
The IUPAC name of the given structure:
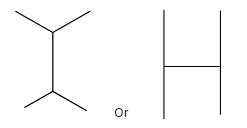
A.2,2- dimethylbutane
B.isohexane
C.2,3- dimethyl butane
D.di-isohexane

Answer
576.6k+ views
Hint: IUPAC stands for the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. For the nomenclature of chemical compounds, the IUPAC nomenclature in organic chemistry is a method used for the naming of organic chemical compounds. In the IUPAC system, the name of an organic compound consists of three parts:
-Word root- It is the basic unit of the name of the chemical compound. It depends upon the number of carbon atoms in the longest continuous carbon chain selected, called the parent chain. Depending upon the number of carbons in the chain the compound is assigned a word. For example, a chain containing ${C_2}$ carbons will be Eth, ${C_3}$ which will be a prop.
-The suffix- A suffix is added after the word root to indicate the nature of the carbon-carbon bond. For if the carbon chains contain a double bond then a suffix will be added as “ene”.
-Prefix- The groups which are not regarded as functional but present in the carbon chain as substituents are written before the word root as a prefix.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us draw the given structure in details:
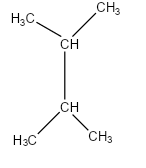
-In this structure, we can see that it is a symmetrical alkane. So if we count the longest carbon chain from any side it will be the same. The longest chain which is known as the parent chain contains four carbon atoms. In the second and third carbon, there is a methyl group attached to it.
-The IUPAC name of the given structure is 2,3- dimethyl butane.
-Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note:
-2,3-dimethyl butane is an isomer of hexane. It is a colorless liquid that boils at ${57.9^ \circ }C$.
-It is used in organic synthesis, as a catalytic agent, and petrochemical additive.
-The density of 2,3-dimethyl butane is $662mgm{L^{ - 1}}$
-Word root- It is the basic unit of the name of the chemical compound. It depends upon the number of carbon atoms in the longest continuous carbon chain selected, called the parent chain. Depending upon the number of carbons in the chain the compound is assigned a word. For example, a chain containing ${C_2}$ carbons will be Eth, ${C_3}$ which will be a prop.
-The suffix- A suffix is added after the word root to indicate the nature of the carbon-carbon bond. For if the carbon chains contain a double bond then a suffix will be added as “ene”.
-Prefix- The groups which are not regarded as functional but present in the carbon chain as substituents are written before the word root as a prefix.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us draw the given structure in details:

-In this structure, we can see that it is a symmetrical alkane. So if we count the longest carbon chain from any side it will be the same. The longest chain which is known as the parent chain contains four carbon atoms. In the second and third carbon, there is a methyl group attached to it.
-The IUPAC name of the given structure is 2,3- dimethyl butane.
-Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note:
-2,3-dimethyl butane is an isomer of hexane. It is a colorless liquid that boils at ${57.9^ \circ }C$.
-It is used in organic synthesis, as a catalytic agent, and petrochemical additive.
-The density of 2,3-dimethyl butane is $662mgm{L^{ - 1}}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




