
The minimum value of refractive index of the material of the prism for which the ray (1) undergoes total internal reflection on the face \[AC\] is:
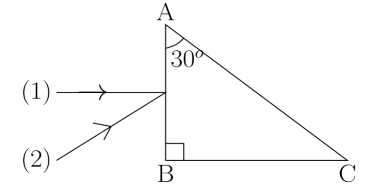
A. \[22\]
B. \[2\]
C. \[5\]
D. \[\sqrt 2 \]

Answer
507.9k+ views
Hint: Refractive Index is a value calculated from the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to that in a second medium of greater density. We know that if the angle between two lines is the same as the angle between their perpendiculars and one of right angles, the prism is always \[{90^o}\]. The angle of incidence should be minimum for total internal reflection (i.e., \[\theta \geqslant {i_c}\]). Using Snell's law we find the minimum value of the refractive index.
Complete step by step answer:
Snell's Law states that the ratio of the sine of the angles of incidence and reflection is equal to the ratio of the refractive index of the materials at the interface.
i.e., \[{n_1}\sin {\theta _1} = {n_2}\sin {\theta _2}\]
where \[{n_1}\]and \[{n_2}\] are refractive indices of first and second materials respectively. \[{\theta _1}\]and \[{\theta _2}\] be the angle of incidence and angle of reflection respectively.
Since the given first medium is air with angle of incidence is \[{90^o}\]. Let \[\mu \] be the refractive index and \[{i_c}\]be the angle of reflection of the material of the prism. Then by Snell’s law we get
\[1 = \mu \sin {i_c}\]--(2)
Since the angle between two lines is same as the angle between their perpendiculars so the given figures can be as follows
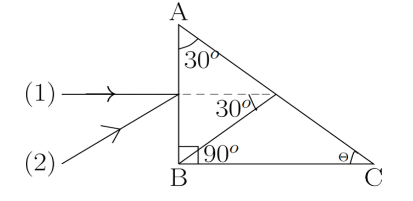
Let \[ABC\] is a right angled prism. A ray (1) is incident on the face \[AB\] along the normal. Now the condition is, ray (1) undergoes total internal reflection on the face \[AC\]. Since, ray (1) falls on \[AC\] at an angle of incidence \[{30^o}\].
So, from the condition of total internal reflection, we have
\[{30^o} \geqslant {i_c}\]--(3)
Taking sine in the expression (3), we get
\[\sin {30^o} \geqslant \sin {i_c}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\dfrac{1}{2} \geqslant \sin {i_c}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\dfrac{1}{2} \geqslant \dfrac{1}{\mu }\]
\[\therefore \mu \geqslant 2\]
Therefore, the minimum value of \[\mu \] is \[2\].
Hence the correct option is B.
Note: We know that the minimum angle for total internal reflection is the critical angle. The angle of the right-angled prism is \[{90^o}\]. Then the maximum value of the \[\theta \] is calculated corresponding to the minimum value of the angle of incidence. Total internal reflection occurs when light passes through denser medium to the lighter medium.
Complete step by step answer:
Snell's Law states that the ratio of the sine of the angles of incidence and reflection is equal to the ratio of the refractive index of the materials at the interface.
i.e., \[{n_1}\sin {\theta _1} = {n_2}\sin {\theta _2}\]
where \[{n_1}\]and \[{n_2}\] are refractive indices of first and second materials respectively. \[{\theta _1}\]and \[{\theta _2}\] be the angle of incidence and angle of reflection respectively.
Since the given first medium is air with angle of incidence is \[{90^o}\]. Let \[\mu \] be the refractive index and \[{i_c}\]be the angle of reflection of the material of the prism. Then by Snell’s law we get
\[1 = \mu \sin {i_c}\]--(2)
Since the angle between two lines is same as the angle between their perpendiculars so the given figures can be as follows

Let \[ABC\] is a right angled prism. A ray (1) is incident on the face \[AB\] along the normal. Now the condition is, ray (1) undergoes total internal reflection on the face \[AC\]. Since, ray (1) falls on \[AC\] at an angle of incidence \[{30^o}\].
So, from the condition of total internal reflection, we have
\[{30^o} \geqslant {i_c}\]--(3)
Taking sine in the expression (3), we get
\[\sin {30^o} \geqslant \sin {i_c}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\dfrac{1}{2} \geqslant \sin {i_c}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\dfrac{1}{2} \geqslant \dfrac{1}{\mu }\]
\[\therefore \mu \geqslant 2\]
Therefore, the minimum value of \[\mu \] is \[2\].
Hence the correct option is B.
Note: We know that the minimum angle for total internal reflection is the critical angle. The angle of the right-angled prism is \[{90^o}\]. Then the maximum value of the \[\theta \] is calculated corresponding to the minimum value of the angle of incidence. Total internal reflection occurs when light passes through denser medium to the lighter medium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




