
The net yield of ATP, except substrate-level phosphorylation, from Krebs cycle per glucose molecule is:
A. \[12\]
B. \[24\]
C. \[22\]
D. \[36\]
Answer
394.8k+ views
Hint: The citric acid cycle is another term for the Krebs cycle. The technique of aerobic respiration is used to create energy in this cycle. The oxidation of carbohydrates, known as acetyl, Co-A, happens during this process.
Complete step by step answer:
The Krebs cycle, also known as the Citric acid cycle, is a sequence of enzyme-catalysed events that take place in the mitochondrial matrix, where acetyl-CoA is oxidised to carbon dioxide and coenzymes are reduced, resulting in the production of ATP in the electron transport chain.
It's an eight-step process in which the acetyl group of acetyl-CoA is oxidised to form two molecules of \[C{O_2}\] and one ATP in the process. \[NADH\]and\[FAD{H_2}\], which are reduced high-energy molecules, are also created.
Cellular respiration is a catabolic process that occurs within cells. Nutrients are broken down to produce energy, which is stored in the form of ATP, and waste products are released in this biochemical process. Aerobic respiration necessitates the use of oxygen. The process of cellular respiration is divided into four stages. Glucose is converted to carbon dioxide and oxygen is reduced to water during this process. ATPs are used to store the energy released throughout the operation. Each glucose molecule produces \[36\] to \[38\]ATPs.
During cellular respiration, one molecule of glucose can yield \[38\] ATP molecules. Phosphorylation at the substrate level produces net \[2\] ATP molecules during glycolysis. Phosphorylation of the substrate results in the production of two ATP molecules in the Krebs cycle. Phosphorylation by oxidation produces about \[34\]ATP. Six molecules of \[NA{D^ + }\]are reduced to \[NADH\]and two molecules of \[FAD\]are converted to \[FAD{H_2}\] during the Krebs cycle. \[6\]\[NADH\] now generates \[6 \times 3 = 18\] ATP molecules. \[2\] \[FAD{H_2}\] produces \[2 \times 2 = 4\] ATP molecules in the same way. Except for substrate-level phosphorylation, the Krebs cycle produces a total of \[18 + 4 = 22\] molecules of ATP per glucose molecule.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C \[22\].
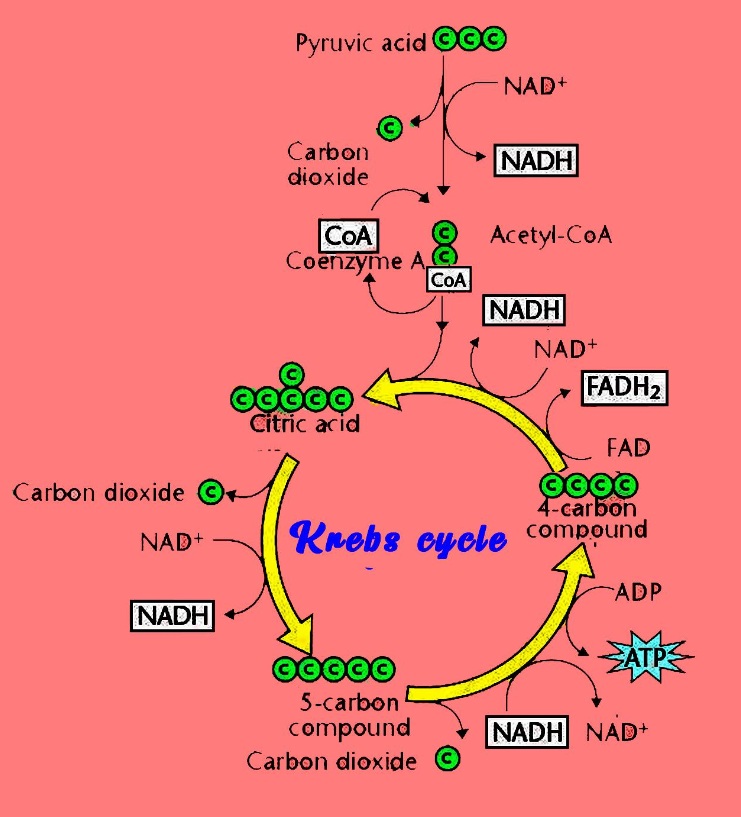
Image: Krebs Cycle
Note: The TCA cycle is another name for the citric acid cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle). The oxidation of acetyl-CoA acquired from carbs, lipids, and proteins is a set of events employed by all aerobic species to generate stored energy. The cycle also generates precursors for certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent \[NADH\], which is employed in a variety of other processes.
Complete step by step answer:
The Krebs cycle, also known as the Citric acid cycle, is a sequence of enzyme-catalysed events that take place in the mitochondrial matrix, where acetyl-CoA is oxidised to carbon dioxide and coenzymes are reduced, resulting in the production of ATP in the electron transport chain.
It's an eight-step process in which the acetyl group of acetyl-CoA is oxidised to form two molecules of \[C{O_2}\] and one ATP in the process. \[NADH\]and\[FAD{H_2}\], which are reduced high-energy molecules, are also created.
Cellular respiration is a catabolic process that occurs within cells. Nutrients are broken down to produce energy, which is stored in the form of ATP, and waste products are released in this biochemical process. Aerobic respiration necessitates the use of oxygen. The process of cellular respiration is divided into four stages. Glucose is converted to carbon dioxide and oxygen is reduced to water during this process. ATPs are used to store the energy released throughout the operation. Each glucose molecule produces \[36\] to \[38\]ATPs.
During cellular respiration, one molecule of glucose can yield \[38\] ATP molecules. Phosphorylation at the substrate level produces net \[2\] ATP molecules during glycolysis. Phosphorylation of the substrate results in the production of two ATP molecules in the Krebs cycle. Phosphorylation by oxidation produces about \[34\]ATP. Six molecules of \[NA{D^ + }\]are reduced to \[NADH\]and two molecules of \[FAD\]are converted to \[FAD{H_2}\] during the Krebs cycle. \[6\]\[NADH\] now generates \[6 \times 3 = 18\] ATP molecules. \[2\] \[FAD{H_2}\] produces \[2 \times 2 = 4\] ATP molecules in the same way. Except for substrate-level phosphorylation, the Krebs cycle produces a total of \[18 + 4 = 22\] molecules of ATP per glucose molecule.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C \[22\].

Image: Krebs Cycle
Note: The TCA cycle is another name for the citric acid cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle). The oxidation of acetyl-CoA acquired from carbs, lipids, and proteins is a set of events employed by all aerobic species to generate stored energy. The cycle also generates precursors for certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent \[NADH\], which is employed in a variety of other processes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE




