
The main reaction, $RC \equiv CR\xrightarrow[{Lindlar's Catalyst}]{{{H_2}}}$gives the main product as:
A.Cis-alkene
B.Trans-alkene
C.Alkane
D.None of theses
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Lindlar’s catalyst is a catalyst which is used for the reduction of alkynes into alkene. The lead serves to deactivate the palladium sites, further deactivation of the catalyst with quinolone enhances its selectivity, preventing formation of alkanes.
Complete step by step answer:
Lindlar’s transformation of alkynes to cis-alkenes because of the hydrogenation occurring on the surface of metal. Both hydrogen are added to the same side of the alkyne as according to the syn- addition.
$RC \equiv CR\xrightarrow[{Lindlar's Catalyst}]{{{H_2}}}$
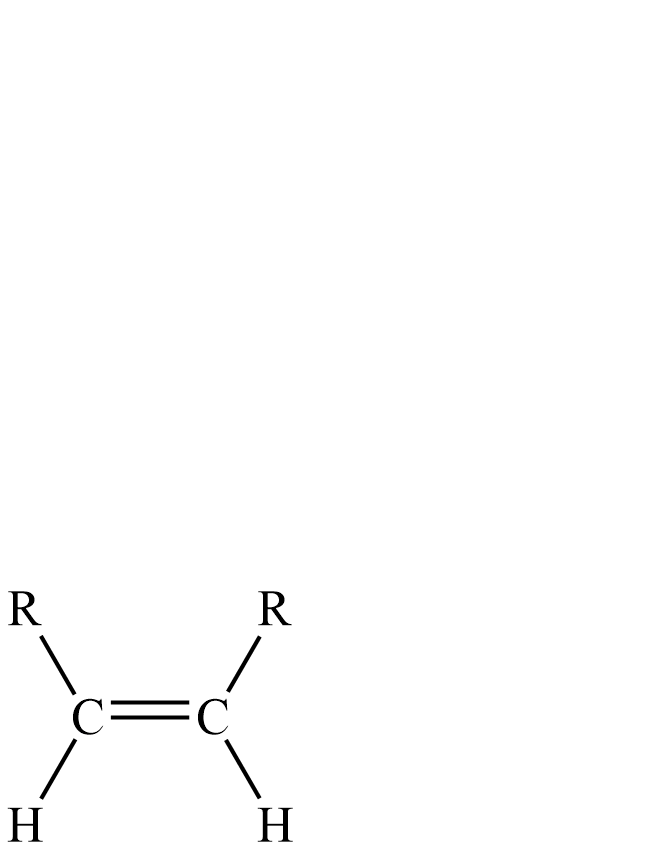
Lindlar’s catalyst has three components: palladium-calcium carbonate, lead acetate and quinoline. The quinoline prevents complete hydrogenation of alkyne to an alkane.
Now if we talk about syn-addition, it is an Addition reaction in which all new bonds are formed on the same face of the reactant molecule. As a result of the syn-addition there is decrease in bond order but increase in number of substituents.
Hence our answer is option A.
Note:
Addition reaction: Addition reaction is defined as that reaction in which two or more reactants combine together to form a single product. Addition reactions are limited to molecular compounds that have multiple bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
Lindlar’s transformation of alkynes to cis-alkenes because of the hydrogenation occurring on the surface of metal. Both hydrogen are added to the same side of the alkyne as according to the syn- addition.
$RC \equiv CR\xrightarrow[{Lindlar's Catalyst}]{{{H_2}}}$

Lindlar’s catalyst has three components: palladium-calcium carbonate, lead acetate and quinoline. The quinoline prevents complete hydrogenation of alkyne to an alkane.
Now if we talk about syn-addition, it is an Addition reaction in which all new bonds are formed on the same face of the reactant molecule. As a result of the syn-addition there is decrease in bond order but increase in number of substituents.
Hence our answer is option A.
Note:
Addition reaction: Addition reaction is defined as that reaction in which two or more reactants combine together to form a single product. Addition reactions are limited to molecular compounds that have multiple bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




