
The metal ion involved in the stomatal regulation is
A. Iron
B. Magnesium
C. Zinc
D. Potassium
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: Plants need to exchange gasses and remove excess water via stomata
Stomatal regulation is controlling the opening and closing of stomata with the help of osmotic pressure.
Complete answer:
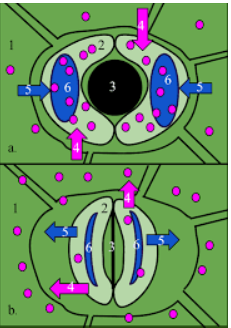
(1) Epidermal cell
(2) Guard cell
(3) Stoma
(4) Movement of potassium ions
(5) Movement of water molecules
(6) Vacuole
The opening and closing of stomata are regulated by guard cells with the help of osmotic pressure.
Stomata open when the guard cells fill up with water (becomes turgid).
Here the inner and outer layer of the guard cells moves outwards and stomata close when water comes out of the guard cells (becomes flaccid).
Here inner and outer layers of the guard cells move towards the pore.
Most widely it is accepted that due to potassium ions movement, the turgidity of the guard cells changes. The guard cells become turgid as the potential ions move inside the guard cells, which lowers the concentration of water inside the guard cells. So water moves inside the guard cells.
Similarly, when the potassium ions move outside of guard cells, the concentration of water becomes higher on the outside. So water moves outside of the guard cells.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Stomata (singular: stoma) are pores present in the leaves of the plant.
A higher number of stomata are present on the lower surface of the leaves. The pore is surrounded by two bean-shaped cells (parenchyma cells) called guard cells.
Stomatal regulation is controlling the opening and closing of stomata with the help of osmotic pressure.
Complete answer:

(1) Epidermal cell
(2) Guard cell
(3) Stoma
(4) Movement of potassium ions
(5) Movement of water molecules
(6) Vacuole
The opening and closing of stomata are regulated by guard cells with the help of osmotic pressure.
Stomata open when the guard cells fill up with water (becomes turgid).
Here the inner and outer layer of the guard cells moves outwards and stomata close when water comes out of the guard cells (becomes flaccid).
Here inner and outer layers of the guard cells move towards the pore.
Most widely it is accepted that due to potassium ions movement, the turgidity of the guard cells changes. The guard cells become turgid as the potential ions move inside the guard cells, which lowers the concentration of water inside the guard cells. So water moves inside the guard cells.
Similarly, when the potassium ions move outside of guard cells, the concentration of water becomes higher on the outside. So water moves outside of the guard cells.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Stomata (singular: stoma) are pores present in the leaves of the plant.
A higher number of stomata are present on the lower surface of the leaves. The pore is surrounded by two bean-shaped cells (parenchyma cells) called guard cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




