
The major product of the Raschig process was taken for a litmus test. It was observed that it turned:
A.Red litmus blue
B.Blue litmus red
C.No change in colour
D.Very slight change in colour from red towards blue
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: We have to know that the chemical process for the synthesizing of phenol is Raschig-Hooker process. We have two main steps in this synthesis of phenol. The first step is the chlorination of benzene to form chlorobenzene and the second step is hydrolyzing chlorobenzene to form phenol.
Complete step by step answer:
We can use the Raschig-Hooker process for producing phenol. This reaction has two main steps.
In the first step, we have to chlorinate benzene to form chlorobenzene. The catalyst used in the first step is copper chloride (or) iron chloride. Once the catalyst is added, we have to expose the compounds to air at a temperature of ${250^ \circ }C$. We can write the chemical reaction for the first step as,
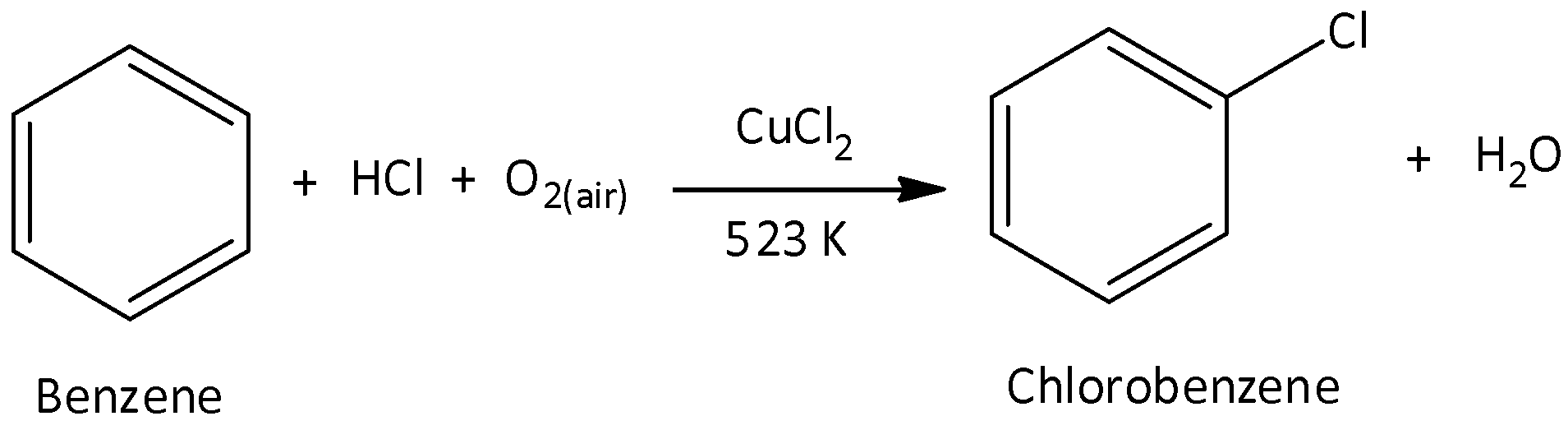
In the second step, chlorobenzene is steamed at ${450^ \circ }C$ in the presence of catalyst silicon. The catalyst hydrolyses chlorobenzene to yield phenol and hydrogen chloride. Hydrogen chloride is recycled. We can write the chemical reaction as,
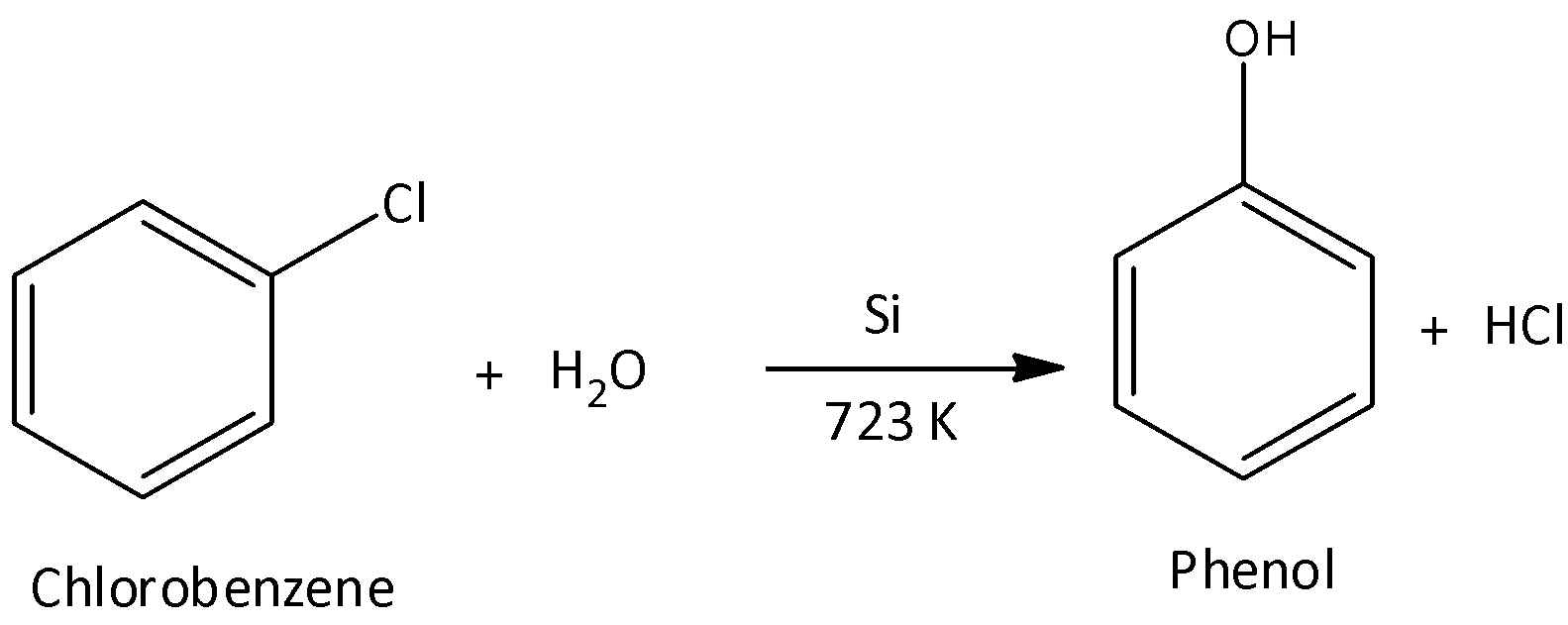
We know that phenols are slightly acidic because phenols can easily lose ion and the formed phenoxide ion is stabilized to some extent. The acidity of the phenol is due to the delocalization of the benzylic electron along with the higher value of the electronegativity of the atom of oxygen. The major product of the Raschig process is phenol. In nature, phenol is acidic, so it changes blue litmus to red.
$\therefore $Option (B) is correct.
Note:
We can use the Raschig process to prepare either chlorobenzene (or) phenol. The Raschig-Hooker process is preferable to the Dow and Bayer process as it has the ability to recover hydrogen chloride. We have to know that this reaction occurs at high temperature in an acidic environment along with hydrogen chloride. The selectivity of the reaction is from 70% to 85%.
Complete step by step answer:
We can use the Raschig-Hooker process for producing phenol. This reaction has two main steps.
In the first step, we have to chlorinate benzene to form chlorobenzene. The catalyst used in the first step is copper chloride (or) iron chloride. Once the catalyst is added, we have to expose the compounds to air at a temperature of ${250^ \circ }C$. We can write the chemical reaction for the first step as,

In the second step, chlorobenzene is steamed at ${450^ \circ }C$ in the presence of catalyst silicon. The catalyst hydrolyses chlorobenzene to yield phenol and hydrogen chloride. Hydrogen chloride is recycled. We can write the chemical reaction as,

We know that phenols are slightly acidic because phenols can easily lose ion and the formed phenoxide ion is stabilized to some extent. The acidity of the phenol is due to the delocalization of the benzylic electron along with the higher value of the electronegativity of the atom of oxygen. The major product of the Raschig process is phenol. In nature, phenol is acidic, so it changes blue litmus to red.
$\therefore $Option (B) is correct.
Note:
We can use the Raschig process to prepare either chlorobenzene (or) phenol. The Raschig-Hooker process is preferable to the Dow and Bayer process as it has the ability to recover hydrogen chloride. We have to know that this reaction occurs at high temperature in an acidic environment along with hydrogen chloride. The selectivity of the reaction is from 70% to 85%.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




