
The most stable alkene is:
[A] $C{{H}_{2}}=CH-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{3}}$
[B] $C{{H}_{2}}=C\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$
[C] $C{{H}_{2}}=CH-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$
[D] $C{{H}_{3}}-CH=CH-C{{H}_{3}}$
Answer
587.7k+ views
HINT: Stability of an alkene depends on several factors. To find the correct answer here check the substituents as well as the conjugation of the alkenes. Conjugated alkenes are more stable than non-conjugated alkenes.
COMPLETE STEP BY STEP SOLUTION: We know that in chemistry an alkene is a hydrocarbon (it contains carbon and hydrogen atoms) and it has a carbon-carbon double bond.
The stability of alkenes depends upon several factors. Let us discuss those factors and then try to find the correct answer of the given question.
- The alkenes which are attached to a greater number of alkyl groups that have a greater number of substituents are more stable.
Tetra-substituted alkene is the most stable followed by tri-substituted and di-substituted and then mono-substituted.
- Alkenes that have a higher number of alkylated carbon atoms are more stable due to +R (resonance of a positive charge) effect. Alkenes that have a higher number of hyper-conjugation structures are more stable.
- Conjugated alkenes are more stable due to resonance between two double bonds. Conjugate alkenes are alkenes with two or more alternative double bonds in a single structure.
- Cis-isomer of an alkene is more stable than a trans-isomer.
Now let us go through the options and find out the correct among them.
In the first option we have $C{{H}_{2}}=CH-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{3}}$. To understand the substituents better we can draw it as-
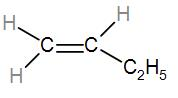
We can see that it is mono-substituted. Let us check the other options similarly and find out the most stable alkene.
Then we have $C{{H}_{2}}=C\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$. We can see that it is a conjugated alkene.
In the next option we have $C{{H}_{2}}=CH-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$which is also a conjugated alkene.
And lastly we have $C{{H}_{3}}-CH=CH-C{{H}_{3}}$which we can also draw as-
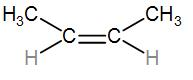
It has two substitutes.
We can see from the above discussion that the alkene in option [A] has only one substituent. Therefore, it can’t be the most stable. The alkene in option [D] has two substituents but the other two alkenes are conjugated and thus have higher stability.
Now, among the alkenes in option [B] and [C] we can see that [B] has an extra alkyl group which makes it more alkylated than [C] therefore [B] it is the most stable alkene.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [B] $C{{H}_{2}}=C\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$.
NOTE: A double bond is a covalent bond which means it is formed by sharing of electrons between two atoms. Atoms which do not have their valence shells fulfilled forms covalent bonding with a similar atom to complete its octet and hence gain stability. When four electrons are shared by the two atoms, it gives rise to a sigma bond and a pi-bond which is known as the double bond.
COMPLETE STEP BY STEP SOLUTION: We know that in chemistry an alkene is a hydrocarbon (it contains carbon and hydrogen atoms) and it has a carbon-carbon double bond.
The stability of alkenes depends upon several factors. Let us discuss those factors and then try to find the correct answer of the given question.
- The alkenes which are attached to a greater number of alkyl groups that have a greater number of substituents are more stable.
Tetra-substituted alkene is the most stable followed by tri-substituted and di-substituted and then mono-substituted.
- Alkenes that have a higher number of alkylated carbon atoms are more stable due to +R (resonance of a positive charge) effect. Alkenes that have a higher number of hyper-conjugation structures are more stable.
- Conjugated alkenes are more stable due to resonance between two double bonds. Conjugate alkenes are alkenes with two or more alternative double bonds in a single structure.
- Cis-isomer of an alkene is more stable than a trans-isomer.
Now let us go through the options and find out the correct among them.
In the first option we have $C{{H}_{2}}=CH-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{3}}$. To understand the substituents better we can draw it as-

We can see that it is mono-substituted. Let us check the other options similarly and find out the most stable alkene.
Then we have $C{{H}_{2}}=C\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$. We can see that it is a conjugated alkene.
In the next option we have $C{{H}_{2}}=CH-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$which is also a conjugated alkene.
And lastly we have $C{{H}_{3}}-CH=CH-C{{H}_{3}}$which we can also draw as-

It has two substitutes.
We can see from the above discussion that the alkene in option [A] has only one substituent. Therefore, it can’t be the most stable. The alkene in option [D] has two substituents but the other two alkenes are conjugated and thus have higher stability.
Now, among the alkenes in option [B] and [C] we can see that [B] has an extra alkyl group which makes it more alkylated than [C] therefore [B] it is the most stable alkene.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [B] $C{{H}_{2}}=C\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$.
NOTE: A double bond is a covalent bond which means it is formed by sharing of electrons between two atoms. Atoms which do not have their valence shells fulfilled forms covalent bonding with a similar atom to complete its octet and hence gain stability. When four electrons are shared by the two atoms, it gives rise to a sigma bond and a pi-bond which is known as the double bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




