
The larger aperture of telescope are used for
(A) Greater magnification
(B) Greater resolution
(C) Reducing lens aberration
(D) Case of manufacture
Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: Use the mathematical expression of resolving power of the telescope : $RP = \dfrac{D}{{1.22\lambda }}$ to observe the direct proportionality between the resolving power and D, the diameter/ linear aperture of the telescope.
Complete step by step solution
Firstly, the resolution of a telescope means how effectively the telescope can resolve two very closely placed objects as separate images. The resolution of a telescope is determined by its resolving power. The resolving power is basically the inverse of the distance or the angular separation between the two objects to be resolved when viewed through the telescope.
The mathematical expression of resolving power of the telescope: $RP = \dfrac{1}{{{d_{separation}}}} = \dfrac{D}{{1.22\lambda }}$
Where, D is the diameter or the linear aperture of the telescope
and $\lambda $ is the wavelength of the light used
$ \Rightarrow $ Resolving power is directly proportional to diameter/ linear aperture of the telescope.
Often in telescopes, when very close objects such as stars of galaxies have to be observed using telescopes, they subtend really small angles on the telescope. For resolving them as separate objects successfully, the telescopes are made to have diameters as large as 10 m. Thus, larger apertures are used to have greater resolving power and hence, greater resolution.
Therefore, Option (B): ‘Greater resolution’ is the correct option.
Additional Information
Here is a diagram of an astronomical telescope for better understanding:
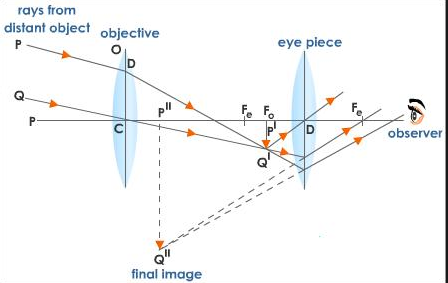
Note: Other than the mathematical expression, we can also look at it logically, larger aperture of the telescope means more number of rays of light coming from the object will enter the telescope, hence, better resolution.
Complete step by step solution
Firstly, the resolution of a telescope means how effectively the telescope can resolve two very closely placed objects as separate images. The resolution of a telescope is determined by its resolving power. The resolving power is basically the inverse of the distance or the angular separation between the two objects to be resolved when viewed through the telescope.
The mathematical expression of resolving power of the telescope: $RP = \dfrac{1}{{{d_{separation}}}} = \dfrac{D}{{1.22\lambda }}$
Where, D is the diameter or the linear aperture of the telescope
and $\lambda $ is the wavelength of the light used
$ \Rightarrow $ Resolving power is directly proportional to diameter/ linear aperture of the telescope.
Often in telescopes, when very close objects such as stars of galaxies have to be observed using telescopes, they subtend really small angles on the telescope. For resolving them as separate objects successfully, the telescopes are made to have diameters as large as 10 m. Thus, larger apertures are used to have greater resolving power and hence, greater resolution.
Therefore, Option (B): ‘Greater resolution’ is the correct option.
Additional Information
Here is a diagram of an astronomical telescope for better understanding:

Note: Other than the mathematical expression, we can also look at it logically, larger aperture of the telescope means more number of rays of light coming from the object will enter the telescope, hence, better resolution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




