
The number of unpaired electrons in the complex ion ${{\left[ \text{Co}{{\text{F}}_{6}} \right]}^{3-}}$ is (atomic no 27)
A.0
B.3
C.4
D.2
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint: As we know that all transition metal forms coordination compounds. The nature of bonding between central metal atoms and ligands in the coordination sphere has been explained by the following theory.
A.Valence bond theory
B.Crystal field theory
C.Molecular orbital theory
Complete answer:
The name of the given coordination compound is hexafluorocobaltate (III) ion, ${{\left[ \text{Co}{{\text{F}}_{6}} \right]}^{3-}}$ . The atomic number of cobalt is 27.
Therefore electronic configuration of cobalt $ =\left[ \text{Ar} \right]3{{\text{d}}^{7}}4{{\text{s}}^{2}}$
$\text{Co}\left( \text{z}=27 \right)$ (in ground state)
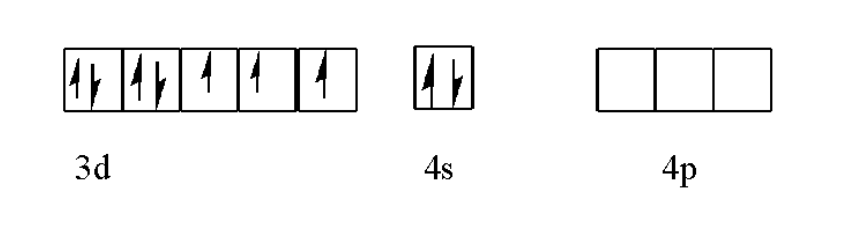
Oxidation state of cobalt
Let O.S of Co = x
O.S of F = $-1$
Total charge on complex ion $=-3$
$\begin{align}
\Rightarrow & \text{x}+6\left( -1 \right)=-3 \\
\Rightarrow & \text{x}-6=-3 \\
\Rightarrow & \text{x}=-3+6 \\
\Rightarrow & \text{x}=3 \\
\end{align}$
Oxidation state of cobalt in ${{\left[ \text{Co}{{\text{F}}_{6}} \right]}^{3-}}=+3$
Here oxidation state is $+3$ it means cobalt loses three electron Co (III) ion to form
Co(III) ion is formed by losing three electrons, two electrons from the 4S orbital and one from the 3d orbital.
Now Co(III) ion is excited state, approached by the ${{\text{F}}^{-}}$ ion for bonding to form coordination compound ${{\left[ \text{Co}{{\text{F}}_{6}} \right]}^{3-}}$ . As fluorine is a weak field ligand so pairing does not occur. Due to this, 3d orbitals undistributed while outer 4d orbital is utilized for hybridization.
The hybridization of the complex ion is $\text{S}{{\text{p}}^{3}}{{\text{d}}^{2}}$ . It is surrounded by six ligands. So that complex has possessed octahedral geometry.
It is clear from the figure that there are four unpaired electrons in the complex in the 3d orbitals whenever there is an unpaired electron present in the complex it possesses paramagnetic character. Such a complex in which the metal ion utilizes outer and orbitals is called outer orbital complex. Outer orbital complexes are formed when weak field liquid is present.
The outer orbital complex has a larger number of unpaired electrons than their number in the inner orbital complex of the same metal ion since configuration of metal ion remains the same on the complexation. Such a complex is also called a high spin complex.
So option ‘D’ is correct i.e. ${{\left[ \text{Co}{{\text{F}}_{6}} \right]}^{3-}}$ present 4 unpaired electron.
Additional information:
The above complex has been explained on the basis of valence bond theory. Valence bond theory has been developed by Pauling. Main postulate of valence bond theory follows.
A.The central metal ion in the complex has provided an adequate number of empty orbits for the formation of coordination bonds with suitable ligands.
B.The appropriate atomic orbitals (S, P, d, f) of the metal hybridize to give an equal number of new orbitals of equivalent energy called hybrid orbitals.
C.The d-orbitals involved in hybridization may be inner or outer orbitals i.e. inner orbital $\left( \text{n}-1 \right)\text{d}$ or outer and orbital. Octahedral complex may be ${{\text{d}}^{2}}\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{3}}$ hybridization called inner orbitals or low spin complex or $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{3}}{{\text{d}}^{2}}$ hybridization known as outer orbital complex or high spin complexes.
D.Each ligand for binding has at least one orbital containing a lone pair of electrons.
E.The empty hybrid orbital of metal ions overlaps with fully filled orbitals of ligand forms the ligand metal bond.
Note: The coordination compound either paramagnetic or diamagnetic in nature.
Paramagnetic complex: Such a complex in which an unpaired electron is present is called the paramagnetic complex.
Diamagnetic complex: Such a complex in which no unpaired electron is present is called diamagnetic complex in nature.
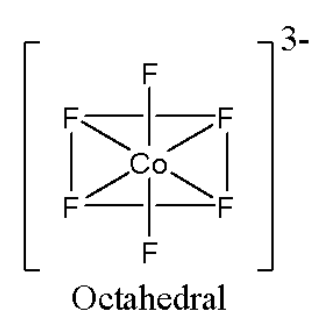
Noted that the given complex ${{\left[ \text{Co}{{\text{F}}_{6}} \right]}^{3-}}$ having octahedral geometry. The structure of octahedral geometry as follows
A.Valence bond theory
B.Crystal field theory
C.Molecular orbital theory
Complete answer:
The name of the given coordination compound is hexafluorocobaltate (III) ion, ${{\left[ \text{Co}{{\text{F}}_{6}} \right]}^{3-}}$ . The atomic number of cobalt is 27.
Therefore electronic configuration of cobalt $ =\left[ \text{Ar} \right]3{{\text{d}}^{7}}4{{\text{s}}^{2}}$
$\text{Co}\left( \text{z}=27 \right)$ (in ground state)

Oxidation state of cobalt
Let O.S of Co = x
O.S of F = $-1$
Total charge on complex ion $=-3$
$\begin{align}
\Rightarrow & \text{x}+6\left( -1 \right)=-3 \\
\Rightarrow & \text{x}-6=-3 \\
\Rightarrow & \text{x}=-3+6 \\
\Rightarrow & \text{x}=3 \\
\end{align}$
Oxidation state of cobalt in ${{\left[ \text{Co}{{\text{F}}_{6}} \right]}^{3-}}=+3$
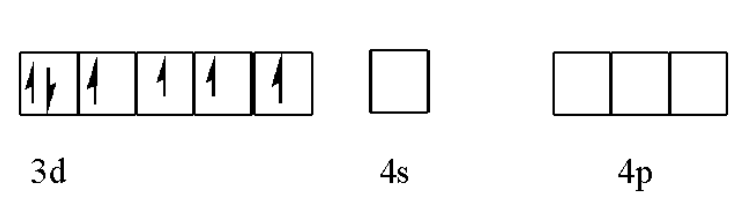
Here oxidation state is $+3$ it means cobalt loses three electron Co (III) ion to form

Co(III) ion is formed by losing three electrons, two electrons from the 4S orbital and one from the 3d orbital.
Now Co(III) ion is excited state, approached by the ${{\text{F}}^{-}}$ ion for bonding to form coordination compound ${{\left[ \text{Co}{{\text{F}}_{6}} \right]}^{3-}}$ . As fluorine is a weak field ligand so pairing does not occur. Due to this, 3d orbitals undistributed while outer 4d orbital is utilized for hybridization.
The hybridization of the complex ion is $\text{S}{{\text{p}}^{3}}{{\text{d}}^{2}}$ . It is surrounded by six ligands. So that complex has possessed octahedral geometry.
It is clear from the figure that there are four unpaired electrons in the complex in the 3d orbitals whenever there is an unpaired electron present in the complex it possesses paramagnetic character. Such a complex in which the metal ion utilizes outer and orbitals is called outer orbital complex. Outer orbital complexes are formed when weak field liquid is present.
The outer orbital complex has a larger number of unpaired electrons than their number in the inner orbital complex of the same metal ion since configuration of metal ion remains the same on the complexation. Such a complex is also called a high spin complex.
So option ‘D’ is correct i.e. ${{\left[ \text{Co}{{\text{F}}_{6}} \right]}^{3-}}$ present 4 unpaired electron.
Additional information:
The above complex has been explained on the basis of valence bond theory. Valence bond theory has been developed by Pauling. Main postulate of valence bond theory follows.
A.The central metal ion in the complex has provided an adequate number of empty orbits for the formation of coordination bonds with suitable ligands.
B.The appropriate atomic orbitals (S, P, d, f) of the metal hybridize to give an equal number of new orbitals of equivalent energy called hybrid orbitals.
C.The d-orbitals involved in hybridization may be inner or outer orbitals i.e. inner orbital $\left( \text{n}-1 \right)\text{d}$ or outer and orbital. Octahedral complex may be ${{\text{d}}^{2}}\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{3}}$ hybridization called inner orbitals or low spin complex or $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{3}}{{\text{d}}^{2}}$ hybridization known as outer orbital complex or high spin complexes.
D.Each ligand for binding has at least one orbital containing a lone pair of electrons.
E.The empty hybrid orbital of metal ions overlaps with fully filled orbitals of ligand forms the ligand metal bond.
Note: The coordination compound either paramagnetic or diamagnetic in nature.
Paramagnetic complex: Such a complex in which an unpaired electron is present is called the paramagnetic complex.
Diamagnetic complex: Such a complex in which no unpaired electron is present is called diamagnetic complex in nature.
Noted that the given complex ${{\left[ \text{Co}{{\text{F}}_{6}} \right]}^{3-}}$ having octahedral geometry. The structure of octahedral geometry as follows

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




