
The only alcohol that can be prepared by indirect hydration of an alkene is
A. Methyl alcohol
B. Ethyl alcohol
C. Propyl alcohol
D. Isobutyl alcohol
Answer
513.3k+ views
Hint: Markovnikov’s addition rule: According to this rule, when a protic acid is added to an asymmetrical alkene then the attack of hydrogen ion takes place at the least substituted carbon atom of the alkenes. Most of the alkenes follow this rule to undergo addition reactions.
Complete answer: In the indirect hydration process, the alkene reacts with sulphuric acids to give respective sulphates by following Markovnikov’s addition rule, which are further hydrolysed to give respective alcohols. Among given options, the alcohol which can be prepared by the indirect hydration of alkene is ethyl alcohol.
The reaction mechanism for the preparation of ethyl alcohol through indirect hydration is as follows:
Step-1: Attack of sulphuric acid on ethene.
$C{H_2} = C{H_2} + {H_2}S{O_4} \to C{H_3} - C{H_2} - HS{O_4}$
Step-2: Hydration reaction of the sulphate formed in the step-1:
$C{H_3} - C{H_2} - HS{O_4}\xrightarrow{{{H_2}O}}C{H_3} - C{H_2} - OH + {H_2}S{O_4}$
The structures of alcohols given in the options other than ethyl alcohol are as follows:
Methyl alcohol: $C{H_3} - OH$
As it consists of only one carbon atom, so it cannot be prepared by hydration of alkene either by direct or indirect method because an alkene consists of a minimum of two carbon atoms.
Propyl alcohol:
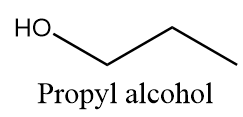
It is a primary alcohol and it cannot be formed by indirect hydration method because it follows Markovnikov addition rule and hydroxyl group will be attached to more substituted carbon atoms i.e., secondary alcohol will be formed. The reaction is as follows:
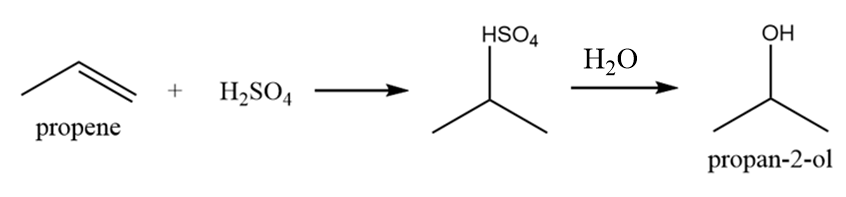
Isobutyl alcohol:
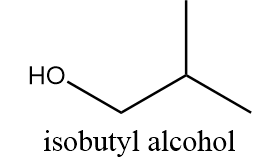
It is also a primary alcohol and it cannot be formed by indirect hydration method because it follows Markovnikov addition rule and hydroxyl group will be attached to more substituted carbon atoms i.e., secondary alcohol will be formed. The reaction is as follows:

Hence, among given options the alcohol that can be prepared by indirect hydration of an alkene is ethyl alcohol.
So, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that except ethyl alcohol no other primary alcohol can be prepared using indirect hydration because it is a symmetrical alkene and both the carbon atoms bonded to double bond have equal tendency to get attacked by a nucleophile.
Complete answer: In the indirect hydration process, the alkene reacts with sulphuric acids to give respective sulphates by following Markovnikov’s addition rule, which are further hydrolysed to give respective alcohols. Among given options, the alcohol which can be prepared by the indirect hydration of alkene is ethyl alcohol.
The reaction mechanism for the preparation of ethyl alcohol through indirect hydration is as follows:
Step-1: Attack of sulphuric acid on ethene.
$C{H_2} = C{H_2} + {H_2}S{O_4} \to C{H_3} - C{H_2} - HS{O_4}$
Step-2: Hydration reaction of the sulphate formed in the step-1:
$C{H_3} - C{H_2} - HS{O_4}\xrightarrow{{{H_2}O}}C{H_3} - C{H_2} - OH + {H_2}S{O_4}$
The structures of alcohols given in the options other than ethyl alcohol are as follows:
Methyl alcohol: $C{H_3} - OH$
As it consists of only one carbon atom, so it cannot be prepared by hydration of alkene either by direct or indirect method because an alkene consists of a minimum of two carbon atoms.
Propyl alcohol:
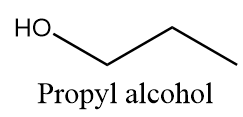
It is a primary alcohol and it cannot be formed by indirect hydration method because it follows Markovnikov addition rule and hydroxyl group will be attached to more substituted carbon atoms i.e., secondary alcohol will be formed. The reaction is as follows:

Isobutyl alcohol:

It is also a primary alcohol and it cannot be formed by indirect hydration method because it follows Markovnikov addition rule and hydroxyl group will be attached to more substituted carbon atoms i.e., secondary alcohol will be formed. The reaction is as follows:

Hence, among given options the alcohol that can be prepared by indirect hydration of an alkene is ethyl alcohol.
So, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that except ethyl alcohol no other primary alcohol can be prepared using indirect hydration because it is a symmetrical alkene and both the carbon atoms bonded to double bond have equal tendency to get attacked by a nucleophile.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




