
The most stable Carbanion is ___________
A.$PhC{H_2}\mathop C\limits^ - {H_2}$
B. $Ph\mathop C\limits^ - {H_2}$
C.
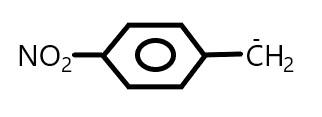
D.



Answer
542.7k+ views
Hint: As we know that a Carbanion is basically an electron rich species which possess a complete octet. We also know that $N{O_2}$ is an electron withdrawing group and presence of an electron withdrawing group stabilizes the carbanion.
Complete step by step answer:
Carbanion is the carbon atom having negative charge present on it. An electron withdrawing group increases the stability of carbanion. Resonance is another factor by which stability of carbanion increases. Now talking about the stability order of carbanion is: $1^\circ > 2^\circ > 3^\circ $.
As we all know that methyl group has a $ + I$ effect which increases the intensity of negative charge on central carbon of $3^\circ $ carbanion which further makes it unstable.
So let us analyze the above given options:
In Option (A), the carbocation present is a primary carbocation so the chances of its stability is high.
In Option (B), the carbocation is $1^\circ $ and the presence of the phenyl group also stabilizes the carbanion.
In Option (C), the carbocation $1^\circ $ and there is also $ - N{O_2}$ group which shows both $ - M$ and $ - I$ effect. As we know that the electron withdrawing group increases the stability of carbanion and stabilizes the negative charge.
In Option (D), ${C^ - }$is $1^\circ $ but at the para position of phenyl group $ - OC{H_3}$ group is present which shows $ + I$ effect. And as we know the group that shows $ + I$ effect generally decreases the stability of carbanion. So, we can say that it will destabilize the negative charge present on the carbon atom.
So, we can conclude that OPTION (C) is the right answer. Due to the presence of electron withdrawing $ - N{O_2}$ group which increases the stability of carbanion.
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Always remember the order of stability of carbanion where primary carbocations are most stable followed by the secondary and tertiary and the factors by which its stability is attained i.e. resonance effect, inductive effect and degree of the central carbon atom having negative charge.
Complete step by step answer:
Carbanion is the carbon atom having negative charge present on it. An electron withdrawing group increases the stability of carbanion. Resonance is another factor by which stability of carbanion increases. Now talking about the stability order of carbanion is: $1^\circ > 2^\circ > 3^\circ $.
As we all know that methyl group has a $ + I$ effect which increases the intensity of negative charge on central carbon of $3^\circ $ carbanion which further makes it unstable.
So let us analyze the above given options:
In Option (A), the carbocation present is a primary carbocation so the chances of its stability is high.
In Option (B), the carbocation is $1^\circ $ and the presence of the phenyl group also stabilizes the carbanion.
In Option (C), the carbocation $1^\circ $ and there is also $ - N{O_2}$ group which shows both $ - M$ and $ - I$ effect. As we know that the electron withdrawing group increases the stability of carbanion and stabilizes the negative charge.
In Option (D), ${C^ - }$is $1^\circ $ but at the para position of phenyl group $ - OC{H_3}$ group is present which shows $ + I$ effect. And as we know the group that shows $ + I$ effect generally decreases the stability of carbanion. So, we can say that it will destabilize the negative charge present on the carbon atom.
So, we can conclude that OPTION (C) is the right answer. Due to the presence of electron withdrawing $ - N{O_2}$ group which increases the stability of carbanion.
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Always remember the order of stability of carbanion where primary carbocations are most stable followed by the secondary and tertiary and the factors by which its stability is attained i.e. resonance effect, inductive effect and degree of the central carbon atom having negative charge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




