
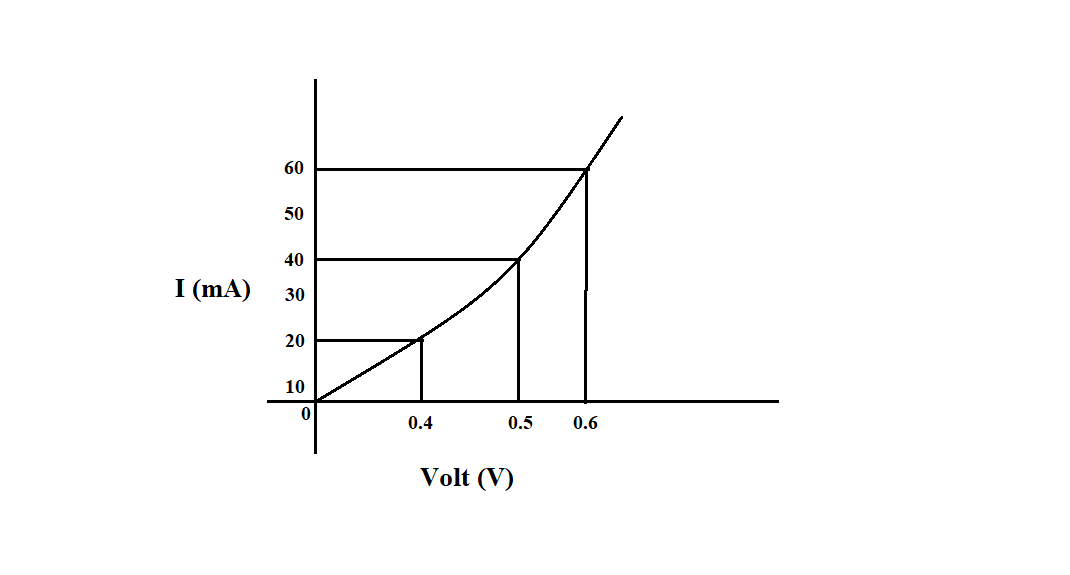
The forward characteristics curve of a junction diode is shown in the figure. Calculate the resistance of the diode at:
1) $ V=0.5V $
2) $ I=60mA $

Answer
600.9k+ views
Hint: By reading the graph, we will find the value of current passing through diode when voltage is $ 0.5V $ and the value of corresponding voltage when the current passing through diode is $ 60mA $. Now we will have V and I for both the condition. Then we just need to use the Ohm’s law to find the Resistance of the Diode.
Formula used:
$ V=IR $
Where $ V $ stands for voltage across component (here diode)
$ I $ stands for current passing through the component
$ R $ stands for the resistance of component
Complete step-by-step answer:
The Current-Voltage characteristics curve defines the operating characteristics of an electronic device. These are the set of graphical curves that are used to define operation of a component within an electric circuit. I-V characteristic curves represent the relationship between the current flowing through an electrical component or device and the voltage applied across its terminals.
When the diode is in forward biased state, a positive or forward current passes through the diode and this function operates in the top right quadrant of an I-V characteristics graph. When the diode is present in reverse biased mode, it blocks the flow of current except for very small values of leakage current and this function operates in the bottom left quadrant of an I-V characteristics graph.
a) When $ V=0.5V $ , current corresponding to it is $ 40mA $
Using equation $ R=\dfrac{V}{I} $
We get $ R=\dfrac{0.5}{40\times {{10}^{-3}}}=0.0125\times {{10}^{3}}=12.5 $
Resistance of diode at $ V=0.5V $ is $ 12.5\Omega $ .
b) When $ I=60mA $ , voltage across diode is $ 0.6V $
Using equation $ R=\dfrac{V}{I} $
We get $ R=\dfrac{0.6}{60\times {{10}^{-3}}}=0.01\times {{10}^{3}}=10 $
Resistance of diode at $ I=60mA $ is $ 10\Omega $ .
Note: Students should keep in mind how a diode functions and how to look at the plot of voltage across a diode and the current passing through the diode. Always remember when an ideal diode turns on, it is a short circuit and therefore the voltage across an ideal diode when it is on is always equal to zero.
Formula used:
$ V=IR $
Where $ V $ stands for voltage across component (here diode)
$ I $ stands for current passing through the component
$ R $ stands for the resistance of component
Complete step-by-step answer:
The Current-Voltage characteristics curve defines the operating characteristics of an electronic device. These are the set of graphical curves that are used to define operation of a component within an electric circuit. I-V characteristic curves represent the relationship between the current flowing through an electrical component or device and the voltage applied across its terminals.
When the diode is in forward biased state, a positive or forward current passes through the diode and this function operates in the top right quadrant of an I-V characteristics graph. When the diode is present in reverse biased mode, it blocks the flow of current except for very small values of leakage current and this function operates in the bottom left quadrant of an I-V characteristics graph.
a) When $ V=0.5V $ , current corresponding to it is $ 40mA $
Using equation $ R=\dfrac{V}{I} $
We get $ R=\dfrac{0.5}{40\times {{10}^{-3}}}=0.0125\times {{10}^{3}}=12.5 $
Resistance of diode at $ V=0.5V $ is $ 12.5\Omega $ .
b) When $ I=60mA $ , voltage across diode is $ 0.6V $
Using equation $ R=\dfrac{V}{I} $
We get $ R=\dfrac{0.6}{60\times {{10}^{-3}}}=0.01\times {{10}^{3}}=10 $
Resistance of diode at $ I=60mA $ is $ 10\Omega $ .
Note: Students should keep in mind how a diode functions and how to look at the plot of voltage across a diode and the current passing through the diode. Always remember when an ideal diode turns on, it is a short circuit and therefore the voltage across an ideal diode when it is on is always equal to zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




