
The length, breadth and height of a rectangular parallelepiped are in the ratio 6:3:1 .if the surface area of a cube is equal to the surface area of this parallelepiped; then what is the ratio of volume of cube to volume of parallelepiped?
A.1:1
B.5:4
C.7:5
D.3:2
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: We will follow the simple approach to solve this problem. First we will find the side of the cube with the help of the first condition given that is the surface area of a cube is equal to the surface area of this parallelepiped. Then we will go to find the ratio of their volumes.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given that the length, breadth and height of a rectangular parallelepiped are in the ratio 6:3:1
Let \[l = 6x,b = 3x,h = x\]
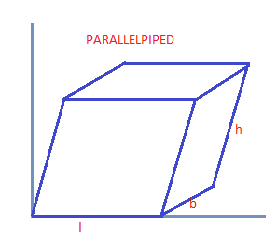
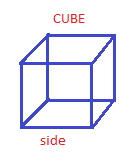
Now we know that
Total surface area of parallelepiped \[ = lateral\;surface\;area{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}2{\text{ }}base{\text{ }}area\]
\[ \Rightarrow perimeter{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}base \times height + length \times height\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2\left( {l + b} \right) \times h + 2 \times l \times b\]
Putting the values of length, breadth and height
\[
\Rightarrow 2\left( {6x + 3x} \right) \times x + 2 \times 6x \times 3x \\
\Rightarrow 2\left( {9x} \right) \times x + 2 \times 6x \times 3x........... \to 1 \\
\]
Now total surface area of cube \[ = 6 \times sid{e^2}....... \to 2\]
But it is given that the surface areas of both the diagrams are the same. Thus from 1 and 2,
\[ \Rightarrow 2\left( {9x} \right) \times x + 2 \times 6x \times 3x = 6 \times sid{e^2}\]
Dividing the above equation by 2
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {9x} \right) \times x + 6x \times 3x = 3 \times sid{e^2}\]
Multiplying the terms
\[ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} + 18{x^2} = 3 \times sid{e^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 27{x^2} = 3 \times sid{e^2}\]
Dividing both sides by 3
\[ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} = sid{e^2}\]
Taking square root on both sides
\[ \Rightarrow 3x = side\]
This gives the side of the cube.
Now let’s proceed towards the volume.
\[\dfrac{{V\left( {cube} \right)}}{{V\left( {parallelepiped} \right)}} = \dfrac{{sid{e^3}}}{{l \times b \times h}}\]
Substituting the values
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\left( {3x} \right)}^3}}}{{6x \times 3x \times x}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{27{x^3}}}{{18{x^3}}}\]
Dividing both numerator and denominator by 9 and cancelling the \[{x^3}\] term.
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{2}\]
Here is the ratio of volumes.
\[\dfrac{{V\left( {cube} \right)}}{{V\left( {parallelpiped} \right)}} = \dfrac{3}{2}\]
So the correct option is D.
Note: Here only the most important thing students generally do wrong is the ratio of the quantities in the way they are asked. It means which quantity is in numerator and which in denominator. Also note that we are given the ratio of dimensions which are taken here with x.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given that the length, breadth and height of a rectangular parallelepiped are in the ratio 6:3:1
Let \[l = 6x,b = 3x,h = x\]


Now we know that
Total surface area of parallelepiped \[ = lateral\;surface\;area{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}2{\text{ }}base{\text{ }}area\]
\[ \Rightarrow perimeter{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}base \times height + length \times height\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2\left( {l + b} \right) \times h + 2 \times l \times b\]
Putting the values of length, breadth and height
\[
\Rightarrow 2\left( {6x + 3x} \right) \times x + 2 \times 6x \times 3x \\
\Rightarrow 2\left( {9x} \right) \times x + 2 \times 6x \times 3x........... \to 1 \\
\]
Now total surface area of cube \[ = 6 \times sid{e^2}....... \to 2\]
But it is given that the surface areas of both the diagrams are the same. Thus from 1 and 2,
\[ \Rightarrow 2\left( {9x} \right) \times x + 2 \times 6x \times 3x = 6 \times sid{e^2}\]
Dividing the above equation by 2
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {9x} \right) \times x + 6x \times 3x = 3 \times sid{e^2}\]
Multiplying the terms
\[ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} + 18{x^2} = 3 \times sid{e^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 27{x^2} = 3 \times sid{e^2}\]
Dividing both sides by 3
\[ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} = sid{e^2}\]
Taking square root on both sides
\[ \Rightarrow 3x = side\]
This gives the side of the cube.
Now let’s proceed towards the volume.
\[\dfrac{{V\left( {cube} \right)}}{{V\left( {parallelepiped} \right)}} = \dfrac{{sid{e^3}}}{{l \times b \times h}}\]
Substituting the values
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\left( {3x} \right)}^3}}}{{6x \times 3x \times x}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{27{x^3}}}{{18{x^3}}}\]
Dividing both numerator and denominator by 9 and cancelling the \[{x^3}\] term.
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{2}\]
Here is the ratio of volumes.
\[\dfrac{{V\left( {cube} \right)}}{{V\left( {parallelpiped} \right)}} = \dfrac{3}{2}\]
So the correct option is D.
Note: Here only the most important thing students generally do wrong is the ratio of the quantities in the way they are asked. It means which quantity is in numerator and which in denominator. Also note that we are given the ratio of dimensions which are taken here with x.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

What is the color of ferrous sulphate crystals? How does this color change after heating? Name the products formed on strongly heating ferrous sulphate crystals. What type of chemical reaction occurs in this type of change.

What is the Full Form of ICSE / ISC ?

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Write the 6 fundamental rights of India and explain in detail




