
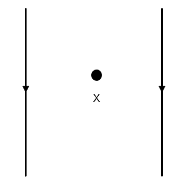
The following diagram shows two parallel straight conductors carrying the same current. Copy the diagram and draw the pattern of the magnetic axes around them showing their directions. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field at point X which is equidistant from the conductors? Give justification for your answer.

Answer
570.6k+ views
Hint : The magnetic field between two current-carrying wires in the same direction cancel each other in between the two wires if both the wires have the same amount of current flowing through them. The direction of the magnetic field can be determined by the right-hand rule.
Formula used: In this question, we will use the following formula,
$\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{{2\pi R}} $ where $ B $ is the magnetic field generated by a current-carrying wire at a point that is distance $ R $ from it.
Complete step by step answer
The direction of the magnetic field formed by a current-carrying wire can be determined by the right-hand rule. If we place our thumb in the direction of the current, we can determine the direction of the magnetic field as the direction our fingers point in.
For the cable on the left side, the magnetic field will be coming out of the page in the region between the two wires from the right-hand rule.
For the cable on the right side, the magnetic field will be going into the page in the region between the two wires.
So, we can expect the magnetic field in the region between the two wires to oppose each other. Since both the wires are carrying an identical amount of current, the magnetic field in the region between the two wires at the point X which is equidistant from each cable can be calculated assuming the distance of the point as $ x $ from both wires as:
$ B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{{2\pi x}} - \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2\pi x}} = 0 $
In the above equation, there is a negative sign in between because of the direction of the magnetic fields due to the two cables opposing each other. So, the magnetic field due to the two cables cancel each other out in the middle of the two wires.
Note
We must be very careful in determining the direction of the magnetic field while using the right-hand rule since the direction of the magnetic field also depends on which side of a cable we are calculating the magnetic field on. On the left side of the left cable and the right side of the right cable, the magnetic fields due to the two cables will add up and the net magnetic field will never be zero in those regions.
Formula used: In this question, we will use the following formula,
$\Rightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{{2\pi R}} $ where $ B $ is the magnetic field generated by a current-carrying wire at a point that is distance $ R $ from it.
Complete step by step answer
The direction of the magnetic field formed by a current-carrying wire can be determined by the right-hand rule. If we place our thumb in the direction of the current, we can determine the direction of the magnetic field as the direction our fingers point in.
For the cable on the left side, the magnetic field will be coming out of the page in the region between the two wires from the right-hand rule.
For the cable on the right side, the magnetic field will be going into the page in the region between the two wires.
So, we can expect the magnetic field in the region between the two wires to oppose each other. Since both the wires are carrying an identical amount of current, the magnetic field in the region between the two wires at the point X which is equidistant from each cable can be calculated assuming the distance of the point as $ x $ from both wires as:
$ B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}I}}{{2\pi x}} - \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2\pi x}} = 0 $
In the above equation, there is a negative sign in between because of the direction of the magnetic fields due to the two cables opposing each other. So, the magnetic field due to the two cables cancel each other out in the middle of the two wires.
Note
We must be very careful in determining the direction of the magnetic field while using the right-hand rule since the direction of the magnetic field also depends on which side of a cable we are calculating the magnetic field on. On the left side of the left cable and the right side of the right cable, the magnetic fields due to the two cables will add up and the net magnetic field will never be zero in those regions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




