
The number of common tangents to \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x-6y-12=0\] and \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+6x+18y+26=0\], is
\[\begin{align}
& A)1 \\
& B)2 \\
& C)3 \\
& D)4 \\
\end{align}\]
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: Let us assume the centre of the circles \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x-6y-12=0\] and \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+6x+18y+26=0\] as \[{{C}_{1}}\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and \[{{C}_{2}}\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\] respectively . We will also assume the radius of the circles\[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x-6y-12=0\] and \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+6x+18y+26=0\] as \[{{r}_{1}}\] and \[{{r}_{2}}\] respectively. Now we find the value of \[{{C}_{1}}\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] ,\[{{C}_{2}}\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\], \[{{r}_{1}}\] and \[{{r}_{2}}\]. Now we will find the distance between \[{{C}_{1}}\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and \[{{C}_{2}}\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\]. Now we will find the sum of \[{{r}_{1}}\] and \[{{r}_{2}}\]. Now we will check whether the distance between \[{{C}_{1}}\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and \[{{C}_{2}}\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\] is equal to the sum of \[{{r}_{1}}\] and \[{{r}_{2}}\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us assume the centre of the circles \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x-6y-12=0\] and \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+6x+18y+26=0\] as \[{{C}_{1}}\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and \[{{C}_{2}}\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\] respectively . We will also assume the radius of the circles\[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x-6y-12=0\] and \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+6x+18y+26=0\] as \[{{r}_{1}}\] and \[{{r}_{2}}\] respectively.
Now we should find the centres of \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x-6y-12=0\] and \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+6x+18y+26=0\].
We know that an equation of the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0\] is equal to \[\left( -g,-f \right)\] and we also know that the radius of this circle is equal to \[\sqrt{{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-c}\].
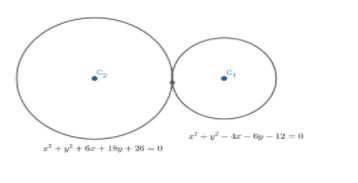
Now let us compare the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x-6y-12=0\] with \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0\].
Then, we get
\[\begin{align}
& 2g=-4\Rightarrow g=-2.....(1) \\
& 2f=-6\Rightarrow f=-3.....(2) \\
& c=-12......(3) \\
\end{align}\]
So, it is clear that the centre of circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x-6y-12=0\] is equal to \[\left( 2,3 \right)\].
We know that the radius of the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x-6y-12=0\]is equal to \[{{r}_{1}}\].
\[\Rightarrow {{r}_{1}}=\sqrt{{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-c}....(4)\]
Now let us substitute equation (1), equation (2) and equation (3) in equation (4), then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{r}_{1}}=\sqrt{{{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -3 \right)}^{2}}-\left( -12 \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}_{1}}=\sqrt{4+9+12} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}_{1}}=\sqrt{25} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}_{1}}=5.....(5) \\
\end{align}\]
Now let us compare the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+6x+18y+26=0\] with \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0\].
Then, we get
\[\begin{align}
& 2g=6\Rightarrow g=3.....(6) \\
& 2f=18\Rightarrow f=9....(7) \\
& c=26......(8) \\
\end{align}\]
So, it is clear that the centre of circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+6x+18y+26=0\] is equal to \[\left( -3,-9 \right)\].
We know that the radius of the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+6x+18y+26=0\] is equal to \[{{r}_{2}}\].
\[\Rightarrow {{r}_{2}}=\sqrt{{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-c}....(9)\]
Now let us substitute equation (1), equation (2) and equation (3) in equation (4), then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{r}_{2}}=\sqrt{{{3}^{2}}+81-26} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}_{2}}=\sqrt{9+81-26} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}_{2}}=\sqrt{64} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}_{2}}=8.....(10) \\
\end{align}\]
We know that the distance between \[A\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and \[B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\] is equal to\[\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}\].
Now we should find the distance between \[{{C}_{1}}\left( 2,3 \right)\] and \[{{C}_{2}}\left( -3,-9 \right)\].
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}=\sqrt{{{\left( -3-2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -9-3 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}=\sqrt{{{\left( -5 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -12 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}=\sqrt{25+144} \\
& \Rightarrow {{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}=\sqrt{169} \\
& \Rightarrow {{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}=13.....(11) \\
\end{align}\]
Now let us find the sum of \[{{r}_{1}}\] and \[{{r}_{2}}\].
From equation (5) and equation (10), then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}}=5+8 \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}}=13.....(12) \\
\end{align}\]
From equation (11) and equation (12), it is clear that
\[\Rightarrow {{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}={{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}}\]
We know that if the distance between two centres is equal to the sum of radius of two circles, then the two circles are said to have three common tangents.
So, we can say that the number of common tangents to \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x-6y-12=0\] and \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+6x+18y+26=0\] are equal to 3.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: If there are two circles \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2{{g}_{1}}x+2{{f}_{1}}y+{{c}_{1}}=0\]and \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2{{g}_{2}}x+2{{f}_{2}}y+{{c}_{2}}=0\] has the centres as \[{{C}_{1}}\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and \[{{C}_{2}}\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\] respectively and the radius of the circles as \[{{r}_{1}}\] and \[{{r}_{2}}\] respectively, then `
So, students should remember this concept.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us assume the centre of the circles \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x-6y-12=0\] and \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+6x+18y+26=0\] as \[{{C}_{1}}\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and \[{{C}_{2}}\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\] respectively . We will also assume the radius of the circles\[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x-6y-12=0\] and \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+6x+18y+26=0\] as \[{{r}_{1}}\] and \[{{r}_{2}}\] respectively.
Now we should find the centres of \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x-6y-12=0\] and \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+6x+18y+26=0\].
We know that an equation of the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0\] is equal to \[\left( -g,-f \right)\] and we also know that the radius of this circle is equal to \[\sqrt{{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-c}\].

Now let us compare the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x-6y-12=0\] with \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0\].
Then, we get
\[\begin{align}
& 2g=-4\Rightarrow g=-2.....(1) \\
& 2f=-6\Rightarrow f=-3.....(2) \\
& c=-12......(3) \\
\end{align}\]
So, it is clear that the centre of circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x-6y-12=0\] is equal to \[\left( 2,3 \right)\].
We know that the radius of the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x-6y-12=0\]is equal to \[{{r}_{1}}\].
\[\Rightarrow {{r}_{1}}=\sqrt{{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-c}....(4)\]
Now let us substitute equation (1), equation (2) and equation (3) in equation (4), then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{r}_{1}}=\sqrt{{{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -3 \right)}^{2}}-\left( -12 \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}_{1}}=\sqrt{4+9+12} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}_{1}}=\sqrt{25} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}_{1}}=5.....(5) \\
\end{align}\]
Now let us compare the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+6x+18y+26=0\] with \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0\].
Then, we get
\[\begin{align}
& 2g=6\Rightarrow g=3.....(6) \\
& 2f=18\Rightarrow f=9....(7) \\
& c=26......(8) \\
\end{align}\]
So, it is clear that the centre of circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+6x+18y+26=0\] is equal to \[\left( -3,-9 \right)\].
We know that the radius of the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+6x+18y+26=0\] is equal to \[{{r}_{2}}\].
\[\Rightarrow {{r}_{2}}=\sqrt{{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-c}....(9)\]
Now let us substitute equation (1), equation (2) and equation (3) in equation (4), then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{r}_{2}}=\sqrt{{{3}^{2}}+81-26} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}_{2}}=\sqrt{9+81-26} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}_{2}}=\sqrt{64} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}_{2}}=8.....(10) \\
\end{align}\]
We know that the distance between \[A\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and \[B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\] is equal to\[\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}\].
Now we should find the distance between \[{{C}_{1}}\left( 2,3 \right)\] and \[{{C}_{2}}\left( -3,-9 \right)\].
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}=\sqrt{{{\left( -3-2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -9-3 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}=\sqrt{{{\left( -5 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -12 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}=\sqrt{25+144} \\
& \Rightarrow {{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}=\sqrt{169} \\
& \Rightarrow {{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}=13.....(11) \\
\end{align}\]
Now let us find the sum of \[{{r}_{1}}\] and \[{{r}_{2}}\].
From equation (5) and equation (10), then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}}=5+8 \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}}=13.....(12) \\
\end{align}\]
From equation (11) and equation (12), it is clear that
\[\Rightarrow {{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}={{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}}\]
We know that if the distance between two centres is equal to the sum of radius of two circles, then the two circles are said to have three common tangents.
So, we can say that the number of common tangents to \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x-6y-12=0\] and \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+6x+18y+26=0\] are equal to 3.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: If there are two circles \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2{{g}_{1}}x+2{{f}_{1}}y+{{c}_{1}}=0\]and \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2{{g}_{2}}x+2{{f}_{2}}y+{{c}_{2}}=0\] has the centres as \[{{C}_{1}}\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and \[{{C}_{2}}\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\] respectively and the radius of the circles as \[{{r}_{1}}\] and \[{{r}_{2}}\] respectively, then `
| Condition | Number of tangents |
| \[{{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}<{{r}_{1}}-{{r}_{2}}\] | 0 |
| \[{{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}={{r}_{1}}-{{r}_{2}}\] | 1 |
| \[{{r}_{1}}-{{r}_{2}}<{{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}<{{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}}\] | 2 |
| \[{{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}={{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}}\] | 3 |
| \[{{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}>{{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}}\] | 4 |
So, students should remember this concept.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




