
The frequency of direct current (DC) is:
$A)0Hz$
$B)25Hz$
$C)75Hz$
$D)100Hz$
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: Direct current (DC) is the flow of electric charge in one direction. Frequency of current refers to the number of times the direction of flow of electric charge, gets reversed, in one second. A direct current can be converted to alternating current and vice versa.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that current is the flow of electric charge. Current is mainly differentiated into AC current as well as DC current, on the basis of direction of flow of electric charge. A direct current (DC) source produces a constant current, and thus, a constant voltage whereas an alternating current (AC) source produces an alternating current, and thus, an alternating voltage. The most common examples of DC current sources are batteries and torchlights.
DC current refers to the unidirectional flow of electric charge. In a battery, electrons move from negative region to positive region, to produce DC current from positive region to negative region. If alternating current (AC) is flowing through a circuit, the direction of current gets reversed at definite intervals. But if direct current (DC) is flowing through a circuit, the direction of current flow remains the same, in a single direction.
Frequency of alternating current (AC) refers to the number of times, the current reverses its direction, in one second. It is said that the frequency of alternating current is $60Hz$, if the current reverses its direction $60$ times, in one second. Frequency of direct current (DC) is zero because the flow of current is unidirectional here. There is no scope for a reverse in direction and the frequency of direct current (DC) always remains zero. Additionally, the magnitude of current produced from a DC current source is always constant whereas that produced from an AC current source keeps on alternating. Thus, a DC source produces a constant voltage while an AC source produces an alternating voltage as shown in the following figures.
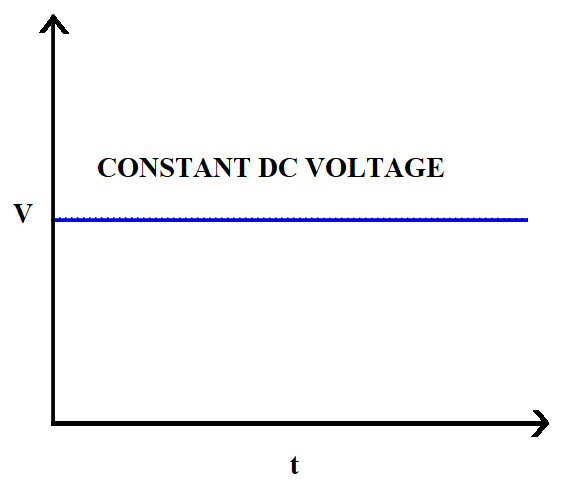
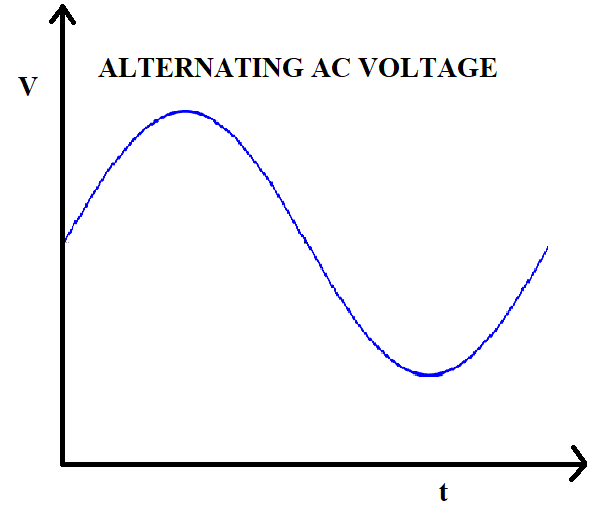
Therefore, the correct answer is option $A$.
Additional information:
An AC current can be converted to a DC current with the help of a rectifier. At the same time, a DC current can be converted to an AC current with the help of an inverter.
Note:
Students need to understand the type of current used in daily life situations. For example, as already mentioned, a battery generates DC current. Our mobile phones and chargers too, use DC current. So do electric vehicles and telecommunication networks. Another important application of DC is high voltage direct current (HVDC) power transmission system, in which DC is used for bulk transmission of power. This method of using HVDC transmission for long distance transmission is cost efficient and suffers less energy loss.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that current is the flow of electric charge. Current is mainly differentiated into AC current as well as DC current, on the basis of direction of flow of electric charge. A direct current (DC) source produces a constant current, and thus, a constant voltage whereas an alternating current (AC) source produces an alternating current, and thus, an alternating voltage. The most common examples of DC current sources are batteries and torchlights.
DC current refers to the unidirectional flow of electric charge. In a battery, electrons move from negative region to positive region, to produce DC current from positive region to negative region. If alternating current (AC) is flowing through a circuit, the direction of current gets reversed at definite intervals. But if direct current (DC) is flowing through a circuit, the direction of current flow remains the same, in a single direction.
Frequency of alternating current (AC) refers to the number of times, the current reverses its direction, in one second. It is said that the frequency of alternating current is $60Hz$, if the current reverses its direction $60$ times, in one second. Frequency of direct current (DC) is zero because the flow of current is unidirectional here. There is no scope for a reverse in direction and the frequency of direct current (DC) always remains zero. Additionally, the magnitude of current produced from a DC current source is always constant whereas that produced from an AC current source keeps on alternating. Thus, a DC source produces a constant voltage while an AC source produces an alternating voltage as shown in the following figures.


Therefore, the correct answer is option $A$.
Additional information:
An AC current can be converted to a DC current with the help of a rectifier. At the same time, a DC current can be converted to an AC current with the help of an inverter.
Note:
Students need to understand the type of current used in daily life situations. For example, as already mentioned, a battery generates DC current. Our mobile phones and chargers too, use DC current. So do electric vehicles and telecommunication networks. Another important application of DC is high voltage direct current (HVDC) power transmission system, in which DC is used for bulk transmission of power. This method of using HVDC transmission for long distance transmission is cost efficient and suffers less energy loss.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




