
The laws of reflection hold good for –
A) Plane mirror only
B) Concave mirror only
C) Convex mirror only
D) All mirrors irrespective of their shape.
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: We need to understand the laws of reflection and the parameter involved in the law to analyse whether these laws hold good for spherical mirrors or plane mirrors or for both. We can use this information to solve the given problem easily.
Complete answer:
We know that there are two laws of reflection. These laws help us understand the possible ways for a light incident on a reflecting surface to follow with much precision. The laws of reflection of light falling on a reflecting surface are –
1.The normal, the incident ray and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane. i.e., we can easily draw a schematic representation on a paper without considering a third dimension.
2.The angle of incidence of the light ray, i, is always equal to the angle of reflection of the light ray, r. It is given mathematically as –
\[i=r\]
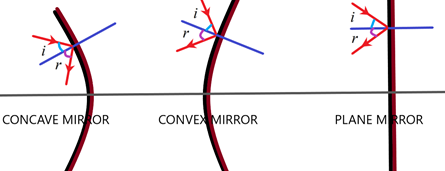
Now, let us consider different mirrors or reflecting surfaces. The normal is the perpendicular line to the face of the surface for a plane mirror or a perpendicular to the tangent at a point for a spherical mirror. The first law holds good for both the mirrors.
The angle of reflection and the angle of incidence are determined by the normal as we can see in the above figure. These values are always constant no matter what the shape of the mirror is.
Therefore, we understand that the laws of reflection hold good for all types of reflecting surfaces.
The correct answer is option D.
Note:
We have to strictly follow the laws of reflection when we draw a ray diagram to get the most accurate drawings and observations. Unlike the other drawings in Physics which are for reference, the ray diagrams give correct inference if drawn well.
Complete answer:
We know that there are two laws of reflection. These laws help us understand the possible ways for a light incident on a reflecting surface to follow with much precision. The laws of reflection of light falling on a reflecting surface are –
1.The normal, the incident ray and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane. i.e., we can easily draw a schematic representation on a paper without considering a third dimension.
2.The angle of incidence of the light ray, i, is always equal to the angle of reflection of the light ray, r. It is given mathematically as –
\[i=r\]

Now, let us consider different mirrors or reflecting surfaces. The normal is the perpendicular line to the face of the surface for a plane mirror or a perpendicular to the tangent at a point for a spherical mirror. The first law holds good for both the mirrors.
The angle of reflection and the angle of incidence are determined by the normal as we can see in the above figure. These values are always constant no matter what the shape of the mirror is.
Therefore, we understand that the laws of reflection hold good for all types of reflecting surfaces.
The correct answer is option D.
Note:
We have to strictly follow the laws of reflection when we draw a ray diagram to get the most accurate drawings and observations. Unlike the other drawings in Physics which are for reference, the ray diagrams give correct inference if drawn well.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




