
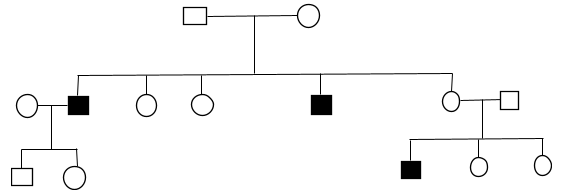
The given pedigree chart indicate
A) Autosomal dominant
B) Autosomal recessive
C) X-linked dominant
D) X-linked recessive
E) Insufficient information

Answer
545.1k+ views
Hint: The passing on of traits from parents to offspring is known as Inheritance. All organisms acquire genetic information from their parents. Gregor John Mendel is the Father of genetics and he described the principles of inheritance.
Complete answer :
Mendel gave principles of inheritance that explained how the chromosomes segregated before being transferred into the daughter cells. He gave laws of inheritance on the basis of which genetic disorders were explained. These disorders were divided into Mendelian disorders and chromosomal disorders. Alteration or mutation in a single gene produces Mendelian disorders and abnormalities in the structure, number or arrangement of chromosomes yield chromosomal disorders.
Mendelian disorders can be tracked with the help of family tree or pedigree analysis. Most prevalent Mendelian disorders are colour blindness, haemophilia, phenylketonuria, sickle cell anaemia and thalassemia. These disorders can be dominant or recessive and this can be studied with the help of pedigree analysis. Traits can also be linked with sex chromosomes as in haemophilia where X linked trait which is recessive transfers itself from a carrier female to male progeny.
The given pedigree analysis indicates X linked recessive inheritance in which a mutation is observed in the X chromosome which causes the phenotype to be expressed in the males and the females act only as carriers in heterozygous conditions. In homozygous conditions both male and female express the phenotype. X linked inheritance explains that the gene causing disease or having a mutation is located on the X chromosome. A unique pattern is followed in 3 ways by X linked recessive trait –
Father having mutation on an X chromosome is affected by the disorder but he cannot pass on the defective X chromosome to his son as he gives only a Y chromosome to his son. Males having X linked recessive traits get it from their mother.
Males are more affected by X linked recessive inheritance as compared to females because they need only one mutated X chromosome to express the mutation whereas a female needs both X chromosomes to be mutated in order to express the mutation.
X linked recessive trait shows skip in generations as in an affected grandfather will not have an affected son but an affected grandson. All daughters of an affected man will either be carriers or affected themselves with the X linked recessive disorder.
So the answer for this question is option (D).
This pedigree indicates X linked recessive inheritance as among the parent of first generation the mother can be a carrier so in the next generation 2 sons are affected and the daughters are carriers again and in the next generation one son is affected as his other was a carrier of mutated X chromosome but one son is not affected though he has an affected father cause his father cannot transfer the mutated X chromosome to him.
Note
Haemophilia is a blood clotting disorder which occurs due to mutation in Factor VIII gene which leads to its deficiency. It is known as Royal disease as it is found in the descendants of Queen Victoria. It is divided into Haemophilia A and Haemophilia B (Christmas disease).
Complete answer :
Mendel gave principles of inheritance that explained how the chromosomes segregated before being transferred into the daughter cells. He gave laws of inheritance on the basis of which genetic disorders were explained. These disorders were divided into Mendelian disorders and chromosomal disorders. Alteration or mutation in a single gene produces Mendelian disorders and abnormalities in the structure, number or arrangement of chromosomes yield chromosomal disorders.
Mendelian disorders can be tracked with the help of family tree or pedigree analysis. Most prevalent Mendelian disorders are colour blindness, haemophilia, phenylketonuria, sickle cell anaemia and thalassemia. These disorders can be dominant or recessive and this can be studied with the help of pedigree analysis. Traits can also be linked with sex chromosomes as in haemophilia where X linked trait which is recessive transfers itself from a carrier female to male progeny.
The given pedigree analysis indicates X linked recessive inheritance in which a mutation is observed in the X chromosome which causes the phenotype to be expressed in the males and the females act only as carriers in heterozygous conditions. In homozygous conditions both male and female express the phenotype. X linked inheritance explains that the gene causing disease or having a mutation is located on the X chromosome. A unique pattern is followed in 3 ways by X linked recessive trait –
Father having mutation on an X chromosome is affected by the disorder but he cannot pass on the defective X chromosome to his son as he gives only a Y chromosome to his son. Males having X linked recessive traits get it from their mother.
Males are more affected by X linked recessive inheritance as compared to females because they need only one mutated X chromosome to express the mutation whereas a female needs both X chromosomes to be mutated in order to express the mutation.
X linked recessive trait shows skip in generations as in an affected grandfather will not have an affected son but an affected grandson. All daughters of an affected man will either be carriers or affected themselves with the X linked recessive disorder.
So the answer for this question is option (D).
This pedigree indicates X linked recessive inheritance as among the parent of first generation the mother can be a carrier so in the next generation 2 sons are affected and the daughters are carriers again and in the next generation one son is affected as his other was a carrier of mutated X chromosome but one son is not affected though he has an affected father cause his father cannot transfer the mutated X chromosome to him.
Note
Haemophilia is a blood clotting disorder which occurs due to mutation in Factor VIII gene which leads to its deficiency. It is known as Royal disease as it is found in the descendants of Queen Victoria. It is divided into Haemophilia A and Haemophilia B (Christmas disease).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




