
The gap between the plates of a plate capacitor if filled with an isotropic insulator whose di-electric constant varies in the direction perpendicular to the plates according to the law $ K={{K}_{1}}\left[ 1+\sin \dfrac{\pi }{4}X \right] $ , where d is the separation, between the plates and $ {{K}_{1}} $ is a constant. The area of the plates is S. Determine the capacitance of the capacitor.
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint
We should know that capacitance is the ratio of the change in electric charge of a system to the corresponding change in its electrical potential. There are two closely related notions of the capacitance, which are self-capacitance and mutual capacitance. Any object that can be electrically charged always exhibits the property of self-capacitance. Based on this concept we have to solve the question.
Complete step by step answer
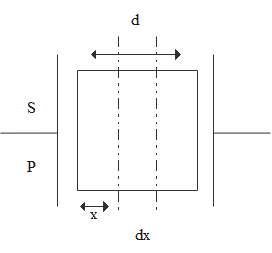
Let us consider a small element dx width at a distance x from P and let us calculate the small capacitor:
Here is the diagram that is given below:
The main formula is given as:
$ (dc)=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}K(S)}{dx} $
So, now we have to evaluate the expression as:
$ dc=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{K}_{1}}[1+\sin \dfrac{\pi }{d}x]}{dx} $
Now we have to integrate the above expression:
$ \int{\dfrac{1}{dc}}=\dfrac{1}{c_{eff}}=\int{_{0}^{d}}\dfrac{dx}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{K}_{1}}[1+\sin \dfrac{\pi }{d}x](S)} $
So, after the evaluation we get that:
$ =\dfrac{1}{S{{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{K}_{1}}}\int{_{0}^{d}}\dfrac{dx}{1+\sin \dfrac{\pi }{d}x}\times \dfrac{1-\sin \dfrac{\pi }{d}x}{1-\sin \dfrac{\pi }{d}x} $
$ =\dfrac{1}{S{{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{K}_{1}}}\int{_{0}^{d}}\dfrac{1-\sin \dfrac{\pi }{d}\times (dx)}{1-{{\sin }^{2}}\dfrac{\pi }{d}x} $
$ =\dfrac{2d}{S{{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{K}_{1}}\pi }=\dfrac{1}{c_{eff}} $
Now on the further evaluation we get:
$ =\dfrac{1}{S{{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{K}_{1}}}[\int{_{0}^{d}{{\sec }^{2}}\dfrac{\pi }{d}\times dx-\int{_{0}^{d}\sec \times \dfrac{\pi }{d}}}\tan \dfrac{\pi }{d}\times dx] $
$ =\dfrac{1}{S{{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{K}_{1}}}\left[ \left[ \dfrac{d}{\pi }\tan \dfrac{\pi }{d}x \right]_{0}^{d}-\left[ \dfrac{d}{\pi }\sec \dfrac{\pi }{d}x \right]_{0}^{d} \right] $
$ =\dfrac{2d}{S{{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{K}_{1}}\pi }=\dfrac{1}{c_{eff}} $
So, we get that:
$ c_{eff}=\dfrac{S{{\varepsilon }_{0}}\pi {{K}_{1}}}{2d} $
Hence, we can say that the capacitance of the capacitor is given as: $ c_{eff}=\dfrac{S{{\varepsilon }_{0}}\pi {{K}_{1}}}{2d} $ .
Note
We should know that self-capacitance is defined as the coupling of one plate capacitor to the virtual ground. This change in the self- capacitance can be determined by us as the distance to the finger. Self-capacitance is often used in the button, slider or in some cases we can use the wheel sensors which are also known as BSW.
Now let us define the concept of mutual capacitance. When we say mutual capacitance, which is denoted by C we mean that between any two conductors, let Q be the charge that is stored on each of the plates, V be the per unit voltage difference between the plates.
The main classical calculation of the capacitance is given by us in the form of Gauss’s and Poisson’s equation for any given system.
We should know that capacitance is the ratio of the change in electric charge of a system to the corresponding change in its electrical potential. There are two closely related notions of the capacitance, which are self-capacitance and mutual capacitance. Any object that can be electrically charged always exhibits the property of self-capacitance. Based on this concept we have to solve the question.
Complete step by step answer
Let us consider a small element dx width at a distance x from P and let us calculate the small capacitor:
Here is the diagram that is given below:

The main formula is given as:
$ (dc)=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}K(S)}{dx} $
So, now we have to evaluate the expression as:
$ dc=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{K}_{1}}[1+\sin \dfrac{\pi }{d}x]}{dx} $
Now we have to integrate the above expression:
$ \int{\dfrac{1}{dc}}=\dfrac{1}{c_{eff}}=\int{_{0}^{d}}\dfrac{dx}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{K}_{1}}[1+\sin \dfrac{\pi }{d}x](S)} $
So, after the evaluation we get that:
$ =\dfrac{1}{S{{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{K}_{1}}}\int{_{0}^{d}}\dfrac{dx}{1+\sin \dfrac{\pi }{d}x}\times \dfrac{1-\sin \dfrac{\pi }{d}x}{1-\sin \dfrac{\pi }{d}x} $
$ =\dfrac{1}{S{{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{K}_{1}}}\int{_{0}^{d}}\dfrac{1-\sin \dfrac{\pi }{d}\times (dx)}{1-{{\sin }^{2}}\dfrac{\pi }{d}x} $
$ =\dfrac{2d}{S{{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{K}_{1}}\pi }=\dfrac{1}{c_{eff}} $
Now on the further evaluation we get:
$ =\dfrac{1}{S{{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{K}_{1}}}[\int{_{0}^{d}{{\sec }^{2}}\dfrac{\pi }{d}\times dx-\int{_{0}^{d}\sec \times \dfrac{\pi }{d}}}\tan \dfrac{\pi }{d}\times dx] $
$ =\dfrac{1}{S{{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{K}_{1}}}\left[ \left[ \dfrac{d}{\pi }\tan \dfrac{\pi }{d}x \right]_{0}^{d}-\left[ \dfrac{d}{\pi }\sec \dfrac{\pi }{d}x \right]_{0}^{d} \right] $
$ =\dfrac{2d}{S{{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{K}_{1}}\pi }=\dfrac{1}{c_{eff}} $
So, we get that:
$ c_{eff}=\dfrac{S{{\varepsilon }_{0}}\pi {{K}_{1}}}{2d} $
Hence, we can say that the capacitance of the capacitor is given as: $ c_{eff}=\dfrac{S{{\varepsilon }_{0}}\pi {{K}_{1}}}{2d} $ .
Note
We should know that self-capacitance is defined as the coupling of one plate capacitor to the virtual ground. This change in the self- capacitance can be determined by us as the distance to the finger. Self-capacitance is often used in the button, slider or in some cases we can use the wheel sensors which are also known as BSW.
Now let us define the concept of mutual capacitance. When we say mutual capacitance, which is denoted by C we mean that between any two conductors, let Q be the charge that is stored on each of the plates, V be the per unit voltage difference between the plates.
The main classical calculation of the capacitance is given by us in the form of Gauss’s and Poisson’s equation for any given system.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




