
The logical symbols shown here are logically equivalent to:
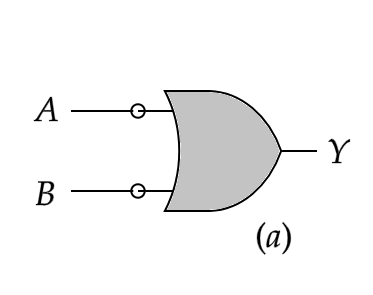
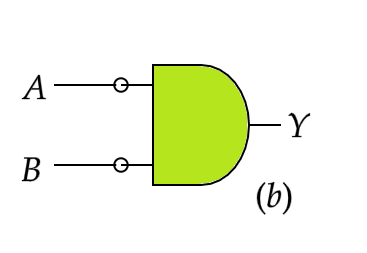
A) AND and OR gate
B) NOR and NAND gate
C) OR and AND gate
D) NAND and NOR gate


Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: The given logic gates are OR and AND gates respectively but there’s a catch. The inputs being given to these logic gates have negated values. Since we are taking the sum and the product of the complements of terms A and B, we can approach this question using De Morgan’s Theorem.
Complete step by step solution:
De Morgan’s theorem is a powerful tool in digital design. The theorem explains that the complement of the product of all the terms is equal to the sum of the complement of each term.
Logically, we can depict this as \[\overline{(A.B)}=\overline{A}+\overline{B}\].
The inverse of the above statement is equally true. This means that the complement of the sum of all the terms is equal to the product of the complements of each term.
Logically, we can depict this as \[\overline{(A+B)}=(\overline{A}).(\overline{B})\]
If we look at the two equations above from the right-hand side, the first equation is a representation of the logic gate marked \[(a)\] and the second equation is a representation of the logic gate marked \[(b)\] .
The truth table for the logic gate in figure (a) can be drawn as
Similarly, we can draw the truth table for the logic gate in figure (b) as follows
Thus we can now say, both based on our argument, the truth tables and De Morgan’s theorem, that the two logic gates represent a NAND and a NOR gate respectively.
Hence the correct option is (D).
Note: We can check the validity of our argument and De Morgan’s theorem as well using a truth table. If we’ll make a truth table of the above two logic gates and compare them with the truth tables for a NAND and a NOR gate respectively. It should be noted that De Morgan’s theorem stands for any number of inputs.
Complete step by step solution:
De Morgan’s theorem is a powerful tool in digital design. The theorem explains that the complement of the product of all the terms is equal to the sum of the complement of each term.
Logically, we can depict this as \[\overline{(A.B)}=\overline{A}+\overline{B}\].
The inverse of the above statement is equally true. This means that the complement of the sum of all the terms is equal to the product of the complements of each term.
Logically, we can depict this as \[\overline{(A+B)}=(\overline{A}).(\overline{B})\]
If we look at the two equations above from the right-hand side, the first equation is a representation of the logic gate marked \[(a)\] and the second equation is a representation of the logic gate marked \[(b)\] .
The truth table for the logic gate in figure (a) can be drawn as
| \[A\] | \[B\] | \[\overline{A}\] | \[\overline{B}\] | \[A.B\] | \[\overline{(A.B)}\] | \[\overline{A}+\overline{B}\] |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Similarly, we can draw the truth table for the logic gate in figure (b) as follows
| \[A\] | \[B\] | \[\overline{A}\] | \[\overline{B}\] | \[A+B\] | \[\overline{(A+B)}\] | \[(\overline{A}).(\overline{B})\] |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Thus we can now say, both based on our argument, the truth tables and De Morgan’s theorem, that the two logic gates represent a NAND and a NOR gate respectively.
Hence the correct option is (D).
Note: We can check the validity of our argument and De Morgan’s theorem as well using a truth table. If we’ll make a truth table of the above two logic gates and compare them with the truth tables for a NAND and a NOR gate respectively. It should be noted that De Morgan’s theorem stands for any number of inputs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




