
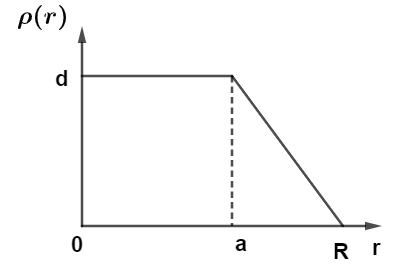
The nuclear charge (Ze) is non-uniformly distributed within a nucleus of radius R. The charge density $\rho (r)$ [charge per unit volume] is dependent only on radial distance r from the centre of the nucleus as shown in figure. The electric field is only along the radial direction. For $a = 0$ the value of d (maximum value of $\rho $ as shown in figure ) is :
(A) $\dfrac{{3Ze}}{{4\pi {R^3}}}$
(B) $\dfrac{{3Ze}}{{\pi {R^3}}}$
(C) $\dfrac{{3Ze}}{{2\pi {R^3}}}$
(D) $\dfrac{{Ze}}{{3\pi {R^3}}}$

Answer
493.5k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we will first write the charge inside the spherical shell in terms of radial distance x. and then we will write the equation of charge density from given figure and later by substituting various parameters we will find the value of d the maximum value of charge density.
Complete step by step answer:
The elementary charge of a sphere at any distance x from the centre of a sphere is calculated using the charge density formula as $dq = 4\pi {x^2}.\rho (x)dx$ and total charge can be found by integrating the elementary charge equation over volume of sphere from $x = 0,x = R$ where R is the radius of sphere. so we get,
$Q = \int\limits_0^R {4\pi {x^2}.\rho (x)dx} \to (i)$
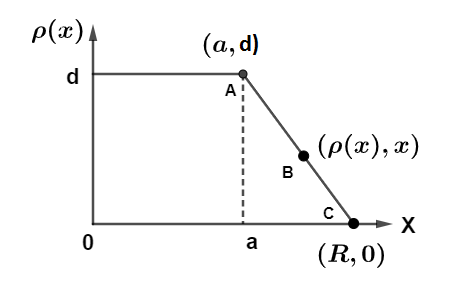
Now, from the given diagram we can write the equation of charge density as equation of straight line passing through points A, B, C as shown in diagram
$\dfrac{{\rho (x) - d}}{{x - a}} = \dfrac{{ - d}}{R}$ and for maximum value of charge density put $a = 0$ we get,
$\rho (x) = - \dfrac{d}{R}x + d$
now put this value of charge density in the equation (i) we get,
$Q = \int\limits_0^R {4\pi {x^2}.( - \dfrac{d}{R}x + d)dx} $
or
$Q = 4\pi \dfrac{d}{R}\int\limits_0^R {{x^2}( - x + R)dx} $
now using integration rules as $\int {{x^n}dx = \dfrac{{{x^{n + 1}}}}{{n + 1}}} $ so,
$Q = 4\pi \dfrac{d}{R}[ - \dfrac{{{x^4}}}{4} + R\dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3}]_0^R$
on putting the limits value we get,
$Q = 4\pi \dfrac{d}{R}[ - \dfrac{{{R^4}}}{4} + \dfrac{{{R^4}}}{3} - 0]$
$Q = 4\pi \dfrac{d}{R}.\dfrac{{{R^4}}}{{12}}$
$ \Rightarrow Q = \dfrac{{\pi d{R^3}}}{3}$
Now, as we have given in the question that, $Q = Ze$ so on putting the value of charge we get,
$\dfrac{{\pi d{R^3}}}{3} = Ze$
$ \Rightarrow d = \dfrac{{3Ze}}{{\pi {R^3}}}$
Hence, the correct option is (B) $\dfrac{{3Ze}}{{\pi {R^3}}}$.
Note: It should be remembered that charge density is charge per unit of volume so we have to consider a sphere and then we have taken the elementary charge for the whole volume of the sphere. While writing down the equation of a straight line, always check the correct coordinates of points passing through the line.
Complete step by step answer:
The elementary charge of a sphere at any distance x from the centre of a sphere is calculated using the charge density formula as $dq = 4\pi {x^2}.\rho (x)dx$ and total charge can be found by integrating the elementary charge equation over volume of sphere from $x = 0,x = R$ where R is the radius of sphere. so we get,
$Q = \int\limits_0^R {4\pi {x^2}.\rho (x)dx} \to (i)$
Now, from the given diagram we can write the equation of charge density as equation of straight line passing through points A, B, C as shown in diagram

$\dfrac{{\rho (x) - d}}{{x - a}} = \dfrac{{ - d}}{R}$ and for maximum value of charge density put $a = 0$ we get,
$\rho (x) = - \dfrac{d}{R}x + d$
now put this value of charge density in the equation (i) we get,
$Q = \int\limits_0^R {4\pi {x^2}.( - \dfrac{d}{R}x + d)dx} $
or
$Q = 4\pi \dfrac{d}{R}\int\limits_0^R {{x^2}( - x + R)dx} $
now using integration rules as $\int {{x^n}dx = \dfrac{{{x^{n + 1}}}}{{n + 1}}} $ so,
$Q = 4\pi \dfrac{d}{R}[ - \dfrac{{{x^4}}}{4} + R\dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3}]_0^R$
on putting the limits value we get,
$Q = 4\pi \dfrac{d}{R}[ - \dfrac{{{R^4}}}{4} + \dfrac{{{R^4}}}{3} - 0]$
$Q = 4\pi \dfrac{d}{R}.\dfrac{{{R^4}}}{{12}}$
$ \Rightarrow Q = \dfrac{{\pi d{R^3}}}{3}$
Now, as we have given in the question that, $Q = Ze$ so on putting the value of charge we get,
$\dfrac{{\pi d{R^3}}}{3} = Ze$
$ \Rightarrow d = \dfrac{{3Ze}}{{\pi {R^3}}}$
Hence, the correct option is (B) $\dfrac{{3Ze}}{{\pi {R^3}}}$.
Note: It should be remembered that charge density is charge per unit of volume so we have to consider a sphere and then we have taken the elementary charge for the whole volume of the sphere. While writing down the equation of a straight line, always check the correct coordinates of points passing through the line.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




