
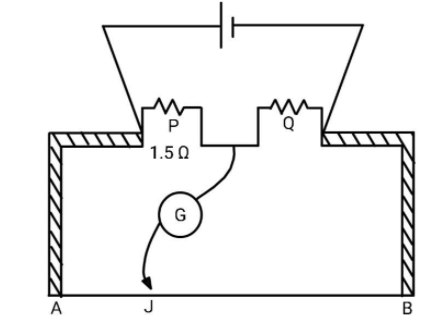
The meter bridge circuit shown in figure is balanced when jockey$J$ divides wire AB in two parts AJ and BJ in the ratio of $1:2$. The unknown resistance Q has value
(A) $1$$\Omega $
(B) $3$$\Omega $
(C) $4$$\Omega $
(D) $7$$\Omega $

Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: It is given that the meter bridge circuit is balanced, which means that the above circuit can be considered as a Wheatstone bridge. Find the resistance of the resistor Q by applying the condition for Wheatstone bridge.
Complete step by step answer:
The meter bridge works on the principle of Wheatstone bridge. The condition for balanced Wheatstone bridge is given as $\dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{{R_2}}} = \dfrac{{{R_3}}}{{{R_4}}}$.
In meter bridge ${R_1},{R_2},{R_3}\& {R_4}$ are as follows:
${R_1} = P$, ${R_2} = \rho \dfrac{{{l_1}}}{A}$ where ${l_1}$ is the length AJ, ${R_3} = Q$ and ${R_4} = \rho \dfrac{{{l_2}}}{A}$ where ${l_2}$ is the length BJ.
Here, $\rho $ is the resistivity of the wire and $A$ is the cross section of the wire.
Now, using the given data and applying the condition for Wheatstone bridge
$
\dfrac{P}{{\rho \dfrac{{{l_1}}}{A}}} = \dfrac{Q}{{\rho \dfrac{{{l_2}}}{A}}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{P}{{{l_1}}} = \dfrac{Q}{{{l_2}}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{P}{Q} = \dfrac{{{l_1}}}{{{l_2}}} \\
$
Given that $\dfrac{{{l_1}}}{{{l_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{P}{Q} = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\Rightarrow Q = 2P \\
\Rightarrow Q = \left( 2 \right)\left( {1.5} \right) \\
$
$Q = 3$$\Omega $
Therefore, the unknown resistance Q has value $3$$\Omega $.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Remember that while finding the resistance of the wire, it is possible that the wire may have variable resistivity and area of cross section which will change the resistances of the wire in the two parts. The meter bridge is used to find the unknown resistance. The jockey is slide on wire until there is no deflection in the galvanometer. This is known as the null point.
Complete step by step answer:
The meter bridge works on the principle of Wheatstone bridge. The condition for balanced Wheatstone bridge is given as $\dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{{R_2}}} = \dfrac{{{R_3}}}{{{R_4}}}$.
In meter bridge ${R_1},{R_2},{R_3}\& {R_4}$ are as follows:
${R_1} = P$, ${R_2} = \rho \dfrac{{{l_1}}}{A}$ where ${l_1}$ is the length AJ, ${R_3} = Q$ and ${R_4} = \rho \dfrac{{{l_2}}}{A}$ where ${l_2}$ is the length BJ.
Here, $\rho $ is the resistivity of the wire and $A$ is the cross section of the wire.
Now, using the given data and applying the condition for Wheatstone bridge
$
\dfrac{P}{{\rho \dfrac{{{l_1}}}{A}}} = \dfrac{Q}{{\rho \dfrac{{{l_2}}}{A}}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{P}{{{l_1}}} = \dfrac{Q}{{{l_2}}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{P}{Q} = \dfrac{{{l_1}}}{{{l_2}}} \\
$
Given that $\dfrac{{{l_1}}}{{{l_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{P}{Q} = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\Rightarrow Q = 2P \\
\Rightarrow Q = \left( 2 \right)\left( {1.5} \right) \\
$
$Q = 3$$\Omega $
Therefore, the unknown resistance Q has value $3$$\Omega $.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Remember that while finding the resistance of the wire, it is possible that the wire may have variable resistivity and area of cross section which will change the resistances of the wire in the two parts. The meter bridge is used to find the unknown resistance. The jockey is slide on wire until there is no deflection in the galvanometer. This is known as the null point.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




