
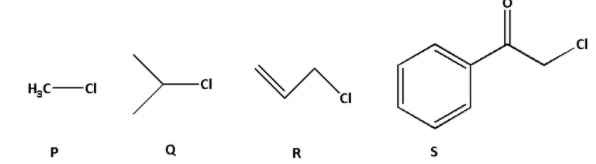
The ${\text{KI}}$ in acetone, undergoes ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{2}}$ reaction with each of P, Q, R and S. The rates of reaction vary as:
A) P > Q > R > S
B) S > P > R > Q
C) P > R > Q > S
D) R > P > S > Q

Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: We are given four compounds in which chlorine atom is attached to the aliphatic part of the molecule. Also remember that the methyl groups are electron donating groups and they increase the electron density around the carbon atom.
Complete answer:
We are given four compounds. In the compounds we can see that chlorine atoms are attached. Thus, the given compounds are alkyl halides. First we will see what happens in a ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{2}}$ reaction.
In a ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ reaction i.e. bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction, the nucleophile attacks the alkyl halide from the back side and thus, the product formed has a reversed configuration. It is a one-step reaction. In the reaction, the bond breaking and bond making occurs simultaneously. No intermediate is formed in the reaction.
The order of rate of ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ reaction is as follows: ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ alkyl halide > Primary alkyl halide > Secondary alkyl halide > Tertiary alkyl halide. This order is because the steric hindrance increases from methyl to tertiary alkyl halide and thus, the attack of nucleophiles becomes difficult.
Another reason for the order is the increase in the number of methyl substituents. The methyl substituent is electron donating. As the number of methyl substituents increases, the electron density around the carbon increases and thus, the electrophilicity of carbon decreases. Thus, the attack of nucleophiles becomes difficult.
Consider compound P: In compound P, there is only one methyl group. The chlorine atom is attached to the methyl group directly.
Consider compound Q: In compound Q, the chlorine atom is attached to the secondary carbon atom. Thus, it is a secondary alkyl halide.
Consider compound R: In compound R, the chlorine atom is attached to a primary carbon atom. Thus, it is a primary alkyl halide. Thus, the order of rate of ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ reaction is as follows: P > R > Q.
Consider compound S: In compound S, there is a phenyl group and a carbonyl group. Both the phenyl and carbonyl groups are electron withdrawing groups. Thus, the electron density on the carbon to which chlorine atom is attached decreases. Thus, the electrophilicity of carbon increases and the attack of nucleophilic becomes easier.
Thus, the rate of ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ reaction for compound S is highest. Thus, the order of rate of ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ reaction is as follows: S > P > R > Q.
Thus, the correct answer is option (B) S > P > R > Q.
Note: The electron donating substituents increase the electron density around the carbon atom. Thus, the electrophilicity of the carbon atom decreases and thus, the attack of nucleophiles becomes difficult. The electron withdrawing substituents decrease the electron density around the carbon atom. Thus, the electrophilicity of the carbon atom increases and thus, the attack of nucleophiles becomes easier.
Complete answer:
We are given four compounds. In the compounds we can see that chlorine atoms are attached. Thus, the given compounds are alkyl halides. First we will see what happens in a ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{2}}$ reaction.
In a ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ reaction i.e. bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction, the nucleophile attacks the alkyl halide from the back side and thus, the product formed has a reversed configuration. It is a one-step reaction. In the reaction, the bond breaking and bond making occurs simultaneously. No intermediate is formed in the reaction.
The order of rate of ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ reaction is as follows: ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ alkyl halide > Primary alkyl halide > Secondary alkyl halide > Tertiary alkyl halide. This order is because the steric hindrance increases from methyl to tertiary alkyl halide and thus, the attack of nucleophiles becomes difficult.
Another reason for the order is the increase in the number of methyl substituents. The methyl substituent is electron donating. As the number of methyl substituents increases, the electron density around the carbon increases and thus, the electrophilicity of carbon decreases. Thus, the attack of nucleophiles becomes difficult.
Consider compound P: In compound P, there is only one methyl group. The chlorine atom is attached to the methyl group directly.
Consider compound Q: In compound Q, the chlorine atom is attached to the secondary carbon atom. Thus, it is a secondary alkyl halide.
Consider compound R: In compound R, the chlorine atom is attached to a primary carbon atom. Thus, it is a primary alkyl halide. Thus, the order of rate of ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ reaction is as follows: P > R > Q.
Consider compound S: In compound S, there is a phenyl group and a carbonyl group. Both the phenyl and carbonyl groups are electron withdrawing groups. Thus, the electron density on the carbon to which chlorine atom is attached decreases. Thus, the electrophilicity of carbon increases and the attack of nucleophilic becomes easier.
Thus, the rate of ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ reaction for compound S is highest. Thus, the order of rate of ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ reaction is as follows: S > P > R > Q.
Thus, the correct answer is option (B) S > P > R > Q.
Note: The electron donating substituents increase the electron density around the carbon atom. Thus, the electrophilicity of the carbon atom decreases and thus, the attack of nucleophiles becomes difficult. The electron withdrawing substituents decrease the electron density around the carbon atom. Thus, the electrophilicity of the carbon atom increases and thus, the attack of nucleophiles becomes easier.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




