
The intestine and stomach in mammals are lined up which of the following tissue types?
A. Cuboidal epithelium
B. Columnar epithelium
C. Squamous epithelium
D. Stratified epithelium
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: At 100X you can begin to see the layer of this epithelium. The suitable place to look for it is on the surface of the villi. You can see what look like round white bubbles in the epithelium cells. These are called goblet cells and they secrete mucus.
Complete answer: Stomach and intestine in mammals helps in the digestion (also requires secretion of enzymes) and absorption of the food.
So, the lining of the stomach and intestine should be made of epithelial tissue that can support the above-mentioned functions.
Let us have a look at the options given in the question-
1. Cuboidal epithelium- It consists of cube-like cells that are arranged to form a single thick layer. It is located in the secretory ducts of the small glands and kidney tubules. It is associated with secretion and absorption.
2. Columnar epithelium- It is located in the bronchi, uterine tubes, digestive tract (ciliated), urinary bladder (non-ciliated). It helps in the absorption and also secretes mucus and various enzymes that help in the digestion and easy absorption of the small biomolecules.
3. Squamous epithelium- It consists of a layer of fat cells that are arranged in a single layer. It is found in the blood, lymphatic vesicles, heart lining, and the air sacs of the lungs. It helps in the secretion of the lubricating substance, filtration. The columnar epithelium is the epithelial cells that are long and are arranged like several pillars in a row.
4. Stratified epithelium- It consists of multiple layers one above another. It is found in the trachea and most of the upper respiratory tract. It secretes mucus.
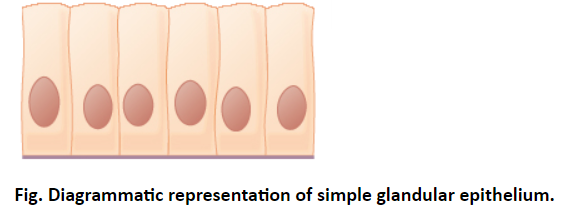
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is B. Columnar epithelium.
Note: Epithelial tissues are widely spread throughout the body. They form the outer covering of all body surfaces, line body cavities, and hollow organs, and are the important tissue in glands.
They perform functions that include protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, diffusion, and sensory reception.
Complete answer: Stomach and intestine in mammals helps in the digestion (also requires secretion of enzymes) and absorption of the food.
So, the lining of the stomach and intestine should be made of epithelial tissue that can support the above-mentioned functions.
Let us have a look at the options given in the question-
1. Cuboidal epithelium- It consists of cube-like cells that are arranged to form a single thick layer. It is located in the secretory ducts of the small glands and kidney tubules. It is associated with secretion and absorption.
2. Columnar epithelium- It is located in the bronchi, uterine tubes, digestive tract (ciliated), urinary bladder (non-ciliated). It helps in the absorption and also secretes mucus and various enzymes that help in the digestion and easy absorption of the small biomolecules.
3. Squamous epithelium- It consists of a layer of fat cells that are arranged in a single layer. It is found in the blood, lymphatic vesicles, heart lining, and the air sacs of the lungs. It helps in the secretion of the lubricating substance, filtration. The columnar epithelium is the epithelial cells that are long and are arranged like several pillars in a row.
4. Stratified epithelium- It consists of multiple layers one above another. It is found in the trachea and most of the upper respiratory tract. It secretes mucus.

Therefore, the correct answer to the question is B. Columnar epithelium.
Note: Epithelial tissues are widely spread throughout the body. They form the outer covering of all body surfaces, line body cavities, and hollow organs, and are the important tissue in glands.
They perform functions that include protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, diffusion, and sensory reception.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




