
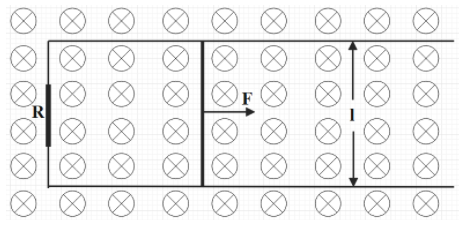
The given figure shows a wire sliding on two parallel conducting rails placed at a separation ‘l’. A magnetic field B exists in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails. What is the force necessary to keep the wire moving at a Constant velocity v will be:
$\begin{align}
& A)\dfrac{{{B}^{2}}{{l}^{2}}v}{R} \\
& B)\dfrac{2{{B}^{2}}{{l}^{2}}v}{R} \\
& C)\dfrac{{{B}^{2}}{{l}^{2}}v}{2R} \\
& D)\text{None of these} \\
\end{align}$

Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we will use the expression for magnetic Lorentz force. Also, we will need ohm’s law and faraday's law for induced emf to find the current induced in the circuit as there is change in magnetic field, which results in creating induced emf in a closed loop. Then, by substituting the expression for current in the Lorentz force equation, we can find the force.
Formula used:
$\begin{align}
& F=Bil \\
& \text{emf}=Blv \\
& i=\dfrac{\text{emf}}{R} \\
\end{align}$
Complete step by step answer:
The force experienced by the wire while moving on the parallel conducting wire through the magnetic field is given by the equation,
\[\begin{align}
& F=i\left( \overrightarrow{B}\times \overrightarrow{l} \right) \\
& F=Bil \\
\end{align}\]
Where, $i$ is the induced current flowing through the loop.
\[\overrightarrow{B}\] is the magnetic field.
And \[\overrightarrow{l}\]is the length of the wire.
Now, the current developed inside the loop can be found using ohm’s law.
$\Rightarrow i=\dfrac{emf}{R}$
Where, emf is the induced emf due to change in magnetic flex as the wire is moving.
And R is the resistance of the loop.
Here, the induced emf is given by Faraday's law for metallic wire as,
$\begin{align}
& emf=\dfrac{d\phi }{dt} \\
& \Rightarrow emf=\dfrac{d\left( Blx \right)}{dt}\text{ where, x is the distance moved by the wire} \\
& \Rightarrow emf=Bl\dfrac{d\left( x \right)}{dt} \\
& \therefore emf=Blv \\
\end{align}$
Where, v is the velocity of the wire.
\[\overrightarrow{B}\] is the magnetic field.
And \[\overrightarrow{l}\]is the length of the wire.
Now, substituting this value for emf in ohm’s law, we will get the current induced in the loop.
$\begin{align}
& i=\dfrac{emf}{R} \\
& \Rightarrow i=\dfrac{Blv}{R} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we can find the force necessary to keep the wire moving with a constant velocity by substituting this current in the expression for Lorentz force.
$\begin{align}
& F=Bil \\
& \Rightarrow F=B\left( \dfrac{Blv}{R} \right)l\text{ }\left( \because i=\dfrac{Blv}{R} \right) \\
& \therefore F=\dfrac{{{B}^{2}}{{l}^{2}}v}{R} \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the force needed is found to be $\dfrac{{{B}^{2}}{{l}^{2}}v}{R}$.
So, option A is correct.
Note:
While solving these types of questions, the key idea is to link the formulas we have with one another and deduce the correct expression. So, we must be having a clear memory of formulas and theories of basic laws and equations to solve. Also, these types of questions may come as an open circuit instead of closed loop as this question. Then no current will be flowing through the circuit and force becomes zero.
Formula used:
$\begin{align}
& F=Bil \\
& \text{emf}=Blv \\
& i=\dfrac{\text{emf}}{R} \\
\end{align}$
Complete step by step answer:
The force experienced by the wire while moving on the parallel conducting wire through the magnetic field is given by the equation,
\[\begin{align}
& F=i\left( \overrightarrow{B}\times \overrightarrow{l} \right) \\
& F=Bil \\
\end{align}\]
Where, $i$ is the induced current flowing through the loop.
\[\overrightarrow{B}\] is the magnetic field.
And \[\overrightarrow{l}\]is the length of the wire.
Now, the current developed inside the loop can be found using ohm’s law.
$\Rightarrow i=\dfrac{emf}{R}$
Where, emf is the induced emf due to change in magnetic flex as the wire is moving.
And R is the resistance of the loop.
Here, the induced emf is given by Faraday's law for metallic wire as,
$\begin{align}
& emf=\dfrac{d\phi }{dt} \\
& \Rightarrow emf=\dfrac{d\left( Blx \right)}{dt}\text{ where, x is the distance moved by the wire} \\
& \Rightarrow emf=Bl\dfrac{d\left( x \right)}{dt} \\
& \therefore emf=Blv \\
\end{align}$
Where, v is the velocity of the wire.
\[\overrightarrow{B}\] is the magnetic field.
And \[\overrightarrow{l}\]is the length of the wire.
Now, substituting this value for emf in ohm’s law, we will get the current induced in the loop.
$\begin{align}
& i=\dfrac{emf}{R} \\
& \Rightarrow i=\dfrac{Blv}{R} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we can find the force necessary to keep the wire moving with a constant velocity by substituting this current in the expression for Lorentz force.
$\begin{align}
& F=Bil \\
& \Rightarrow F=B\left( \dfrac{Blv}{R} \right)l\text{ }\left( \because i=\dfrac{Blv}{R} \right) \\
& \therefore F=\dfrac{{{B}^{2}}{{l}^{2}}v}{R} \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the force needed is found to be $\dfrac{{{B}^{2}}{{l}^{2}}v}{R}$.
So, option A is correct.
Note:
While solving these types of questions, the key idea is to link the formulas we have with one another and deduce the correct expression. So, we must be having a clear memory of formulas and theories of basic laws and equations to solve. Also, these types of questions may come as an open circuit instead of closed loop as this question. Then no current will be flowing through the circuit and force becomes zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




