
The helical structure of protein is stabilized by
A.Peptide bond
B.Dipeptide bond
C.Hydrogen bond
D.Vander Waal bond
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint:
The helical structure of a protein is formed in proteins belonging to the secondary protein group. There are two types of structure ,that is $\alpha $- helix and $\beta $- pleated structures. Folded proteins have to be stabilised by bonds that can connect consecutive turns of the helix together so that it is stabilised and will not unravel.
Complete step by step answer:
As mentioned, the secondary proteins are divided into two types: the $\alpha $- helix and $\beta $- pleated structures. The $\alpha $- helical structure is more common and is usually found in globular proteins found in the body. This is the most abundant form of the secondary structure.
A protein in general is made of amino acids. They are linked together by a peptide bond. The formation of peptide bonds between amino acids releases water. When many amino acids are linked together, they are called polypeptides or proteins. Proteins usually refer to the polypeptide chain that is very long.
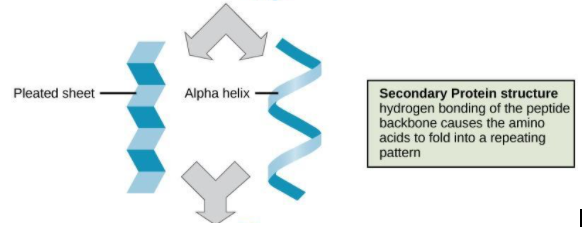
Proteins take different configurations to form different groups of proteins, that is, primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary proteins. Except for the primary proteins, the others undergo folding as shown in the figure above. Proteins are folded in order to fit into the limited spaces that are provided by the body of an animal or plant.
But folding in proteins is unstable and they will unravel if they are not held together in some way. In case of $\alpha $- helical structures, the helix is stabilized by hydrogen bonds that are present between the carbonyl group and hydrogen of amine group.
Therefore, the answer to the above question is option C that is, hydrogen bond.
Note: The helical structure of $\alpha $- helix is stabilized by hydrogen bonds. This is also seen in the other groups of proteins such as tertiary and quaternary groups.
The formation of peptide bonds is also known as condensation addition because it releases water on formation.
Secondary proteins can undergo denaturation which leads to the breaking of these hydrogen bonds and it forms a primary protein.
The helical structure of a protein is formed in proteins belonging to the secondary protein group. There are two types of structure ,that is $\alpha $- helix and $\beta $- pleated structures. Folded proteins have to be stabilised by bonds that can connect consecutive turns of the helix together so that it is stabilised and will not unravel.
Complete step by step answer:
As mentioned, the secondary proteins are divided into two types: the $\alpha $- helix and $\beta $- pleated structures. The $\alpha $- helical structure is more common and is usually found in globular proteins found in the body. This is the most abundant form of the secondary structure.
A protein in general is made of amino acids. They are linked together by a peptide bond. The formation of peptide bonds between amino acids releases water. When many amino acids are linked together, they are called polypeptides or proteins. Proteins usually refer to the polypeptide chain that is very long.

Proteins take different configurations to form different groups of proteins, that is, primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary proteins. Except for the primary proteins, the others undergo folding as shown in the figure above. Proteins are folded in order to fit into the limited spaces that are provided by the body of an animal or plant.
But folding in proteins is unstable and they will unravel if they are not held together in some way. In case of $\alpha $- helical structures, the helix is stabilized by hydrogen bonds that are present between the carbonyl group and hydrogen of amine group.
Therefore, the answer to the above question is option C that is, hydrogen bond.
Note: The helical structure of $\alpha $- helix is stabilized by hydrogen bonds. This is also seen in the other groups of proteins such as tertiary and quaternary groups.
The formation of peptide bonds is also known as condensation addition because it releases water on formation.
Secondary proteins can undergo denaturation which leads to the breaking of these hydrogen bonds and it forms a primary protein.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




