{ NaOH }$ solution and decolorizes when reacted with the bromine water is phenol. The compound is,
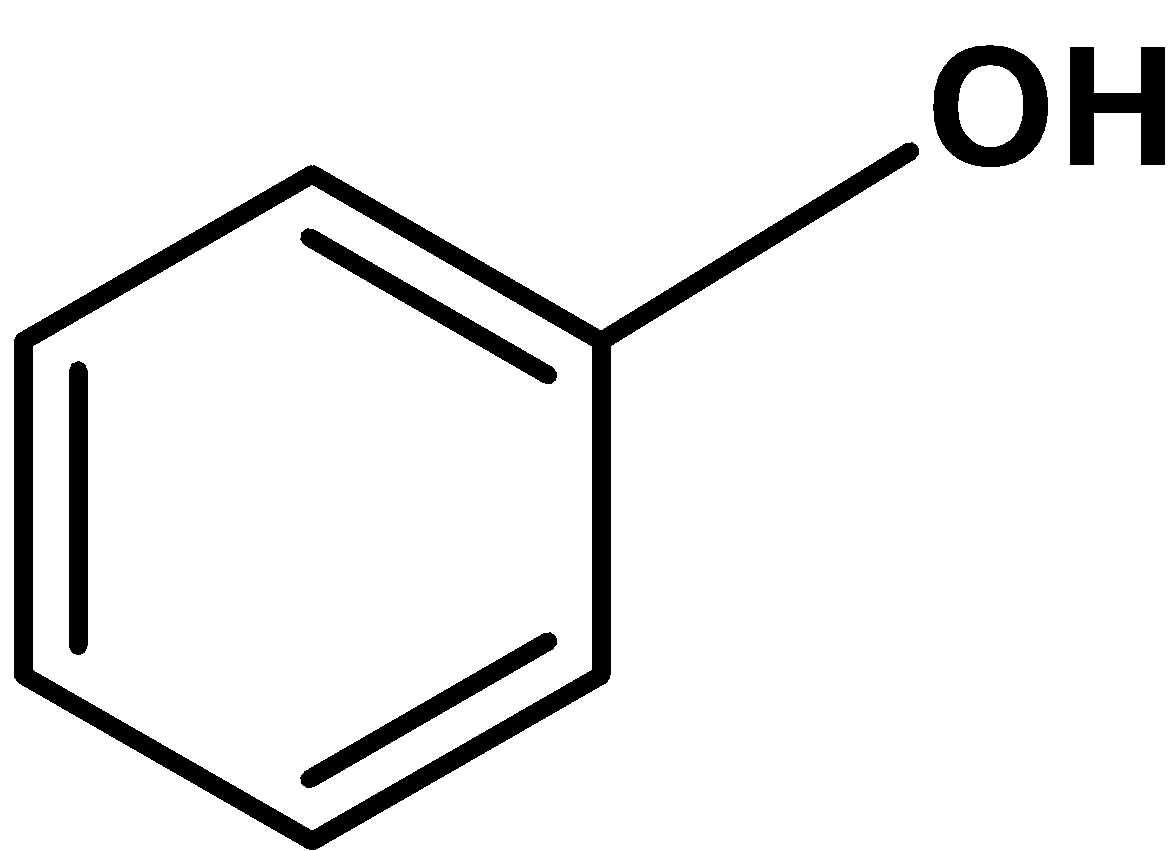
Hence, (A) is the correct option.
Note: The phenols are weak acid compared to the carboxylic acid. Thus phenols do not react with sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate. The reaction with the bromine water is used to distinguish between the alcohol and phenol. The phenol reacts and forms white ppt, but alcohol does not give a white precipitate.
Complete step by step answer:
-We are given that the given compound is insoluble in the dilute hydrochloric acid but soluble in sodium hydroxide. When the compound is added to the $\text{ 1: 1 }$ (or dilute acid) solution.
-The phenol is weakly acidic. Their acidic character is due to the formation of resonance stabilized phenoxide ion which is formed by losing the proton from the $\text{ }-\text{OH }$ group.
-In an acidic medium, the hydrogen ion suppresses the solubility of the phenoxide ion as the equilibrium shifts to the left-hand side. Phenol is insoluble in an acidic medium.

-When alkalis are added to the phenol, the equilibrium between the phenol and phenoxide ions shift towards the right-hand side as the hydrogen ions $\text{ }{{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}\text{ }$ are removed by the $\text{ O}{{\text{H}}^{-}}\text{ }$. -Therefore more phenol in the solution is converted into the phenoxide ion and thus solubility of the phenol is increased. The sodium phenoxide is soluble in water. Since water is a polar solvent the phenoxide easily gets soluble.

-Phenols undergo the electrophilic substitution reaction. The $\text{ }-\text{OH }$ group is a ring activating group, these reactions occur at a faster rate than the reaction of benzene itself. The $\text{ }-\text{OH }$ group is an ortho-para directing and therefore, the incoming group comes at ortho and para position. The phenol undergoes the electrophilic substitution reaction when reacted with the bromine molecule. The bromine acts as an electrophile and attacks on the phenolic ring.
-Phenols react with the bromine in water and give a white precipitate. This precipitate is due to the formation of 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol.
-The reaction of the phenol with the bromine water is as shown below,

-Thus, the compound which is insoluble in dilute$\text{ HCl }$ but soluble in $\text{ NaOH }$ solution and decolorizes when reacted with the bromine water is phenol. The compound is,

Hence, (A) is the correct option.
Note: The phenols are weak acid compared to the carboxylic acid. Thus phenols do not react with sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate. The reaction with the bromine water is used to distinguish between the alcohol and phenol. The phenol reacts and forms white ppt, but alcohol does not give a white precipitate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




