
The interval in which $y = {x^2}{e^{ - x}}$ is increasing is:
A) $( - \infty ,\infty )$
B) $( - 2,0)$
C) $(2,\infty )$
D) $(0,2)$
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: We will first just find the derivative of the function that is f’(x). Now, we know that wherever the function is increasing f’(x) > 0. We will find critical points and then see using f’(x) where it is greater than zero.
Complete step by step answer:
We have $y = {x^2}{e^{ - x}}$.
Let us say that $f(x) = {x^2}{e^{ - x}}$.
So, taking its derivative with respect to x, we will get:-
$ \Rightarrow f'(x) = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{x^2}{e^{ - x}}} \right)$ ……………(1)
Now, we know that if $f(x) = u(x).v(x)$, then $f'(x) = u'(x).v(x) + u(x).v'(x)$.
Applying this in (1), we will get:-
$ \Rightarrow f'(x) = {e^{ - x}}.\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{x^2}} \right) + {x^2}.\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{e^{ - x}}} \right)$.
Now, we will use the formula: $\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{x^n}} \right) = n{x^{n - 1}}$ and $\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{e^{ - x}}} \right) = {e^{ - x}}.\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( { - x} \right) = - {e^{ - x}}$.
So, we will get:-
$ \Rightarrow f'(x) = {e^{ - x}}.(2x) + {x^2}.\left( { - {e^{ - x}}} \right)$
We can write this as:-
$ \Rightarrow f'(x) = x{e^{ - x}}(2 - x)$.
Now, let us find the critical points by equating this derivative to zero.
So, we have:- $f'(x) = x{e^{ - x}}(2 - x) = 0$
This is only possible if either $x{e^{ - x}} = 0$ or $(2 - x) = 0$.
This implies that either $x = 0$ (Because exponential function is always greater than zero) or $x = 2$.
Thus, we have two critical points: $x = 0$ and $x = 2$.
Now, we have divided our number line in three different parts: $( - \infty ,0),(0,2),(2,\infty )$.
Now, we need to check where f’(x) > 0.
That interval will be the required answer.
We see that:
Case I: $x \in ( - \infty ,0)$
Then, $f'(x) = x{e^{ - x}}(2 - x) = ( - ve)( + ve)( + ve) = - ve$
(Because $x < 0,{e^{ - x}} > 0,(2 - x) > 0$
Case II: $x \in (0,2)$
Then, $f'(x) = x{e^{ - x}}(2 - x) = ( + ve)( + ve)( + ve) = + ve$
(Because $x > 0,{e^{ - x}} > 0,(2 - x) > 0$
Case III: $x \in (2,\infty )$
Then, $f'(x) = x{e^{ - x}}(2 - x) = ( + ve)( + ve)( - ve) = - ve$
(Because $x > 0,{e^{ - x}} > 0,(2 - x) < 0$.
Therefore, case II satisfy our needs. So, the answer is $(0,2)$. Hence, the correct option is (D).
Note:
The students must note that we have used the fact that the function is increasing, where its derivative is strictly greater than 0. Do you wonder: Why does this happen?
Let us understand it in brief. The derivative of a function represents its slope at that particular point.
So, we are basically saying that wherever the slope is greater than zero, the function will be increasing. Let us draw its graph to understand it better.
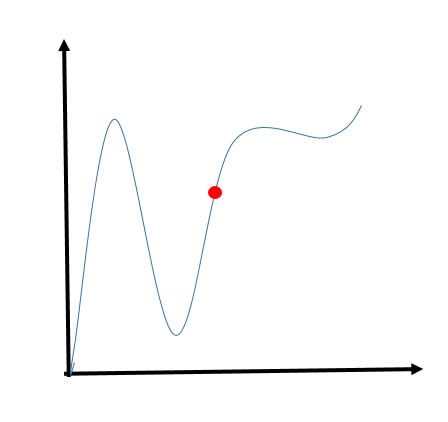
Here, the blue curve represents the arbitrary function, and the redpoint be the point where we are looking at the slope.
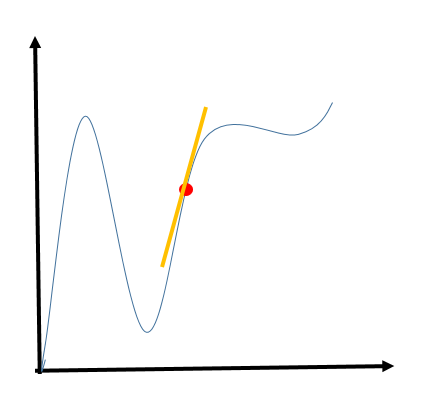
Here, the yellow line represents the slope. Here, the slope is greater than 0 and the function is increasing as well.
Complete step by step answer:
We have $y = {x^2}{e^{ - x}}$.
Let us say that $f(x) = {x^2}{e^{ - x}}$.
So, taking its derivative with respect to x, we will get:-
$ \Rightarrow f'(x) = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{x^2}{e^{ - x}}} \right)$ ……………(1)
Now, we know that if $f(x) = u(x).v(x)$, then $f'(x) = u'(x).v(x) + u(x).v'(x)$.
Applying this in (1), we will get:-
$ \Rightarrow f'(x) = {e^{ - x}}.\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{x^2}} \right) + {x^2}.\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{e^{ - x}}} \right)$.
Now, we will use the formula: $\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{x^n}} \right) = n{x^{n - 1}}$ and $\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{e^{ - x}}} \right) = {e^{ - x}}.\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( { - x} \right) = - {e^{ - x}}$.
So, we will get:-
$ \Rightarrow f'(x) = {e^{ - x}}.(2x) + {x^2}.\left( { - {e^{ - x}}} \right)$
We can write this as:-
$ \Rightarrow f'(x) = x{e^{ - x}}(2 - x)$.
Now, let us find the critical points by equating this derivative to zero.
So, we have:- $f'(x) = x{e^{ - x}}(2 - x) = 0$
This is only possible if either $x{e^{ - x}} = 0$ or $(2 - x) = 0$.
This implies that either $x = 0$ (Because exponential function is always greater than zero) or $x = 2$.
Thus, we have two critical points: $x = 0$ and $x = 2$.
Now, we have divided our number line in three different parts: $( - \infty ,0),(0,2),(2,\infty )$.
Now, we need to check where f’(x) > 0.
That interval will be the required answer.
We see that:
Case I: $x \in ( - \infty ,0)$
Then, $f'(x) = x{e^{ - x}}(2 - x) = ( - ve)( + ve)( + ve) = - ve$
(Because $x < 0,{e^{ - x}} > 0,(2 - x) > 0$
Case II: $x \in (0,2)$
Then, $f'(x) = x{e^{ - x}}(2 - x) = ( + ve)( + ve)( + ve) = + ve$
(Because $x > 0,{e^{ - x}} > 0,(2 - x) > 0$
Case III: $x \in (2,\infty )$
Then, $f'(x) = x{e^{ - x}}(2 - x) = ( + ve)( + ve)( - ve) = - ve$
(Because $x > 0,{e^{ - x}} > 0,(2 - x) < 0$.
Therefore, case II satisfy our needs. So, the answer is $(0,2)$. Hence, the correct option is (D).
Note:
The students must note that we have used the fact that the function is increasing, where its derivative is strictly greater than 0. Do you wonder: Why does this happen?
Let us understand it in brief. The derivative of a function represents its slope at that particular point.
So, we are basically saying that wherever the slope is greater than zero, the function will be increasing. Let us draw its graph to understand it better.

Here, the blue curve represents the arbitrary function, and the redpoint be the point where we are looking at the slope.

Here, the yellow line represents the slope. Here, the slope is greater than 0 and the function is increasing as well.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




