
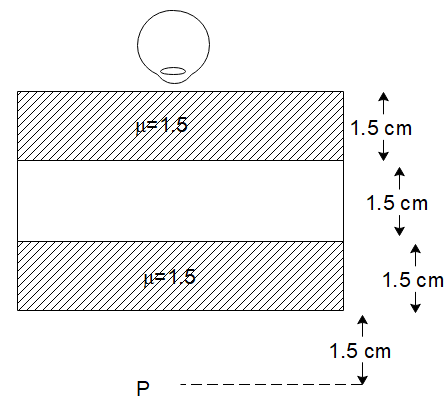
The image of point P when viewed from the top of the slabs will be:
A) $ 2.0 $ cm below P
B) $ 1.5 $ cm above P
C) $ 2.0 $ cm above P
D) 1cm above P

Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: Whenever rays of light will pass from the slabs with a different refractive index than that of air, the image as viewed by the eye will be shifted. We will calculate this shift for the configuration given in the image.
Formula used In this solution, we will use the following formula
$ d = t\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{\mu }} \right) $ where $ t $ is the width of the slabs and $ \mu $ is the refractive index of the material of the slab
Complete step by step answer:
In the image, we can see that the object is located at point P. If there were nothing in between the eye and the slab, we would observe the object at point P itself. But when slabs with different refractive index are inserted between the eye and the object, the image will be shifted.
This magnitude of this shift is given as $ d = t\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{\mu }} \right) $ . This shift will always be in the direction of the observer that is, towards the eye or above P.
Since there are two slabs of different refractive index, the net shift would be calculated as
$ d = 2 \times 1.5\left( {1 - \dfrac{2}{3}} \right) $
$ \Rightarrow d = 1\,cm $
Hence the image would be shifted 1 cm above the point P when observed by the eye which corresponds to option (D).
Note:
When calculating the shift of the image, we should only consider the slabs with a refractive index different than that in which the observer is. So, as the eye is in the air, we should only consider the shift of the image due to slabs of refractive index different from that of air.
Formula used In this solution, we will use the following formula
$ d = t\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{\mu }} \right) $ where $ t $ is the width of the slabs and $ \mu $ is the refractive index of the material of the slab
Complete step by step answer:
In the image, we can see that the object is located at point P. If there were nothing in between the eye and the slab, we would observe the object at point P itself. But when slabs with different refractive index are inserted between the eye and the object, the image will be shifted.
This magnitude of this shift is given as $ d = t\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{\mu }} \right) $ . This shift will always be in the direction of the observer that is, towards the eye or above P.
Since there are two slabs of different refractive index, the net shift would be calculated as
$ d = 2 \times 1.5\left( {1 - \dfrac{2}{3}} \right) $
$ \Rightarrow d = 1\,cm $
Hence the image would be shifted 1 cm above the point P when observed by the eye which corresponds to option (D).
Note:
When calculating the shift of the image, we should only consider the slabs with a refractive index different than that in which the observer is. So, as the eye is in the air, we should only consider the shift of the image due to slabs of refractive index different from that of air.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which country did Danny Casey play for class 12 english CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




