
The magnitude of electric field E in the annular region of a charged cylindrical capacitor:
A. Is the same throughout.
B. Is higher near the outer cylinder than near the inner cylinder.
C. Varies as \[\dfrac{1}{r}\], where r is the distance from the axis.
D. Varies as r, where r is the distance from the axis.
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Using Gauss law this problem can be solved easily by considering the annular region (the region bounded by the two concentric circles) as the Gaussian surface. In the case of a cylindrical capacitor, the inner and outer radius of the capacitor is considered to be the annular region.
Formula used:
\[\begin{align}
& E\times A=\dfrac{Q}{\varepsilon } \\
& A=2\pi r\times L \\
\end{align}\]
Complete step by step answer:
From given, we have the data,
The magnitude of the electric field = E
The diagram representing the Gaussian surface of the cylindrical capacitor.
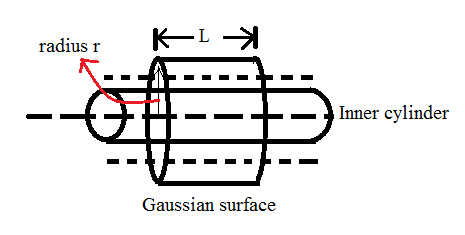
Considering the annular region of the cylindrical capacitor as the Gaussian surface, we have,
\[E\times A=\dfrac{Q}{\varepsilon }\] …… (1)
Where E is the electric field, A is the surface area, Q is the charge enclosed and \[\varepsilon \]is the permittivity of the medium.
The surface area is given by,
\[A=2\pi r\times L\] …… (2)
Where r is the radius of the cylindrical capacitor and L is its length.
Substitute the equation (2) in (1), so, we get,
\[E\times (2\pi r\times L)=\dfrac{Q}{\varepsilon }\]
Considering Q’ as the charge per unit length, we get,
\[Q'=\dfrac{Q}{L}\]
Substitute the above value in the equation of electric field,
Thus, the electric field inside the cylindrical capacitor at a distance r from the centre is,
\[E=\dfrac{Q'}{2\pi \varepsilon r}\]
\[\Rightarrow E\propto \dfrac{1}{r}\]
Where \[Q'\]is the charge per unit length of the capacitor and r is the radius of the cylindrical capacitor.
As the magnitude of electric field E in the annular region of a charged cylindrical capacitor varies as \[\dfrac{1}{r}\], where r is the distance from the axis, thus option (C) is correct.
Note:
The things to be on your finger-tips for further information on solving these types of problems are: The electric field inside the annular region is due to the inner cylinder. Thus, the electric field should be calculated from the centre of the cylinder to the radius of the inner cylinder.
Formula used:
\[\begin{align}
& E\times A=\dfrac{Q}{\varepsilon } \\
& A=2\pi r\times L \\
\end{align}\]
Complete step by step answer:
From given, we have the data,
The magnitude of the electric field = E
The diagram representing the Gaussian surface of the cylindrical capacitor.

Considering the annular region of the cylindrical capacitor as the Gaussian surface, we have,
\[E\times A=\dfrac{Q}{\varepsilon }\] …… (1)
Where E is the electric field, A is the surface area, Q is the charge enclosed and \[\varepsilon \]is the permittivity of the medium.
The surface area is given by,
\[A=2\pi r\times L\] …… (2)
Where r is the radius of the cylindrical capacitor and L is its length.
Substitute the equation (2) in (1), so, we get,
\[E\times (2\pi r\times L)=\dfrac{Q}{\varepsilon }\]
Considering Q’ as the charge per unit length, we get,
\[Q'=\dfrac{Q}{L}\]
Substitute the above value in the equation of electric field,
Thus, the electric field inside the cylindrical capacitor at a distance r from the centre is,
\[E=\dfrac{Q'}{2\pi \varepsilon r}\]
\[\Rightarrow E\propto \dfrac{1}{r}\]
Where \[Q'\]is the charge per unit length of the capacitor and r is the radius of the cylindrical capacitor.
As the magnitude of electric field E in the annular region of a charged cylindrical capacitor varies as \[\dfrac{1}{r}\], where r is the distance from the axis, thus option (C) is correct.
Note:
The things to be on your finger-tips for further information on solving these types of problems are: The electric field inside the annular region is due to the inner cylinder. Thus, the electric field should be calculated from the centre of the cylinder to the radius of the inner cylinder.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




