
The number of isomers of ${C_5}{H_{10}}$ is:
A. $10$
B. $11$
C. $12$
D. $13$
Answer
512.1k+ views
Hint: When more than one compound has the same molecular formula but different structural formula, then the compounds are known as isomers and the phenomenon is known as isomerism. It is broadly divided into two types i.e., structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
Complete answer:
To find the isomers of given organic compound, we first need to find the degree of unsaturation which indicates the total number of pi bonds and ring possible within a structure and it is calculated as follows:
Degree of unsaturation (n) \[ = C - \frac{H}{2} - \frac{X}{2} + \frac{N}{2} + 1\]
Where, C is the number of carbon atoms, X is the number of hydrogen atoms, X is the number of halogen atoms, N is the number of nitrogen atoms within the molecular formula of the given organic compound.
Therefore, the degree of unsaturation for ${C_5}{H_{10}}$ will be as follows:
n $ = 5 - \frac{{10}}{2} + 1$
$ \Rightarrow $ n $ = 1$
The degree of unsaturation is one which indicates that only one double bond is present in the straight chain structure and one complete ring (i.e., without substitution) is possible.
Hence, the possible isomers for ${C_5}{H_{10}}$ are as follows:
1. cyclopentane
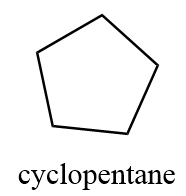
2. methylcyclobutane
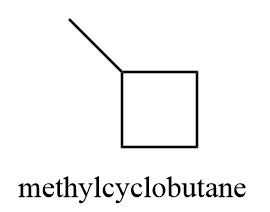
3. ethylcyclopropane
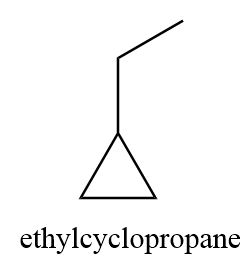
4. 1,1-dimethylcyclopropane
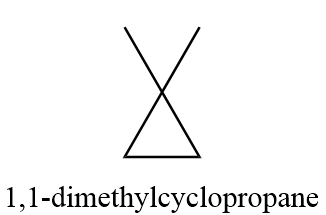
5. (1R,2S)-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane
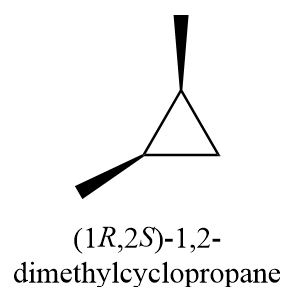
6. (1R,2R)-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane
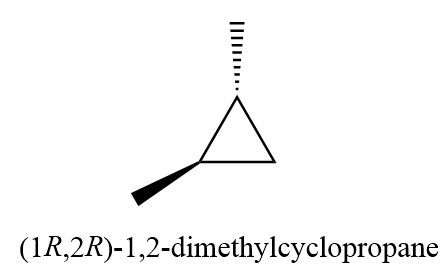
7. (1S,2S)-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane
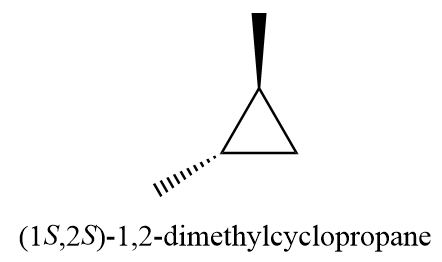
8. pent-1-ene
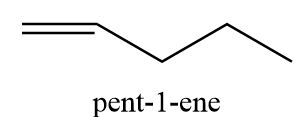
9. (Z)-pent-2-ene
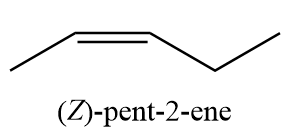
10. (E)-pent-2-ene
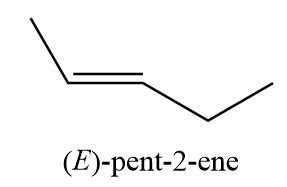
11. 2-methylbut-1-ene
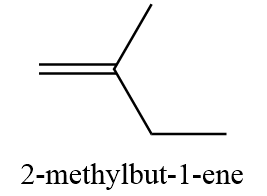
12. 3-methylbut-1-ene
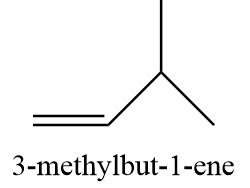
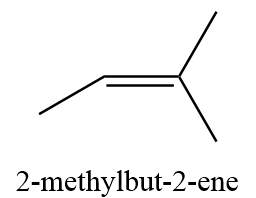
13. 2-methyl-but-2-ene
Therefore, the number of possible isomers (including stereoisomers) for ${C_5}{H_{10}} = 13$.
So, option (D) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that there is no specific formula to calculate the number of isomers possible for an organic compound. You need to draw each possible structure to find the number of isomers. Moreover, we can find the number of geometrical isomers possible for an unsaturated organic compound which is equal to ${2^n}$, where n is the number of double bonds or degree of unsaturation of the compound.
Complete answer:
To find the isomers of given organic compound, we first need to find the degree of unsaturation which indicates the total number of pi bonds and ring possible within a structure and it is calculated as follows:
Degree of unsaturation (n) \[ = C - \frac{H}{2} - \frac{X}{2} + \frac{N}{2} + 1\]
Where, C is the number of carbon atoms, X is the number of hydrogen atoms, X is the number of halogen atoms, N is the number of nitrogen atoms within the molecular formula of the given organic compound.
Therefore, the degree of unsaturation for ${C_5}{H_{10}}$ will be as follows:
n $ = 5 - \frac{{10}}{2} + 1$
$ \Rightarrow $ n $ = 1$
The degree of unsaturation is one which indicates that only one double bond is present in the straight chain structure and one complete ring (i.e., without substitution) is possible.
Hence, the possible isomers for ${C_5}{H_{10}}$ are as follows:
1. cyclopentane

2. methylcyclobutane

3. ethylcyclopropane

4. 1,1-dimethylcyclopropane
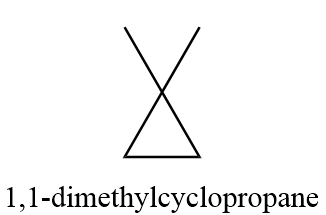
5. (1R,2S)-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane

6. (1R,2R)-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane
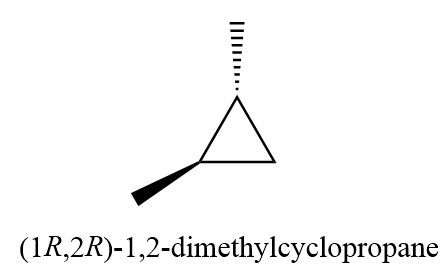
7. (1S,2S)-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane
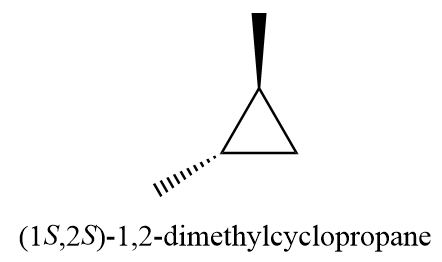
8. pent-1-ene

9. (Z)-pent-2-ene

10. (E)-pent-2-ene

11. 2-methylbut-1-ene
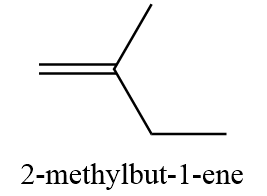
12. 3-methylbut-1-ene

13. 2-methyl-but-2-ene

Therefore, the number of possible isomers (including stereoisomers) for ${C_5}{H_{10}} = 13$.
So, option (D) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that there is no specific formula to calculate the number of isomers possible for an organic compound. You need to draw each possible structure to find the number of isomers. Moreover, we can find the number of geometrical isomers possible for an unsaturated organic compound which is equal to ${2^n}$, where n is the number of double bonds or degree of unsaturation of the compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




