
The number of possible alkynes with molecular formulae, ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{8}}$
A) 1
B) 3
C) 5
D) 8
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: Different types of isomerism will give us different structures-position isomers and chain isomerism can yield us different structures. The number of bonds a C can form is four only. The general formula of alkynes is - ${{C}_{n}}{{H}_{2n-2}}$, n is the number of C atoms present in the compound.
Complete answer:
So here we are asked to give the number of alkynes that can be formed from the equation${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{8}}$by satisfying the number of C and H given in formula.
So let’s start writing the possible structures.
There are five C atoms in the given formulae, so let’s write the possible C skeleton that could be drawn for five C atoms. The structures are as follows-
The straight chain-n-pentane
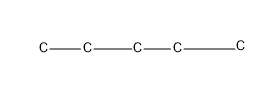
Then giving one C as the substituent, which is a chain isomer, isopentane.
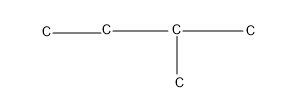
The next one giving two substituent, isomer which comes under neo compounds-neopentane
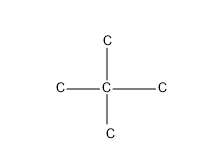
So these are the possible C skeleton for five Carbon atoms.
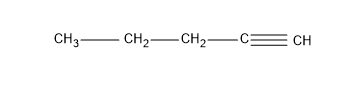
Now the question is about having alkynes, so let’s give a triple bond in the first carbon and yield an alkyne, pent-1-yne.
Then we can change the position of the triple bond and give the triple bond to the second carbon and we will get an alkyne, pent-2-yne
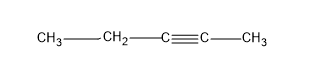
These two structures are examples for positional or position isomers. As the difference in the both structures is only the difference in the C position they are attached to.
And we got two structures, from the straight C chain, by changing the position of the triple bond.
If we again move the triple bond to next C then it will be similar, as in that case we will number from the right side of the molecule.
So now let’s move to the next C skeleton form having one substituent.
For that we will give one $-C{{H}_{3}}$ (methyl group) as the substituent and let’s write the structure by satisfying the valency of C with H atom.
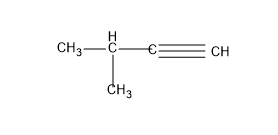
And this structure is called as -3-methyl but-1-yne.
No other structures are possible for this C skeleton. So let’s move to the next C skeleton with 2 groups as the substituent, but in this case it is not possible to give the triple bond since C can have only 4 bonds and in this type of C skeleton they will only possess a single bond.
So the structures we obtained are – pent-1-yne, pent-2-yne and 3-methyl but-1-yne i.e. in total of three structures.
So the correct option for the question is option (B).
Note: While writing the structure we should always satisfy the valency of the C atom and the number of C and H atoms in alkynes should satisfy the general formulae- ${{C}_{n}}{{H}_{2n-2}}$. If the question was for alkenes, the process should be continued through this method and they will have the general formulae -\[{{C}_{n}}{{H}_{2n}}\]\[{{C}_{n}}{{H}_{2n}}\] and for alkanes it is\[{{C}_{n}}{{H}_{2n+2}}\]. There will be more structures possible for alkenes and alkanes than the alkynes.
Complete answer:
So here we are asked to give the number of alkynes that can be formed from the equation${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{8}}$by satisfying the number of C and H given in formula.
So let’s start writing the possible structures.
There are five C atoms in the given formulae, so let’s write the possible C skeleton that could be drawn for five C atoms. The structures are as follows-
The straight chain-n-pentane

Then giving one C as the substituent, which is a chain isomer, isopentane.

The next one giving two substituent, isomer which comes under neo compounds-neopentane

So these are the possible C skeleton for five Carbon atoms.
Now the question is about having alkynes, so let’s give a triple bond in the first carbon and yield an alkyne, pent-1-yne.

Then we can change the position of the triple bond and give the triple bond to the second carbon and we will get an alkyne, pent-2-yne

These two structures are examples for positional or position isomers. As the difference in the both structures is only the difference in the C position they are attached to.
And we got two structures, from the straight C chain, by changing the position of the triple bond.
If we again move the triple bond to next C then it will be similar, as in that case we will number from the right side of the molecule.
So now let’s move to the next C skeleton form having one substituent.
For that we will give one $-C{{H}_{3}}$ (methyl group) as the substituent and let’s write the structure by satisfying the valency of C with H atom.

And this structure is called as -3-methyl but-1-yne.
No other structures are possible for this C skeleton. So let’s move to the next C skeleton with 2 groups as the substituent, but in this case it is not possible to give the triple bond since C can have only 4 bonds and in this type of C skeleton they will only possess a single bond.
So the structures we obtained are – pent-1-yne, pent-2-yne and 3-methyl but-1-yne i.e. in total of three structures.
So the correct option for the question is option (B).
Note: While writing the structure we should always satisfy the valency of the C atom and the number of C and H atoms in alkynes should satisfy the general formulae- ${{C}_{n}}{{H}_{2n-2}}$. If the question was for alkenes, the process should be continued through this method and they will have the general formulae -\[{{C}_{n}}{{H}_{2n}}\]\[{{C}_{n}}{{H}_{2n}}\] and for alkanes it is\[{{C}_{n}}{{H}_{2n+2}}\]. There will be more structures possible for alkenes and alkanes than the alkynes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




