
The maximum value of 5 sin x + 12 cos x is:
(a) 5
(b) 12
(c) 13
(d) None of these
Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint: To find the maximum value of 5 sin x + 12 cos x, we will equate it to a function f(x). Now, we have, f (x) = 5 sin x + 12 cos x. We will differentiate both sides with respect to x and equate it to 0. After equating it to 0, we get two values a and b. Now, we will differentiate the above function once again and put the values a and b in this. The value at which the double differentiation is positive will give the minimum and the value at which double differentiation is negative will give maximum.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we have to equate the given term 5 sin x + 12 cos x to a function f(x). Thus, we have the following equation,
\[f\left( x \right)=5\sin x+12\cos x.....\left( i \right)\]
Now, first, we will find the extrema of the function f(x). The extrema of any function are the points at which the value of the function would either be maximum or minimum. The extrema of any function can be found out by equating the slope of the function to 0. Now, the slope of any function, y = A(x) can be obtained by differentiating both sides. Thus,
\[\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left[ A\left( x \right) \right]={{A}^{'}}\left( x \right)\]
Thus, the slope of f(x) will be given by:
\[\dfrac{d}{dx}\left[ f\left( x \right) \right]={{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( 5\sin x+12\cos x \right)=0\]
Now, by addition rule of differentiation, we have,
\[{{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=5\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \sin x \right)+12\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \cos x \right)\]
Now, the differentiation of sin x is cos x and that of cos x is – sin x. Thus, we will get,
\[{{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=5\cos x+12\left( -\sin x \right)\]
\[{{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=5\cos x-12\sin x\]
Now, for extrema,
\[{{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=0\]
Thus, we have,
\[{{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=5\cos x-12\sin x=0\]
\[\Rightarrow 5\cos x=12\sin x\]
\[\Rightarrow \tan x=\dfrac{5}{12}\]
Here, we have two cases:
Case 1: \[\text{If }\tan x=\dfrac{5}{12}\text{, then }\sin x=\dfrac{-5}{12}\text{ and }\cos x=\dfrac{-12}{13}\text{ as shown:}\]
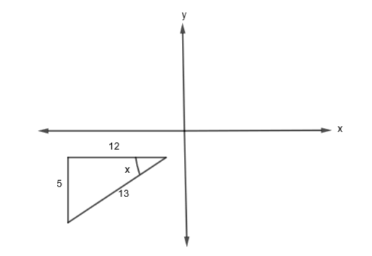
Case 2: \[\text{If }\tan x=\dfrac{5}{12}\text{, then }\sin x=\dfrac{5}{13}\text{ and }\cos x=\dfrac{12}{13}\text{ as shown:}\]
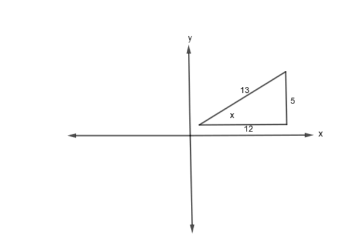
Now, to find which pair will give maximum and which pair will give the minimum, we will double differentiate the function and put these pairs of values. The value at which the double differentiation is positive will give a minimum at the value at which double differentiation is negative will give the maximum. Thus, we have,
\[{{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left[ {{f}^{'}}\left( x \right) \right]=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left[ 5\cos x-12\sin x \right]\]
\[{{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=5\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \cos x \right)-12\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \sin x \right)\]
\[{{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=-5\sin x-12\cos x\]
Now, we will check by putting the values of sin x and cos x in the above equation. Let us consider two cases.
Case 1: \[\sin x=\dfrac{5}{13}\text{ and }\cos x=\dfrac{12}{13}\]
\[{{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=-5\sin x-12\cos x\]
\[\Rightarrow {{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=-5\left( \dfrac{5}{13} \right)-12\left( \dfrac{12}{13} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow {{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{-25}{13}-\dfrac{144}{13}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=-\left( \dfrac{144+25}{13} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow {{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{-169}{13}=-13\]
Case 2: \[\sin x=\dfrac{-5}{13}\text{ and }\cos x=\dfrac{-12}{13}\]
\[{{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=-5\sin x-12\cos x\]
\[\Rightarrow {{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=-5\left( \dfrac{-5}{13} \right)-12\left( \dfrac{-12}{13} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow {{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{25+144}{13}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{169}{13}=13\]
Now, we can see that \[{{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)<0\text{ when }\sin x=\dfrac{5}{13}\text{ and }\cos x=\dfrac{12}{13}.\]Thus, this pair of values will give the maximum value. So, after putting these values in the function, we get,
\[f\left( x \right)=5\left( \dfrac{5}{13} \right)+12\left( \dfrac{12}{13} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{25}{13}+\dfrac{144}{13}\]
\[\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{169}{13}=13\]
Hence, the maximum value of 5 sin x + 12 cos x is 13.
Hence, the option (c) is the right answer.
Note: The maximum value of the above function can be calculated by this method also. Let a function g(x) be given as g(x) = A sin x + B cos x, then the range of this function is:
\[-\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}}\le g\left( x \right)\le \sqrt{{{A}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}}\]
In our case, the value of A is 5 and B is 12. Thus, we have,
\[-\sqrt{{{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 12 \right)}^{2}}}\le f\left( x \right)\le \sqrt{{{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 12 \right)}^{2}}}\]
The maximum value of f(x) is
\[f\left( x \right)=\sqrt{{{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 12 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{25+144}=13\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we have to equate the given term 5 sin x + 12 cos x to a function f(x). Thus, we have the following equation,
\[f\left( x \right)=5\sin x+12\cos x.....\left( i \right)\]
Now, first, we will find the extrema of the function f(x). The extrema of any function are the points at which the value of the function would either be maximum or minimum. The extrema of any function can be found out by equating the slope of the function to 0. Now, the slope of any function, y = A(x) can be obtained by differentiating both sides. Thus,
\[\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left[ A\left( x \right) \right]={{A}^{'}}\left( x \right)\]
Thus, the slope of f(x) will be given by:
\[\dfrac{d}{dx}\left[ f\left( x \right) \right]={{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( 5\sin x+12\cos x \right)=0\]
Now, by addition rule of differentiation, we have,
\[{{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=5\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \sin x \right)+12\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \cos x \right)\]
Now, the differentiation of sin x is cos x and that of cos x is – sin x. Thus, we will get,
\[{{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=5\cos x+12\left( -\sin x \right)\]
\[{{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=5\cos x-12\sin x\]
Now, for extrema,
\[{{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=0\]
Thus, we have,
\[{{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=5\cos x-12\sin x=0\]
\[\Rightarrow 5\cos x=12\sin x\]
\[\Rightarrow \tan x=\dfrac{5}{12}\]
Here, we have two cases:
Case 1: \[\text{If }\tan x=\dfrac{5}{12}\text{, then }\sin x=\dfrac{-5}{12}\text{ and }\cos x=\dfrac{-12}{13}\text{ as shown:}\]

Case 2: \[\text{If }\tan x=\dfrac{5}{12}\text{, then }\sin x=\dfrac{5}{13}\text{ and }\cos x=\dfrac{12}{13}\text{ as shown:}\]

Now, to find which pair will give maximum and which pair will give the minimum, we will double differentiate the function and put these pairs of values. The value at which the double differentiation is positive will give a minimum at the value at which double differentiation is negative will give the maximum. Thus, we have,
\[{{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left[ {{f}^{'}}\left( x \right) \right]=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left[ 5\cos x-12\sin x \right]\]
\[{{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=5\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \cos x \right)-12\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \sin x \right)\]
\[{{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=-5\sin x-12\cos x\]
Now, we will check by putting the values of sin x and cos x in the above equation. Let us consider two cases.
Case 1: \[\sin x=\dfrac{5}{13}\text{ and }\cos x=\dfrac{12}{13}\]
\[{{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=-5\sin x-12\cos x\]
\[\Rightarrow {{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=-5\left( \dfrac{5}{13} \right)-12\left( \dfrac{12}{13} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow {{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{-25}{13}-\dfrac{144}{13}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=-\left( \dfrac{144+25}{13} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow {{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{-169}{13}=-13\]
Case 2: \[\sin x=\dfrac{-5}{13}\text{ and }\cos x=\dfrac{-12}{13}\]
\[{{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=-5\sin x-12\cos x\]
\[\Rightarrow {{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=-5\left( \dfrac{-5}{13} \right)-12\left( \dfrac{-12}{13} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow {{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{25+144}{13}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{169}{13}=13\]
Now, we can see that \[{{f}^{''}}\left( x \right)<0\text{ when }\sin x=\dfrac{5}{13}\text{ and }\cos x=\dfrac{12}{13}.\]Thus, this pair of values will give the maximum value. So, after putting these values in the function, we get,
\[f\left( x \right)=5\left( \dfrac{5}{13} \right)+12\left( \dfrac{12}{13} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{25}{13}+\dfrac{144}{13}\]
\[\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{169}{13}=13\]
Hence, the maximum value of 5 sin x + 12 cos x is 13.
Hence, the option (c) is the right answer.
Note: The maximum value of the above function can be calculated by this method also. Let a function g(x) be given as g(x) = A sin x + B cos x, then the range of this function is:
\[-\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}}\le g\left( x \right)\le \sqrt{{{A}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}}\]
In our case, the value of A is 5 and B is 12. Thus, we have,
\[-\sqrt{{{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 12 \right)}^{2}}}\le f\left( x \right)\le \sqrt{{{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 12 \right)}^{2}}}\]
The maximum value of f(x) is
\[f\left( x \right)=\sqrt{{{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 12 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{25+144}=13\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




