
The gene for blue eyes (b) is recessive to the gene for brown eyes (B). The following figure is given: what is the % of individuals with brown eyes and blue eyes respectively?
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: The genetic crossing is the crossing over of two individuals to produce offspring. There are two types of crosses: monohybrid cross and dihybrid cross.
Complete answer:
George Mendle was the first mathematician to determine an unknown genotype by crossing over. Crossing over is the crossing over of genetic material among two individuals.
Types of traits in a cross: dominant trait and recessive trait.
Dominant trait: The gene which decides the appearance of an organism in presence of another trait is called a dominant trait.
Recessive trait: It is a weak trait that has no effect on organism phenotype in heterozygous cross.
Type of individuals: heterozygous (having two different gene as Tt/Bb) and homozygous (both gene are same as TT/tt/BB/bb)
According to the question BB is brown eye and bb is blue. B is dominant over b. so in presence of B (brown gene) b(blue gene wont express).
F1 generation has bb (blue) Bb (Brown) Bb (brown) bb (blue) so Brown eyed $50\%$ and Blue eyed $50\%$.
Here is a diagrammatic representation of the cross
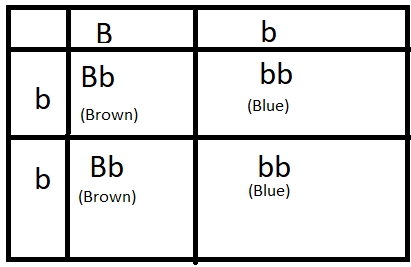
Note:
Monohybrid cross: crossing of two individuals that involve a single trait example height, colour, size etc. The mendelian ratio for monohybrid cross for F2 generation is 3:1.
Dihybrid cross: crossing over of two individuals that involves two traits for example height and colour of the flower. The mendelian ratio for dihybrid cross for F2 generation is 9:3:3:1.
Complete answer:
George Mendle was the first mathematician to determine an unknown genotype by crossing over. Crossing over is the crossing over of genetic material among two individuals.
Types of traits in a cross: dominant trait and recessive trait.
Dominant trait: The gene which decides the appearance of an organism in presence of another trait is called a dominant trait.
Recessive trait: It is a weak trait that has no effect on organism phenotype in heterozygous cross.
Type of individuals: heterozygous (having two different gene as Tt/Bb) and homozygous (both gene are same as TT/tt/BB/bb)
According to the question BB is brown eye and bb is blue. B is dominant over b. so in presence of B (brown gene) b(blue gene wont express).
F1 generation has bb (blue) Bb (Brown) Bb (brown) bb (blue) so Brown eyed $50\%$ and Blue eyed $50\%$.
Here is a diagrammatic representation of the cross

Note:
Monohybrid cross: crossing of two individuals that involve a single trait example height, colour, size etc. The mendelian ratio for monohybrid cross for F2 generation is 3:1.
Dihybrid cross: crossing over of two individuals that involves two traits for example height and colour of the flower. The mendelian ratio for dihybrid cross for F2 generation is 9:3:3:1.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




