
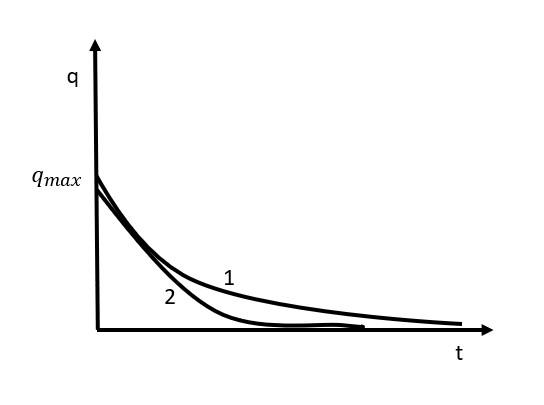
The instantaneous charge on a capacitor in two discharging RC circuits is plotted with respect to time in figure. Choose the correct statement (s) (where $ E_{1}$ and $E_{2}$ are emfs of two DC sources in two different charging circuits and capacitors are fully charged).
a) $ R_{1} C_{1} \gt R_{2} C_{2}$
b) $\dfrac{ R_{1} }{ R_{2} } \lt \dfrac{ C_{2}}{ C_{1}}$
c) $R_{1} \gt R_{2} $ if $ E_{1} = E_{2} $
d) $C_{2} \gt C_{1} $ if $ E_{1} = E_{2} $

Answer
531.6k+ views
Hint: Capacitor is discharging means the capacitor is giving up the charge that is stored in it. Hence, the capacitor's current exponentially reaches zero from its initial value, and the voltage of the capacitor goes exponentially to zero from its initial value. The time constant for RC circuit is -$\tau =RC$. During discharging, current will flow opposite to that of charging current i.e., from a negative terminal to positive terminal of the battery.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Both curves represent discharging of a capacitor.
If we see the graph, then the curve $1$ is steeper (approaching a straight line).
So, the slope of curve $1$ is more than curve$2$. Therefore, the time constant for $1$ is more than the curve $2$.
Time constant for RC circuit is-
$\tau =RC$.
It is known from the graph –
$\tau_{1} \gt \tau_{2}$
$\implies R_{1} C_{1} \gt R_{2} C_{2}$
$\implies \dfrac{ R_{1} }{ R_{2} } \gt \dfrac{ C_{2}}{ C_{1}}$
Time constant for curve 1 is more than the curve 2 .
$R_{1} \gt R_{2}$ and $C_{1} \gt C_{2}$
So, option (a, c) is correct.
Additional Information: - During the discharging of a capacitor, large current flows immediately, the voltage across the capacitor plates decreases as the charges move away from the plate. The current drops as less charges are repelling each other during the discharging.
Note: A charge can be charged gradually to the voltage and then discharged immediately to give the energy needed. The discharging current drops from an initial value, the potential difference over the capacitor plates lowers to zero when the capacitor is fully discharged.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Both curves represent discharging of a capacitor.
If we see the graph, then the curve $1$ is steeper (approaching a straight line).
So, the slope of curve $1$ is more than curve$2$. Therefore, the time constant for $1$ is more than the curve $2$.
Time constant for RC circuit is-
$\tau =RC$.
It is known from the graph –
$\tau_{1} \gt \tau_{2}$
$\implies R_{1} C_{1} \gt R_{2} C_{2}$
$\implies \dfrac{ R_{1} }{ R_{2} } \gt \dfrac{ C_{2}}{ C_{1}}$
Time constant for curve 1 is more than the curve 2 .
$R_{1} \gt R_{2}$ and $C_{1} \gt C_{2}$
So, option (a, c) is correct.
Additional Information: - During the discharging of a capacitor, large current flows immediately, the voltage across the capacitor plates decreases as the charges move away from the plate. The current drops as less charges are repelling each other during the discharging.
Note: A charge can be charged gradually to the voltage and then discharged immediately to give the energy needed. The discharging current drops from an initial value, the potential difference over the capacitor plates lowers to zero when the capacitor is fully discharged.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




