
The maximum possible denticities of a ligand given below towards a common transition and inner-transition metal ion, respectively are:
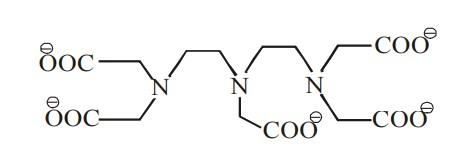
(A) 6 and 8
(B) 8 and 6
(C) 8 and 8
(D) 6 and 6

Answer
531.1k+ views
Hint: The term denticity determines the total number of donor atoms in a molecule and on the basis of the property denticity ligands can be classified as monodentate, bidentate, etc. By finding the coordination number of the complex towards a common transition element and inner transition element we could find the maximum possible denticities of the ligand.
Complete step by step solution:
- Let’s start with the concept of coordination compounds .They are the molecules that possess one or multiple metal centers which are bound to ligands. Ligands bind to a transition metal and donate a pair of its electrons to the metal atom, thus creating a metal-ligand bond.
- The term denticity refers to the number of atoms with which a ligand binds to a metal ion. A ligand could be monodentate, bidentate, tridentate, tetradentate, polydentate and multidentate. The monodentate ligand means that it binds through a lone pair on a single atom and a bidentate ligand means that it binds through lone pairs on two different atoms or it could even be tridentate, with three atoms bearing their own lone pairs, tetradentate, and so on.
- The terms, multidentate and polydentate, are two general names for ligands which can bind through more than one atom. Also the words chelating ligand and chelator are general names used to refer to these ligands.
- The coordination number (denticity) of the complex towards a common transition element is 6 and the co-ordination of inner transition element is 8.
- From the above discussions it’s clear that the maximum possible denticities of the given ligand towards inner transition metal ion is 8 and towards transition metal ion is 6.
Therefore the answer is option (A) 6 and 8.
Note: Do not confuse the terms denticity and hapticity. Hapticity denotes exclusively to the ligands where the coordinating atoms are contiguous and is usually represented by the 'eta' ($\eta $) notation whereas the term denticity can be described as the number of atoms with which a ligand binds to a metal ion.
Complete step by step solution:
- Let’s start with the concept of coordination compounds .They are the molecules that possess one or multiple metal centers which are bound to ligands. Ligands bind to a transition metal and donate a pair of its electrons to the metal atom, thus creating a metal-ligand bond.
- The term denticity refers to the number of atoms with which a ligand binds to a metal ion. A ligand could be monodentate, bidentate, tridentate, tetradentate, polydentate and multidentate. The monodentate ligand means that it binds through a lone pair on a single atom and a bidentate ligand means that it binds through lone pairs on two different atoms or it could even be tridentate, with three atoms bearing their own lone pairs, tetradentate, and so on.
- The terms, multidentate and polydentate, are two general names for ligands which can bind through more than one atom. Also the words chelating ligand and chelator are general names used to refer to these ligands.
- The coordination number (denticity) of the complex towards a common transition element is 6 and the co-ordination of inner transition element is 8.
- From the above discussions it’s clear that the maximum possible denticities of the given ligand towards inner transition metal ion is 8 and towards transition metal ion is 6.
Therefore the answer is option (A) 6 and 8.
Note: Do not confuse the terms denticity and hapticity. Hapticity denotes exclusively to the ligands where the coordinating atoms are contiguous and is usually represented by the 'eta' ($\eta $) notation whereas the term denticity can be described as the number of atoms with which a ligand binds to a metal ion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




