
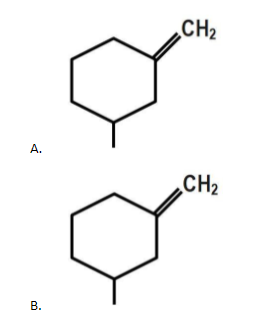
The geometrical isomerism is shown by:



Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: We know that isomerism is one of the phenomena which generally explains that more than one compound will have the same chemical formula but differ isomerism is one of the phenomena which generally explains that more than one compound will have the same chemical formula but different from the same chemical formula usually termed as isomers.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we all know, the chemical compound which has cis-trans structures are usually termed as geometrical isomerism. In organic chemistry, it is also named as configurational isomerism. The geometrical isomerism generally shows by unsaturated organic compounds or by the ring compounds.
When the rotation of the carbon bond is restricted only by the condition, and it can be categorized as cis configuration.
The geometrical isomerism shows the change in the spatial arrangement of the ligand. Geometrical isomers are called either cis-trans isomers or E-Z isomers. In cis or Z isomer, the two groups attached to adjacent carbons are on the same side, whereas in trans or E isomer, two groups attached to adjacent carbons are on opposite sides.
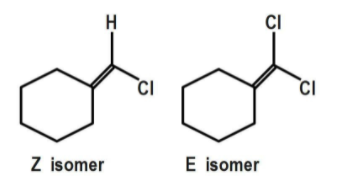
The geometrical isomerism is shown by compound D as each doubly bonded carbon atom carries two different atoms/ groups of atoms. Compound C does not show geometrical isomerism because it has a plane of symmetry which is absent in compound D.
Thus the correct answer is option ‘D’.
Note: Remember that it’s a bit confusing as both of the structures are the same but they differ in n position of attached ligands in space leading to geometrical isomerism. The isomerism’s in categories are several types. They are *Structural isomerism *Chain isomerism *Geometrical isomerism *Optical isomerism *Position isomerism *Functional isomerism *Stereoisomerism.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we all know, the chemical compound which has cis-trans structures are usually termed as geometrical isomerism. In organic chemistry, it is also named as configurational isomerism. The geometrical isomerism generally shows by unsaturated organic compounds or by the ring compounds.
When the rotation of the carbon bond is restricted only by the condition, and it can be categorized as cis configuration.
The geometrical isomerism shows the change in the spatial arrangement of the ligand. Geometrical isomers are called either cis-trans isomers or E-Z isomers. In cis or Z isomer, the two groups attached to adjacent carbons are on the same side, whereas in trans or E isomer, two groups attached to adjacent carbons are on opposite sides.

The geometrical isomerism is shown by compound D as each doubly bonded carbon atom carries two different atoms/ groups of atoms. Compound C does not show geometrical isomerism because it has a plane of symmetry which is absent in compound D.
Thus the correct answer is option ‘D’.
Note: Remember that it’s a bit confusing as both of the structures are the same but they differ in n position of attached ligands in space leading to geometrical isomerism. The isomerism’s in categories are several types. They are *Structural isomerism *Chain isomerism *Geometrical isomerism *Optical isomerism *Position isomerism *Functional isomerism *Stereoisomerism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




