
The major product of the following is:
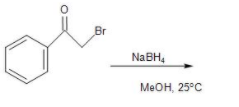
(A)

(B)
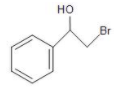
(C)
(D)





Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: The carbonyl group present in the given compound, in presence of the selective reducing agent undergoes reduction with a formation of new C-H bond, followed by the protonation of the oxygen on the carbonyl carbon.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given compound, that is, 2-Bromoacetophenone the reaction taking place in presence of a reducing agent, that is sodium borohydride in methanol solvent. It causes the reduction of the ketone group present in the compound. In the mechanism, the hydride $({{H}^{-}})$ detaches from the sodium borohydride and attacks the partially positive carbonyl carbon of the ketone group. Thus, a new C-H bond is formed, followed by a negative charge on the oxygen. Thus, forming an alkoxide ion.
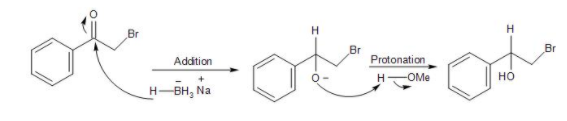
This is followed by the protonation of the ion by the methyl alcohol to form a secondary alcohol, that is, 2-Bromo-1-phenyl-ethanol compound. Thus, the reduction of the ketone to alcohol took place by the sodium borohydride in MeOH solvent.
Therefore, the major product formed from the reduction of the given compound is option (B) 2-Bromo-1-phenyl-ethanol.
Note: The $NaB{{H}_{4}}$ is a very selective reducing agent. It can only cause reduction of the aldehyde, ketones, and acid chloride to alcohols. Even though we get a primary alcohol in case of aldehydes and acid chlorides. Whereas the ketone generally forms secondary alcohol.
Also, due to the minimal difference in the electronegativity of boron (2.0) and hydrogen (2.1). The bond is less polar, thus less electron density of the hydrides. This makes them less nucleophilic and thus a mild reducing agent.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given compound, that is, 2-Bromoacetophenone the reaction taking place in presence of a reducing agent, that is sodium borohydride in methanol solvent. It causes the reduction of the ketone group present in the compound. In the mechanism, the hydride $({{H}^{-}})$ detaches from the sodium borohydride and attacks the partially positive carbonyl carbon of the ketone group. Thus, a new C-H bond is formed, followed by a negative charge on the oxygen. Thus, forming an alkoxide ion.

This is followed by the protonation of the ion by the methyl alcohol to form a secondary alcohol, that is, 2-Bromo-1-phenyl-ethanol compound. Thus, the reduction of the ketone to alcohol took place by the sodium borohydride in MeOH solvent.
Therefore, the major product formed from the reduction of the given compound is option (B) 2-Bromo-1-phenyl-ethanol.
Note: The $NaB{{H}_{4}}$ is a very selective reducing agent. It can only cause reduction of the aldehyde, ketones, and acid chloride to alcohols. Even though we get a primary alcohol in case of aldehydes and acid chlorides. Whereas the ketone generally forms secondary alcohol.
Also, due to the minimal difference in the electronegativity of boron (2.0) and hydrogen (2.1). The bond is less polar, thus less electron density of the hydrides. This makes them less nucleophilic and thus a mild reducing agent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




