
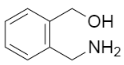
The major products of the following reaction is:
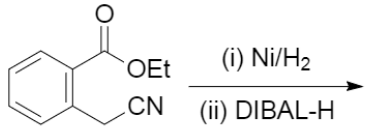
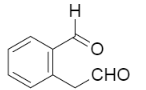
A.
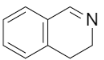
B.
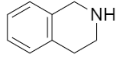
C.
D.
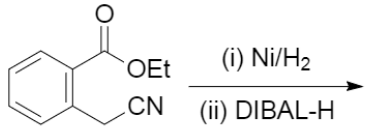




Answer
547.5k+ views
Hint:In organic chemistry, in order to predict the final product, the most effective way is to determine the mechanism of the whole reaction in a stepwise manner.
The properties and functions of specific reagents are a crucial part of any mechanism as it provides a clear idea as to what would happen to the organic compound in the next step.
Complete step-by-step answer:In the given half reaction, we can see that the $Ni/{{H}_{2}}$ or the nickel adsorbed with hydrogen. This reagent is generally used for the reduction of the cyanide groups. And we can see that the second reagent used is $DIBAL-H$ which is known for its reducing nature. It is known for its reductive properties which works on aldehyde and ester groups. And as we can see our main compound has an ester group too, so it will probably get reduced to hydrogen. The whole mechanism of the reaction is shown below,
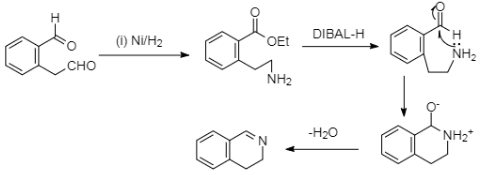
Now, we will consider this mechanism of the reaction in a stepwise manner. At first as we already know, the cyanide group gets reduced to an amine group because of nickel and hydrogen. And, in the next step the ethoxy group which is a part of the ester group, gets reduced to hydrogen because of the reagent di-isobutylaluminium hydride or ‘DIBAL-H’. In the next step the lone pair of electrons which are present in the nitrogen of the amine group gets transferred to the partially positive carbonyl carbon in which the bond polarity developed because of the electronegative character of the oxygen. Now, the loss of proton takes place and the nitrogen gets attached to the carbonyl carbon. In the last step, the loss of water takes place, as in, two protons from the amine group and an oxygen from the carbonyl group, which ultimately creates a double bond between the carbon and the nitrogen in the ring.
Now, if we look at the options which are provided to us in the question, we can see that option B is the correct one.
So, the appropriate answer is option B.
Note:The reagent di-isobutylaluminium hydride or ‘DIBAL-H’ is a type of reducing agent which works on the esters and aldehyde groups on any organic compound.
It is a very specific reagent and does not work on alcoholic groups, it only acts on aldehydes as well as esters containing groups.
The properties and functions of specific reagents are a crucial part of any mechanism as it provides a clear idea as to what would happen to the organic compound in the next step.
Complete step-by-step answer:In the given half reaction, we can see that the $Ni/{{H}_{2}}$ or the nickel adsorbed with hydrogen. This reagent is generally used for the reduction of the cyanide groups. And we can see that the second reagent used is $DIBAL-H$ which is known for its reducing nature. It is known for its reductive properties which works on aldehyde and ester groups. And as we can see our main compound has an ester group too, so it will probably get reduced to hydrogen. The whole mechanism of the reaction is shown below,

Now, we will consider this mechanism of the reaction in a stepwise manner. At first as we already know, the cyanide group gets reduced to an amine group because of nickel and hydrogen. And, in the next step the ethoxy group which is a part of the ester group, gets reduced to hydrogen because of the reagent di-isobutylaluminium hydride or ‘DIBAL-H’. In the next step the lone pair of electrons which are present in the nitrogen of the amine group gets transferred to the partially positive carbonyl carbon in which the bond polarity developed because of the electronegative character of the oxygen. Now, the loss of proton takes place and the nitrogen gets attached to the carbonyl carbon. In the last step, the loss of water takes place, as in, two protons from the amine group and an oxygen from the carbonyl group, which ultimately creates a double bond between the carbon and the nitrogen in the ring.
Now, if we look at the options which are provided to us in the question, we can see that option B is the correct one.
So, the appropriate answer is option B.
Note:The reagent di-isobutylaluminium hydride or ‘DIBAL-H’ is a type of reducing agent which works on the esters and aldehyde groups on any organic compound.
It is a very specific reagent and does not work on alcoholic groups, it only acts on aldehydes as well as esters containing groups.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




