
The focal length of a concave mirror is__________ its radius of curvature.
A) equal to
B) half of
C) two times
D) negative of
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: To find the relation between focal length and radius of curvature of a mirror, we must know about what is focal length and radius of curvature. If we have a value of radius of curvature, then we can find the value of focal length. Focal Length is defined by the distance from the pole of the concave mirror to the focus. Radius of curvature is defined by the distance of the centre of curvature from the pole of the mirror.
Complete step by step solution:
Derivation of relation between focal length and radius of curvature
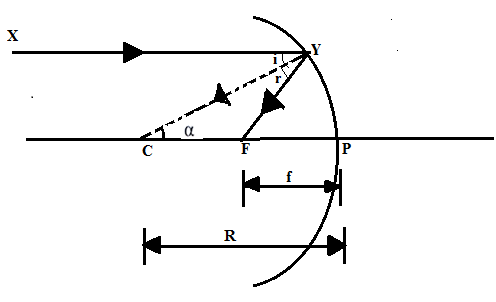
Let us consider the figure as above.
Let a ray XY parallel to the principal axis of the concave mirror. The ray XY incident at the point Y of a concave mirror. This ray passes through its focus F after reflection. As we know that any ray coming from long distance, when incident on a mirror it passes through the focus of the mirror. This phenomenon is known as the law of reflection.
We know that point C is known as the centre of curvature, then CP is known as radius of curvature. Which is given by \[CP = R\].CY is normal to the mirror at point Y.
As XY is parallel to CP i.e. , \[XY||CP\]
Then angle $\alpha$ is equal to incident angle I, i.e.,\[\alpha = i\] (because these angles are alternate angles)
\[\angle \alpha = \angle r\]\[[\because \angle i = \angle r]\]
Thus, $\vartriangle YCF$ is isosceles. Hence, \[CF = FY\].
Let assume the aperture (or size) of the mirror is small. So point Y will lie very near to point P.
this implies,\[FP \simeq FY\]
Or we get, \[FP = CF\]\[\left[ {\because CF = FY} \right]\]
Therefore radius of curvature CP can be calculated as,
\[
CP = CF + FP \\
CP = FP + FP \\
\Rightarrow CP = 2FP \\
\therefore R = 2f \\
\]
\[ \Rightarrow f = \dfrac{R}{2}\]
Hence, we get the relation between focal length and radius of curvature. Which implies that the focal length is half of the radius of curvature.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Additional information: Like a plane mirror, a concave mirror, obeys the laws of reflection of light. The rays of light coming from a distant object can be considered to be parallel to each other. When parallel rays of light fall on a concave mirror along its axis, they reflect from the surface of the mirror. These rays meet at a point in front of the mirror. That point is called the Principal focus of the mirror. The nature of the image formed at the focus of the mirror is real, inverted and very small in size.
Note: Students have clear knowledge of law of reflection for concave mirrors. The student must know about properties of parallel lines. Students must have knowledge about alternate angles in parallel lines.
Complete step by step solution:
Derivation of relation between focal length and radius of curvature

Let us consider the figure as above.
Let a ray XY parallel to the principal axis of the concave mirror. The ray XY incident at the point Y of a concave mirror. This ray passes through its focus F after reflection. As we know that any ray coming from long distance, when incident on a mirror it passes through the focus of the mirror. This phenomenon is known as the law of reflection.
We know that point C is known as the centre of curvature, then CP is known as radius of curvature. Which is given by \[CP = R\].CY is normal to the mirror at point Y.
As XY is parallel to CP i.e. , \[XY||CP\]
Then angle $\alpha$ is equal to incident angle I, i.e.,\[\alpha = i\] (because these angles are alternate angles)
\[\angle \alpha = \angle r\]\[[\because \angle i = \angle r]\]
Thus, $\vartriangle YCF$ is isosceles. Hence, \[CF = FY\].
Let assume the aperture (or size) of the mirror is small. So point Y will lie very near to point P.
this implies,\[FP \simeq FY\]
Or we get, \[FP = CF\]\[\left[ {\because CF = FY} \right]\]
Therefore radius of curvature CP can be calculated as,
\[
CP = CF + FP \\
CP = FP + FP \\
\Rightarrow CP = 2FP \\
\therefore R = 2f \\
\]
\[ \Rightarrow f = \dfrac{R}{2}\]
Hence, we get the relation between focal length and radius of curvature. Which implies that the focal length is half of the radius of curvature.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Additional information: Like a plane mirror, a concave mirror, obeys the laws of reflection of light. The rays of light coming from a distant object can be considered to be parallel to each other. When parallel rays of light fall on a concave mirror along its axis, they reflect from the surface of the mirror. These rays meet at a point in front of the mirror. That point is called the Principal focus of the mirror. The nature of the image formed at the focus of the mirror is real, inverted and very small in size.
Note: Students have clear knowledge of law of reflection for concave mirrors. The student must know about properties of parallel lines. Students must have knowledge about alternate angles in parallel lines.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




